|
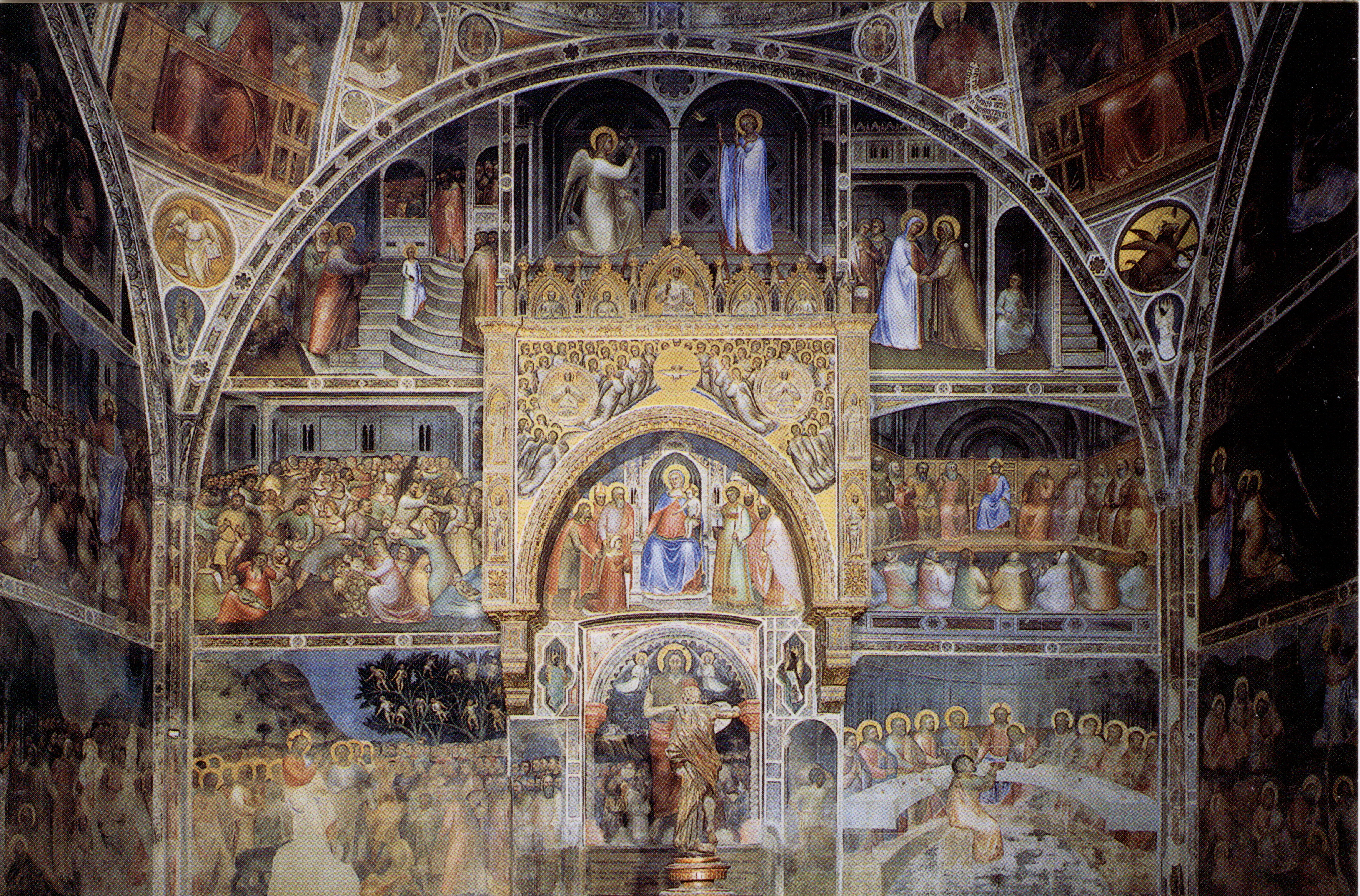
Giusto De' Menabuoi
''Cappella del beato Luca Belludi'' Sant'Antonio (Padua) Giusto de' Menabuoi (c. 1320–1391) was an Italian painter of the early Renaissance. He was born in the Republic of Florence. He was likely a pupil of Giotto but this is not definitive. De' Menabuoi was known for his use of colour and became a court painter for Da Carrara. His style was individual, with no links to the realism of his contemporaries Altichiero and Jacopo d'Avanzi, and he had no influence on the later development of Venetian painting. In Lombardy he executed a fresco of the ''Last Judgement ''in the Abbey of Viboldone, Milan and some frescoes, now very ruined, preserved inside the porch of the Visconti Castle of Pavia. He then moved to Padua where he completed frescos in the Church of the Eremitani, the Basilica of Saint Anthony of Padua and most notably at the Baptistery of the Padua Duomo. Between 1375 and 1378 he undertook decoration of the Padua Duomo Baptistery, for Fina Buzzaccarini, wife of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giusto De' Menabuoi, Paradiso (detail), 1376-78, Battistero Di Padova
A variety of musical terms is encountered in Sheet music, printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms Italian musical terms used in English, are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical conventions. Sometimes, the special musical meanings of these phrases differ from the original or current Italian meanings. Most of the other terms are taken from French language, French and German language, German, indicated by ''Fr.'' and ''Ger.'', respectively. Unless specified, the terms are Italian or English. The list can never be complete: some terms are common, and others are used only occasionally, and new ones are coined from time to time. Some composers prefer terms from their own language rather than the standard terms listed here. 0–9 ; 1 : "sifflet" or one foot organ stop ; I : usually for Violin family, orchestral string instruments, used to indicate that the player should play the passage on the highest-pitched, thinnest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Of The Eremitani
The Church of the Eremitani (), or Church of the Hermits, is a former-Augustinians, Augustinian, 13th-century Gothic architecture, Gothic-style church in Padua, region of the Veneto, Italy. It is also now notable for being adjacent to the Cappella Scrovegni with Giotto frescoes and the municipal archeology and art gallery: the ''Musei Civici agli Eremitani'', which is housed in the former Augustinian monastery located to the left of the entrance. It is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site of Padua's 14th-century fresco cycles (since 2021). History The Augustinian hermit friars, precursors of the present Order of Saint Augustine had arrived in Padua in 1237. Through the patronage of both the wife of the local nobleman Zaccaria dell'Arena and the city, the church was erected between 1260 and 1276 and dedicated to the saints Philip the Apostle, Philip and James, brother of Jesus, James. The friars would remain in the administration of the monastery and church until 1806, when the Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Painters From Florence
Painting is a visual art, which is characterized by the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called "matrix" or " support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush. Other implements, such as palette knives, sponges, airbrushes, the artist's fingers, or even a dripping technique that uses gravity may be used. One who produces paintings is called a painter. In art, the term "painting" describes both the act and the result of the action (the final work is called "a painting"). The support for paintings includes such surfaces as walls, paper, canvas, wood, glass, lacquer, pottery, leaf, copper and concrete, and the painting may incorporate other materials, in single or multiple form, including sand, clay, paper, cardboard, newspaper, plaster, gold leaf, and even entire objects. Painting is an important form of visual art, bringing in elements such as drawing, composition, gesture, narration, and abstraction. Paintings ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italian Male Painters
Italian(s) may refer to: * Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries ** Italians, a Romance ethnic group related to or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom ** Italian language, a Romance language *** Regional Italian, regional variants of the Italian language ** Languages of Italy, languages and dialects spoken in Italy ** Italian culture, cultural features of Italy ** Italian cuisine, traditional foods ** Folklore of Italy, the folklore and urban legends of Italy ** Mythology of Italy, traditional religion and beliefs Other uses * Italian dressing, a vinaigrette-type salad dressing or marination * Italian or Italian-A, alternative names for the Ping-Pong virus, an extinct computer virus * ''Italien'' (magazine), pro-Fascist magazine in Germany between 1927 and 1944 See also * * * Italia (other) * Italic (other) * Italo (other) * The Italian (other) The Italian may refer to: * ''The Ital ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14th-century Italian Painters
The 14th century lasted from 1 January 1301 (represented by the Roman numerals MCCCI) to 31 December 1400 (MCD). It is estimated that the century witnessed the death of more than 45 million lives from political and natural disasters in both Europe and the Mongol Empire. West Africa experienced economic growth and prosperity. In Europe, the Black Death claimed 25 million lives wiping out one third of the European population while the Kingdom of England and the Kingdom of France fought in the protracted Hundred Years' War after the death of King Charles IV of France led to a claim to the French throne by King Edward III of England. This period is considered the height of chivalry and marks the beginning of strong separate identities for both England and France as well as the foundation of the Italian Renaissance and the Ottoman Empire. In Asia, Tamerlane (Timur), established the Timurid Empire, history's third largest empire to have been ever established by a single conqueror. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1390 Deaths
( MCCCXC) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * January 19 – The Treaty of Lyck confirms an alliance between Vytautas and the Teutonic Knights, in the Lithuanian Civil War against Vytautas's cousin, Jogaila. * April 14 – John VII Palaiologos overthrows his grandfather, John V Palaiologos, as Byzantine Emperor. * April 19 – Robert III succeeds his father, Robert II, as King of Scotland. * May 26 – Lithuanian Civil War: The Treaty of Königsberg is signed in Königsberg, between Samogitian nobles and representatives of the Teutonic Knights. * September 11 – Lithuanian Civil War: The coalition of Vytautas and the Teutonic Knights begins a 5-week siege of Vilnius. The Duke of Hereford (the future King Henry IV of England) is among the western European knights serving with the coalition. * September 17 – John VII Palaiologos seeks refuge with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1330 Births
Year 1330 (Roman numerals, MCCCXXX) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. Events January–December * July 28 – Battle of Velbazhd: The Second Bulgarian Empire, Bulgarians under Tsar Michael Shishman of Bulgaria, Michael Shishman (who is mortally wounded) are beaten by the Kingdom of Serbia (medieval), Serbs. Bulgaria does not lose any territory to Serbia, but is powerless to stop the Serbian advance towards the predominantly Bulgarian-populated Macedonia (region), Macedonia. * October 19 – King Edward III of England starts his personal reign, arresting his regent Roger Mortimer, 1st Earl of March, Roger Mortimer, and having him executed. * November 9–November 12, 12 – Battle of Posada: The Wallachians, under Basarab I, defeat the Hungarians, though heavily outnumbered, thus making a firm statement towards the independence of Wallachia. * December 6 – The British Isles are hit by a great storm, creating large areas of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
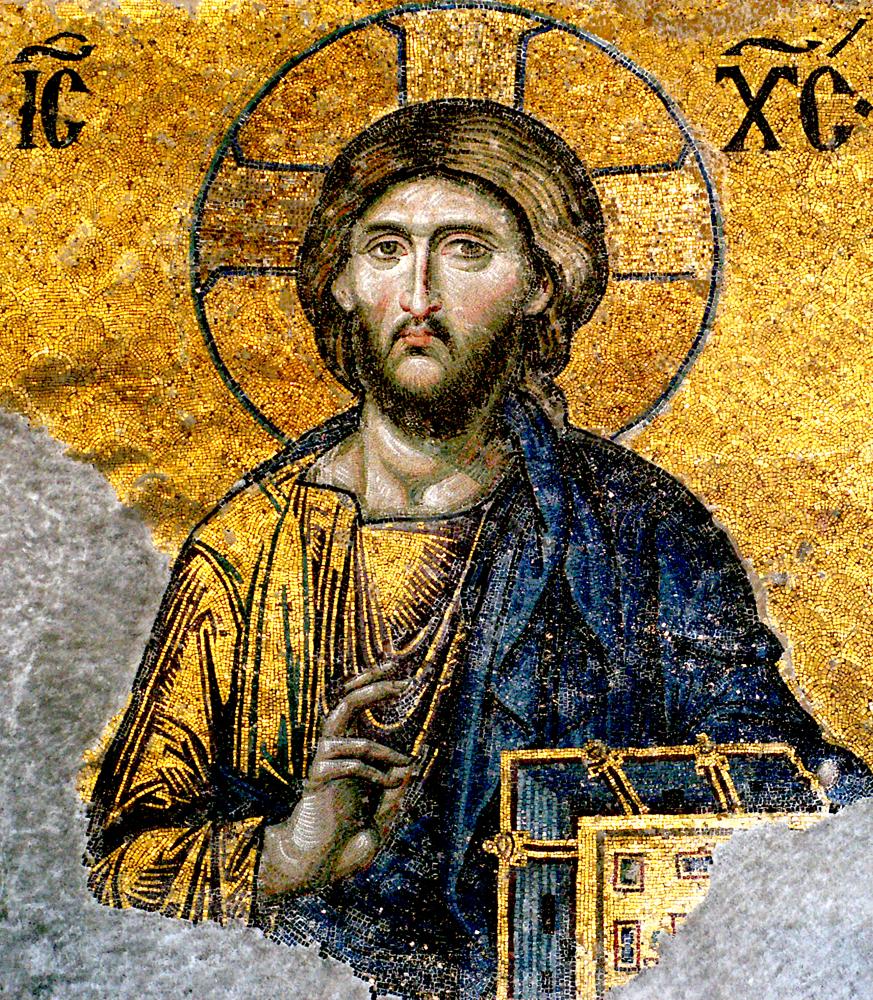
Christ Pantocrator
In Christian iconography, Christ Pantocrator (, ) is a specific depiction of Christ. or , literally 'ruler of all', but usually translated as 'almighty' or 'all-powerful', is derived from one of many names of God in Judaism. The Pantokrator is largely an Eastern Orthodox, Eastern Catholic or Eastern Lutheran theological conception and is less common under that name in Latin Catholicism and Western Lutheranism. In the West, the equivalent image in art is known as Christ in Majesty, which developed a rather different iconography. ''Christ Pantocrator'' has come to suggest Christ as a benevolent, though also stern and all-powerful, judge of humanity. When the Hebrew Bible was translated into Greek as the Septuagint, ''Pantokrator'' was used both for ''YHWH Sabaoth'' () " Lord of Hosts" and for '' El Shaddai'' " God Almighty". In the New Testament, ''Pantokrator'' is used once by Paul () and nine times in the Book of Revelation: , , , , , , , , and . The references to God the F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Art
Byzantine art comprises the body of artistic products of the Eastern Roman Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empire. Though the empire itself emerged from the decline of Rome, decline of western Rome and lasted until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, the start date of the Byzantine period is rather clearer in art history than in political history, if still imprecise. Many Eastern Orthodox states in Eastern Europe, as well as to some degree the Islamic states of the eastern Mediterranean, preserved many aspects of the empire's culture and art for centuries afterward. A number of contemporary states with the Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire were culturally influenced by it without actually being part of it (the "Byzantine commonwealth"). These included Kievan Rus', as well as some non-Orthodox states like the Republic of Venice, which separated from the Byzantine Empire in the 10th century, and the Norman-Arab-Byzantine culture, Kingdom o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanesque Art
Romanesque art is the art of Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic Art, Gothic style in the 12th century, or later depending on region. The preceding period is known as the Pre-Romanesque period. The term was invented by 19th-century art historians, especially for Romanesque architecture, which retained many basic features of Roman architecture, Roman architectural style – most notably round-headed arches, but also barrel vaults, apses, and Acanthus (ornament), acanthus-leaf decoration – but had also developed many very different characteristics. In Southern France, Spain, and Italy there was an architectural continuity with the Late Antique, but the Romanesque style was the first style to spread across the whole of Catholic Europe, from Sicily to Scandinavia. Romanesque art was also greatly influenced by Byzantine art, especially in painting, and by the anti-classical energy of the decoration of the Insular art of the British Isles. From these element ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco I Da Carrara
Francesco I da Carrara (29 September 1325, in Padua – 6 October 1393, in Monza), called il Vecchio, was Lord of Padua from 1350 to 1388. The son of the assassinated Giacomo II da Carrara, he succeeded him as lord of Padua by popular acclamation. In 1356 he was named imperial vicar by emperor Charles IV. In 1360 he obtained by Louis I of Hungary the cities of Feltre and Belluno with their territories, as well as Valsugana, which controlled the trades to Trentino. In 1372-1373 he fought a fruitless war against his powerful neighbor, the Republic of Venice. In 1375-1381 he sided with the Genoa in the War of Chioggia, after which he obtained by Leopold III of Austria the city of Treviso. In 1385, he allied with the Visconti of Milan against the Scaliger of Verona. In 1387 the Paduan troops, led by John Hawkwood and his son Francesco Novello, defeated the Scaliger troops in the Battle of Castagnaro. The following year, however, Venice and Milan formed a coalition against France ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padua Baptistery
The Padua Baptistery, dedicated to St. John the Baptist, is a baptistery on the Piazza del Duomo next to the cathedral in Padua, Italy. Preserved inside is one of the most important fresco cycles of the 14th century, a masterpiece by Giusto de' Menabuoi. It is part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site '' Padua's fourteenth-century fresco cycles'', inscribed in 2021 for its outstanding cultural and artistic significance. History The construction of the baptistery began in the 12th century, probably on top of an existing structure; it underwent various reworkings in the following century, and was consecrated by Guido, patriarch of Grado, in 1281. Between 1370 and 1379 it was restored and adapted as a mausoleum for prince Francesco il Vecchio da Carrara and his wife, Fina Buzzaccarini. The latter oversaw the decorative work, entrusting it to Giusto de' Menabuoi (whose burial site was later found outside the building). With the fall of the House of Da Carrara in 1405, Venetian soldie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |