|
Gesta Hungarorum
''Gesta Hungarorum'', or ''The Deeds of the Hungarians'', is the earliest book about Kingdom of Hungary, Hungarian history which has survived for posterity. Its genre is not chronicle, but ''gesta'', meaning "deeds" or "acts", which is a medieval entertaining literature. It was written in Latin by an unidentified author who has traditionally been called Anonymus (notary of Béla III), Anonymus in scholarly works. According to most historians, the work was completed between around 1200 and 1230. The ''Gesta'' exists in a sole manuscript from the second part of the 13th century, which was for centuries held in Vienna. It is part of the collection of National Széchényi Library, Széchényi National Library in Budapest. The principal subject of the ''Gesta'' is the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin at the turn of the 9th and 10th centuries, and it writes of the Hungarian prehistory, origin of the Hungarians, identifying the Hungarians' ancestors with the ancient Scythia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anonymus (notary Of Béla III)
''Anonymus Bele regis notarius'' (/aˈnɔ.ni.mus ˈbeː.le ˈreː.ɡis noˈtaː.ri.us/) ("Anonymous Notary of King Bela") or Master P. ( late 12th century – early 13th century) was the notary and chronicler of a Hungarian king, probably Béla III. Little is known about him, but his latinized name began with ''P,'' as he referred to himself as ''"P. dictus magister".'' Anonymus is famous for his work ''Gesta Hungarorum'' ("The Deeds of the Hungarians"), written in Medieval Latin around 1200. This work provides the most detailed history of the Hungarian conquest of the Carpathian Basin. Most of his attempts to explain the origin of several Hungarian place names are unsupported by modern etymology. Identity The identity of the author of the ''Gesta'' has always been subject to scholarly debate. Although the first words of the opening sentencean initial ''"P"'' followed with the words ''"dictus magister ac quondam bone memorie gloriosissimi Bele regis Hungarie notarius"''describ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesta Hungarorum Anonymous
Gesta may refer to: Titles of works Gesta is the Latin word for "deeds" or "acts", and Latin titles, especially of medieval chronicles, frequently begin with the word, which thus is also a generic term for medieval biographies: * Gesta Adalberonis or Gesta Alberonis, "Deeds of Albero", Archbishop of Trier (1131–52) *, "Deeds of the Emperor Berengar", epic poem chronicling the career of Berengar of Friuli from to 915 *, "Deeds of the counts of Barcelona and kings of Aragon", 14th century * Gesta Cnutonis Regis or Encomium Emmae Reginae, "Deeds of King Canute" 11th-century, also covers Queen Emma of Normandy *Gesta Danorum, "Deeds of the Danes", 12th century * Dei gesta per Francos, "Deeds of God through the Franks", 12th century, a narrative of the First Crusade *Gesta Francorum, "The Deeds of the Franks", in full Gesta Francorum et aliorum Hierosolimitanorum ("The deeds of the Franks and the other pilgrims to Jerusalem"), 12th century, a different narrative of the First Crusade * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
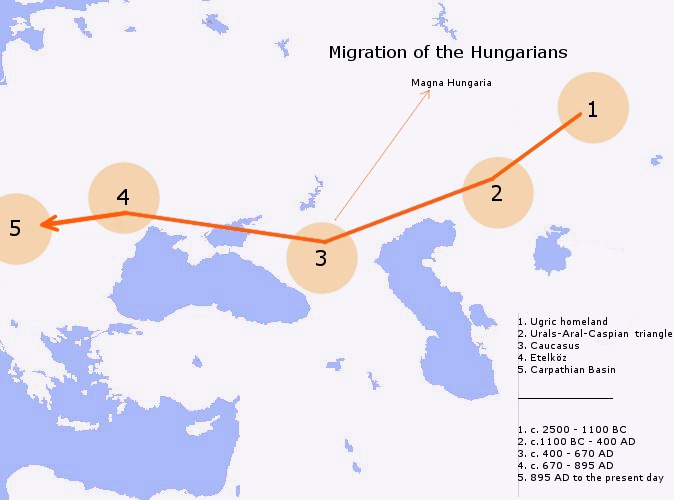
Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are an Ethnicity, ethnic group native to Hungary (), who share a common Culture of Hungary, culture, Hungarian language, language and History of Hungary, history. They also have a notable presence in former parts of the Kingdom of Hungary. The Hungarian language belongs to the Ugric languages, Ugric branch of the Uralic languages, Uralic language family, alongside the Khanty languages, Khanty and Mansi languages, Mansi languages. There are an estimated 14.5 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Hungarians in Slovakia, Slovakia, Hungarians in Ukraine, Ukraine, Hungarians in Romania, Romania, Hungarians in Serbia, Serbia, Hungarians of Croatia, Croatia, Prekmurje, Slovenia, and Hungarians in Austria, Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illuminated Chronicle
The ''Chronicon Pictum'' or ''Illuminated Chronicle'' (, , , also referred to as the ''Illustrated Chronicle'', ''Chronica Hungarorum'', ''Chronicon Hungarie Pictum'', ''Chronica Picta'' or ''Chronica de Gestis Hungarorum'') is a medieval illustrated chronicle from the Kingdom of Hungary from the 14th century. It represents the artistic style of the royal court of King Louis I of Hungary. The codex is a unique source of art, medieval and cultural history. The chronicle's full name is: ''Chronicon Pictum – Marci de Kalt Chronica de Gestis Hungarorum'' (Illustrated Chronicle – Mark of Kalt's Chronicle About the Deeds of the Hungarians). History of the chronicle King Louis I of Hungary commissioned the ''Chronicon Pictum'' and the ''Secretum Secretorum'', which were both produced in a Hungarian workshop. Miklόs Meggyesi, son of Hertul the court painter of Louis, has traditionally been identified as the illuminator, though there is no real evidence for this. The Illuminated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gesta Hunnorum Et Hungarorum
The ''Gesta Hunnorum et Hungarorum''''Reader's encyclopedia of Eastern European literature'', 1993, Robert B. Pynsent, Sonia I. Kanikova, p. 529. (Latin: "Deeds of the Huns and Hungarians") is a medieval chronicle written mainly by Simon of Kéza around 1282–1285. It is one of the sources of early Hungarian history. It is also known as the ''Gesta Hungarorum (II)'' (Latin: "Deeds of the Hungarians"), the "(II)" indicating its status as an expansion of the original '' Gesta Hungarorum'' (written around 1200). The work is dated to 1282–1285 as it includes the Battle of Lake Hód (1282) but does not mention the Second Mongol invasion of Hungary in 1285. The work combines Hunnish legend with history. It consists of two parts: the Hunnish legend ("Hunnish Chronicle"), expanded with Hungarian oral tales; and a history of the Kingdom of Hungary since the original ''Gesta Hungarorum''. Simon of Kéza was a court cleric of King Ladislaus IV of Hungary (reigned 1272–1290). H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Of Kéza
Simon of Kéza () was the most famous Hungarian chronicler of the 13th century. He was a priest in the royal court of king Ladislaus IV of Hungary. In 1270–1271, bearing the title "master" (''magister''), Simon was part of a diplomatic mission led by Sixtus of Esztergom. Andrew of Hungary (historian), Andrew of Hungary was also a part of this mission. Sent by King Stephen V of Hungary to congratulate King Charles I of Sicily on the latter's return from the Eighth Crusade, the delegation travelled via Naples to Catona and Messina in December and January, then back with Charles to Rome in February., at ic–cii. His most important work is ''Gesta Hunnorum et Hungarorum'', written in Latin around 1282, in which he gives a vivid description of the history of the Huns and the Hungarians (whom he considered relatives), from the legendary beginnings until the contemporary period. As a personal secretary of the king, he worked in the royal archives and collected his material from older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
András Róna-Tas
András Róna-Tas (born 30 December 1931) is a Hungarian historian and linguist. Biography He was born in 1931 in Budapest. Róna-Tas studied under such preeminent professors as Gyula Ortutay and Lajos Ligeti, and received a degree in folklore and eastern linguistics ( Tibetan, Mongol, and Turkic.) From 1956, he worked at the Faculty of Humanities of the Eötvös Loránd University. In 1957–1958, Róna-Tas conducted anthropological fieldwork in Mongolia, studying the culture, language, and folklore of the nomadic tribes in that country. During the mid-1960s, Róna-Tas focused his fieldwork on the Chuvash people of the middle Volga River basin. In 1964, Róna-Tas defended his candidates (CSc) degree, and finally in 1971, he earned a doctorate from the Hungarian Academy of Sciences (DSc) with his thesis "The Theory of Linguistic Affinity and the Linguistic Relations between the Chuvash and Mongol Languages", published as ''Linguistic Affinity'' in 1978. From 1968 to 2002, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlile Aylmer Macartney
Carlile Aylmer Macartney FBA (1895–1978) was a British academic specialising in the history and politics of East-Central Europe and in particular the history of Austria and Hungary. He was also a supporter of Hungarian interests and causes in the United Kingdom. Career His education included time at Winchester College (where he was a scholar) and at Trinity College, Cambridge. Macartney was a research fellow of All Souls College, Oxford. From 1936 to 1946 he was in charge of the Hungarian section of the Foreign Office Research Department. From 1951 to 1957 he was Montague Burton Professor of International Relations at the University of Edinburgh. Macartney was a corresponding member of the Austrian and Hungarian academies, and in 1965 he became a member of the British Academy The British Academy for the Promotion of Historical, Philosophical and Philological Studies is the United Kingdom's national academy for the humanities and the social sciences. It was established i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Administrando Imperio
(; ) is a Greek-language work written by the 10th-century Byzantine Emperor Constantine VII. It is a domestic and foreign policy manual for the use of Constantine's son and successor, the Emperor Romanos II. It is a prominent example of Byzantine encyclopaedism. Author and background The emperor Constantine VII "Porphyrogenitus" (905–959) was only surviving son of the emperor Leo VI the Wise (886–912). Leo VI gave the crown to young Constantine VII in 908 and he became the co-emperor. Leo VI died in May 912, and his brother and co-emperor Alexander became the ruler of Constantinople, but Alexander died in 913. Constantine VII was too young to rule on his own, and the governorship was created. Later in May 919 Constantine VII married Helena Lekapene, daughter of Romanos Lekapenos. In December 920, Romanos I Lekapenos (920–944) was crowned a co-emperor, but he really took over the imperial reign in Constantinople. From 920, Constantine VII become increasingly distant f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine VII
Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus (; 17 May 905 – 9 November 959) was the fourth Byzantine emperor of the Macedonian dynasty, reigning from 6 June 913 to 9 November 959. He was the son of Emperor Leo VI and his fourth wife, Zoe Karbonopsina, and the nephew of his predecessor Alexander. Most of his reign was dominated by co-regents: from 913 until 919 he was under the regency of his mother, while from 920 until 945 he shared the throne with Romanos Lekapenos, whose daughter Helena he married, and his sons. Constantine VII is best known for the '' Geoponika'' (τά γεοπονικά), an important agronomic treatise compiled during his reign, and three, perhaps four, books; (bearing in Greek the heading Πρὸς τὸν ἴδιον υἱὸν Ῥωμανόν), (Περὶ τῆς Βασιλείου Τάξεως), '' De Thematibus'' (Περὶ θεμάτων Άνατολῆς καὶ Δύσεως), and '' Vita Basilii'' (Βίος Βασιλείου), though his authorship of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annals Of Fulda
The ''Annales Fuldenses'' or ''Annals of Fulda'' are East Frankish chronicles that cover independently the period from the last years of Louis the Pious (died 840) to shortly after the end of effective Carolingian rule in East Francia with the accession of the child-king, Louis III, in 900. Throughout this period they are a near contemporary record of the events they describe and a primary source for Carolingian historiography. They are usually read as a counterpart to the narrative found in the West Frankish '' Annales Bertiniani''. Authorship and manuscripts The ''Annals'' were composed at the Abbey of Fulda in Hesse. A note in one manuscript has been taken to prove that the entries down to 838 were composed by Einhard (''Enhard'' in the MS), yet it has been convincingly argued that this might only have been a copyist's colophon that has abusively entered the manuscript tradition, a sort of accident far from uncommon in medieval ''scriptoria''. Be that as it may, a second ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Byzantine Scholars
This is a list of Byzantine scientists and other scholars. Before the 9th century Most important scholars known before the Macedonian Renaissance were active under the Byzantium under the Justinian dynasty, Justinian dynasty. * Theon of Alexandria (335–405), mathematician * Hypatia (370–415), mathematician, astronomer, philosopher * Anthemius of Tralles (c. 474–before 558), mathematician and architect of Hagia Sophia * Eutocius of Ascalon (c. 480–c. 540), mathematician * John Philoponus (490–570), mathematician, physicist, theologian * Isidore of Miletus (6th century), mathematicist, physicist and architect of Hagia Sophia * Cassianus Bassus (6th–7th century), author of Geoponika * Leontios (died 706), emperor, astronomer, mathematician and engineer * George of Pisidia (6th–7th century), scholar, zoologist and astronomer * Timotheos of Gaza (6th–7th century), zoologist * Stephen of Byzantium (6th–7th century), geographer * Paul of Aegina (7th century), physician ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |