|
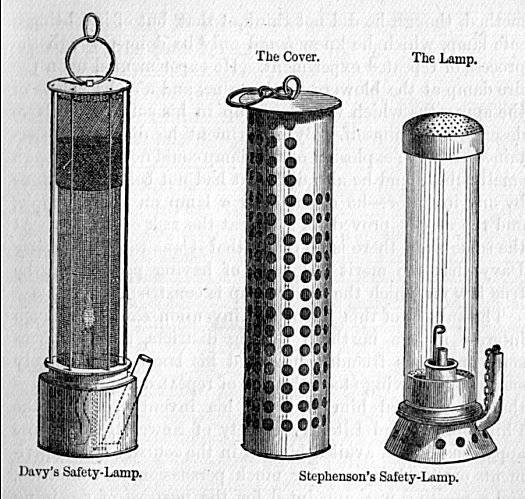
George Stephenson
George Stephenson (9 June 1781 – 12 August 1848) was an English civil engineer and Mechanical engineering, mechanical engineer during the Industrial Revolution. Renowned as the "Father of Railways", Stephenson was considered by the Victorian era, Victorians as a great example of diligent application and thirst for improvement. His chosen Track gauge#The Stockton and Darlington Railway, rail gauge, sometimes called "Stephenson gauge", was the basis for the standard gauge used by most of the world's railways. Pioneered by Stephenson, rail transport was one of the most important technological inventions of the 19th century and a key component of the Industrial Revolution. Built by George and his son Robert Stephenson, Robert's company Robert Stephenson and Company, the Locomotion No. 1, ''Locomotion'' No. 1 was the first steam locomotive to carry passengers on a public rail line, the Stockton and Darlington Railway in 1825. George also built the first public inter-city railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wylam
Wylam is a village and civil parish in the county of Northumberland, England. It is located about west of Newcastle upon Tyne. It is famous for the being the birthplace of George Stephenson, one of the early railway pioneers. George Stephenson's Birthplace, his cottage, can be found on the north bank of the Tyne east of the village. It is owned by the National Trust. Wylam has further connections with the early railway pioneers. The steam locomotive engineer Timothy Hackworth, who worked with Stephenson, was also born here. William Hedley who was born in the nearby village of Newburn attended the village school. He later went on to design and manufacture Puffing Billy in 1813, two years before George Stephenson produced his first locomotive Blücher. Christopher Blackett as lord of the manor in the first 30 years of the 19th century provided the entrepreneurial drive that encouraged these engineers. History Once an industrial workplace with collieries and an ironwor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northumberland
Northumberland ( ) is a ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in North East England, on the Anglo-Scottish border, border with Scotland. It is bordered by the North Sea to the east, Tyne and Wear and County Durham to the south, Cumbria to the west, and the Scottish Borders council area to the north. The town of Blyth, Northumberland, Blyth is the largest settlement. Northumberland is the northernmost county in England. The county has an area of and a population of 320,274, making it the least-densely populated county in England. The south-east contains the largest towns: Blyth, Northumberland, Blyth, Cramlington, Ashington, Bedlington, and Morpeth, Northumberland, Morpeth, the last of which is the administrative centre. The remainder of the county is rural, the largest towns being Berwick-upon-Tweed in the far north and Hexham in the south-west. For local government purposes Northumberland is a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority area. The county Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montrose, Angus
Montrose ( ; ) is a town and former royal burgh in Angus, Scotland. Situated north of Dundee and south of Aberdeen, Montrose lies between the mouths of the River North Esk, Angus, North and River South Esk, South Esk rivers. It is the northernmost coastal town in Angus and developed as a natural harbour that traded in skins, hides, and cured salmon in medieval times. With an estimated population of in , the town functions as a port, but the major employer is GlaxoSmithKline, which was saved from closure in 2006. The skyline of Montrose is dominated by the steeple (architecture), steeple of Montrose Old and St Andrew's Church, Old and St Andrew's Church, designed by James Gillespie Graham and built between 1832 and 1834. Montrose is a town with a wealth of architecture, and is a centre for international trade. It is an important commercial port for the oil and gas industry. It is known for its wide thoroughfare and high street, which leads to picturesque closes containing s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St Bartholomew's Church, Long Benton
St Bartholomew's Church, Long Benton is the Anglican parish church of Longbenton, in Newcastle upon Tyne, Tyne and Wear. It is built in the Gothic Revival style. Background Whilst limited evidence exists of church activity round Benton from the 7th and 8th centuries, it is from the mid-12th century that the existence of the parish of Long Benton can be assured, as the church can name its rectors from 1150 to the present day. Dr G. W. D. Briggs, in his publication 'St. Bartholomew's Church', states that 'there is a reference to transfer of the advowson by Roger de Merlay dated 1251 and then of the foundation of a chantry in honour of the Virgin Mary by 'Adam of Benton' dated 23 December 1310. This foundation names the church of St Andrew in Benton.' In 1339/1340, the church was transferred to the patronage of Balliol College Oxford which still holds it. By 1790, the church had fallen into great disrepair, and had reached a stage where rebuilding was the only remaining option. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Killingworth
Killingworth is a town in North Tyneside, Tyne and Wear, England, within the historic county of Northumberland. Killingworth was built as a new town in the 1960s, next to Killingworth Village, which existed for centuries before the new town was built. Other nearby villages include Forest Hall, West Moor and Backworth. Killingworth has bus links to the rest of Tyne and Wear. The town is not on the Tyne and Wear Metro network; its nearest stations are Palmersville and Benton. The town of Killingworth in Australia is named after the British original because of its extensive coal mines. Culture Killingworth was used as a filming location for the 1973 BBC sitcom ''Whatever Happened to the Likely Lads?'', with one of the houses on Agincourt on the Highfields estate featuring as the home of Bob and Thelma Ferris. In an episode of the architecture series '' Grundy's Wonders'' on Tyne Tees, John Grundy deemed Killingworth's former British Gas Research Centre to be the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Moor
Forest Hall is a village in the borough of North Tyneside, Tyne and Wear, England. It is 4 miles from Newcastle upon Tyne. It borders Killingworth to the north, Holystone to the east and Benton to the south. The village was named after the Forest Hall, which incorporated a medieval tower. Woodside Court was built on the site of the Hall, which was demolished in 1962. History Dial Cottage Dial Cottage, a grade II listed building and home from 1804 to 1823 of railway pioneer George Stephenson, is located on Great Lime Road in Forest Hall. It was while he was living there that Stephenson developed one of the world's earliest locomotives, called the Blücher, as well as several others which ran on the Killingworth Colliery from 1814. The trackbed is now a public footpath which can be accessed from Great Lime Road a kilometre east of the cottage. The cottage is privately owned, though tours occasionally take place. At the cottage there is a sundial, which Stephenson built himse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longbenton - Dial Cottage, Westmoor
Longbenton is a district of North Tyneside, in the county of Tyne and Wear, England. It is largely occupied by an extensive estate originally built as municipal housing by Newcastle City Council in the 1930s and extended in the 1950s. It is served by the Tyne and Wear Metro stations Longbenton Metro station and Four Lane Ends Metro Station. Nearby places are Killingworth, Forest Hall, Four Lane Ends, West Moor, Heaton and South Gosforth, in Newcastle upon Tyne. The Longbenton and Killingworth Urban Area had a population of 34,878 in 2001. This figure increased to 37,070 in 2011. History The name ''Longbenton'' probably means "long (i.e. large) bean town", to distinguish it from the smaller village of Little Benton to its south-east. Longbenton has a long history of coal mining. Meadow Pit, Dyke Pit and First and Second Engine Pits were in operation by 1749. In 1774 an "experimentally-determined" model of the Newcomen atmospheric engine, designed by John Smeaton, was ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Willington Quay
Willington Quay is an area in the borough of North Tyneside in Tyne and Wear in northern England. It is on the north bank of the River Tyne, facing Jarrow, and between Wallsend and North Shields. It is served by the Howdon Metro station in Howdon. The area from 2006 onwards has been an area of new housing built on brownfield land, brownfield sites. The house building continues into 2013 and is changing the social and economic balance in the area. The area has also had a make over of the bowling green off Howdon Lane and further warehousing next to the bowling green has been demolished to make way for further new housing. Local government The area, originally in the parish of Wallsend, on 30 September 1894 Willington Quay became a separate civil parish, being formed from the part of Wallsend parish in Willington Quay Urban District. The Local Government Act 1894 brought together the Howdon and Willington Quay USDs as an Urban district (Great Britain and Ireland), urban district of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ponteland
Ponteland ( ) is a town and civil parish in Northumberland, England. It is northwest of Newcastle upon Tyne. Built on marshland near St Mary's Church and the old bridge, most marshland has now been drained to make way for housing. In the industrial era, the settlement expanded with the development of Darras Hall. Parts of Ponteland have some of North-East England's most expensive houses; being just outside Newcastle, near the airport and on the edge of rural countryside. The civil parish includes the old village of Ponteland, the Darras Hall estate, and the villages of Kirkley, Medburn, Milbourne and Prestwick. Toponymy The name ''Ponteland'', first attested in 1256, means "island in the Pont" or "agricultural land by the Pont", after the River Pont which flows from west to east and joins the River Blyth further downstream, before flowing into the North Sea. The river-name ''Pont'' itself comes from Brittonic *''pant'', 'valley'. Kirkley is thought to originate in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illiterate
Literacy is the ability to read and write, while illiteracy refers to an inability to read and write. Some researchers suggest that the study of "literacy" as a concept can be divided into two periods: the period before 1950, when literacy was understood solely as alphabetical literacy (word and letter recognition); and the period after 1950, when literacy slowly began to be considered as a wider concept and process, including the social and cultural aspects of reading, writing, and functional literacy. Definition The range of definitions of literacy used by NGOs, think tanks, and advocacy groups since the 1990s suggests that this shift in understanding from "discrete skill" to "social practice" is both ongoing and uneven. Some definitions remain fairly closely aligned with the traditional "ability to read and write" connotation, whereas others take a broader view: * The 2003 National Assessment of Adult Literacy (USA) included "quantitative literacy" (numeracy) in its t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |