|
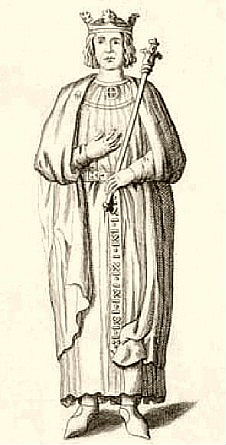
Geoffrey, Duke Of Brittany
Geoffrey II (; , ; 23 September 1158 – 19 August 1186) was Duke of Brittany and Earl of Richmond between 1181 and 1186, through his marriage to Constance, Duchess of Brittany. Geoffrey was the fourth of five sons of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine. Life In the 1160s, Henry II began to alter his policy of indirect rule in Brittany and to exert more direct control. Henry had been at war with Conan IV, Duke of Brittany. Local Breton nobles rebelled against Conan, so Conan sought Henry II's help. In 1164, Henry intervened to seize lands along the border of Brittany and Normandy and, in 1166, he invaded Brittany to punish the local barons.Everard (2000), p. 42. Henry then forced Conan to abdicate as duke and to give Brittany to his five-year-old daughter, Constance, who was handed over and betrothed to Henry's son Geoffrey. This arrangement was quite unusual in terms of medieval law, as Conan might have had sons who could have legitimately inherited the duchy. Geof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of Brittany
This is a list of rulers of Brittany. In different epochs the rulers of Brittany were kings, princes, and dukes. The Breton ruler was sometimes elected, sometimes attained the position by conquest or intrigue, or by hereditary right. Hereditary dukes were sometimes a female ruler, carrying the title duchesse of Brittany. Its principal cities and regions were ruled by counts who often found themselves in conflict with the Breton ruler, or who became the Breton ruler. During the declining years of the Roman Empire, the earliest Bretons, Breton rulers in Gaul were styled "kings" of the small realms of Cornouaille and Domnonée. Some such kings may have had a form of hegemony over all of the Celtic Britons, Brythonic populations in the Armorican peninsula, and Riothamus is called King of the Britons by the chronicler Jordanes. However, there are no certain rulers of the whole of Brittany, which was divided into the fiefdoms of local counts. The Duchy of Brittany had its origins in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gisors
Gisors () is a Communes of France, commune in the Departments of France, French department of Eure, Normandy (administrative region), Normandy, France. It is located northwest from the Kilometre Zero, centre of Paris. Gisors, together with the neighbouring communes of Trie-Château and Trie-la-Ville, form an urban unit, urban area of 13,915 inhabitants (2018). This urban area is a satellite town of Paris. Geography Gisors is located in the Vexin normand region of Normandy, at the confluence of the rivers Epte, Troesne and Réveillon (Epte), Réveillon. Population Transport The Gisors station is the terminus of a Transilien Paris-Saint-Lazare, Transilien suburban rail service from the Paris Gare Saint-Lazare, Saint-Lazare station, and of a TER Normandie local service to Serqueux station, Serqueux. Sights *Château de Gisors, built in the 11th century. *The Saint-Gervais-Saint-Protais parish church is an outstanding monument fusing Gothic architecture, Gothic and French Ren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Notre-Dame De Paris
Notre-Dame de Paris ( ; meaning "Cathedral of Our Lady of Paris"), often referred to simply as Notre-Dame, is a Medieval architecture, medieval Catholic cathedral on the Île de la Cité (an island in the River Seine), in the 4th arrondissement of Paris, France. It is the cathedral church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Paris. The cathedral, dedicated to the Virgin Mary ("Our Lady"), is considered one of the finest examples of French Gothic architecture. Several attributes set it apart from the earlier Romanesque style, including its pioneering use of the rib vault and flying buttress, its enormous and colourful rose windows, and the naturalism (art), naturalism and abundance of its sculptural decoration. Notre-Dame is also exceptional for its three Pipe organ, pipe organs (one historic) and Bells of Notre-Dame de Paris, its immense church bells. The construction of the cathedral began in 1163 under Bishop Maurice de Sully and was largely completed by 1260, though it was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chantry
A chantry is an ecclesiastical term that may have either of two related meanings: # a chantry service, a set of Christian liturgical celebrations for the dead (made up of the Requiem Mass and the Office of the Dead), or # a chantry chapel, a building on private land, or an area in a parish church or cathedral reserved for the performance of these celebrations. In the Medieval Era through to the Age of Enlightenment it was commonly believed such liturgies might help atone for misdeeds and assist the soul to obtain eternal peace. Etymology The word "chantry" derives from Old French ''chanter'' and from the Latin">-4; we might wonder whether there's a point at which it's appropriate to talk of the beginnings of French, that is, when it wa ... ''chanter'' and from the Latin ''cantare'' (to sing). Its medieval derivative ''cantaria'' means "licence to sing mass". The French term for this commemorative institution is ''chapellenie'' (chaplaincy). Overview Liturgy for the dead Firs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marie Of France, Countess Of Champagne
Marie of France (1145 – 11 March 1198) was a Capetian princess who became Countess of Champagne by her marriage to Henry I of Champagne. She ruled the County of Champagne as regent during Henry I's absence from 1179 to 1181; during the minority of their son Henry II from 1181 to 1187; and during Henry II's absence from 1190 to 1197. She was the daughter of Eleanor of Aquitaine and Louis VII of France. Early life Marie's birth was hailed as a "miracle" by Bernard of Clairvaux, an answer to his prayer to bless the marriage between Eleanor of Aquitaine and Louis VII. Marie was just 2 years old when her parents joined the Second Crusade to the Holy Land. With the birth of her sister Alice in 1150 instead of the desperately needed son and heir the couple hoped for, the marriage broke down and was annulled on 21 March 1152; Marie was 7 and Alice was not yet 2. Custody of the girls was awarded to their father as they were at that time the only heirs to the French throne. Elea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rigord
Rigord (Rigordus) ( 1150 – c. 1209) was a French chronicler. He was probably born near Alais in Languedoc The Province of Languedoc (, , ; ) is a former province of France. Most of its territory is now contained in the modern-day region of Occitanie in Southern France. Its capital city was Toulouse. It had an area of approximately . History ..., and became a physician. After becoming a monk he entered the monastery of Argenteuil, and then that of Saint-Denis, and described himself as "regis Francorum chronographus". Rigord wrote the ''Gesta Philippi Augusti'', dealing with the life of the French king, Philip Augustus, from his coronation in 1179 until 1206. The work, which is very valuable, was abridged and continued by William the Breton. The earlier part of the ''Gesta'' speaks of the king in very laudatory terms, but in the latter part it is much less flattering in its tone. Rigord also wrote a short chronicle of the kings of France. Editions The ''Gesta'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Of Hoveden
Roger of Howden or Hoveden (died 1202) was a 12th-century English chronicler, diplomat and head of the minster of Howden in the East Riding of Yorkshire. Roger and Howden minster Roger was born to a clerical family linked to the ancient minster of St Peter of Howden, and succeeded his father Robert of Howden as its head, or ''persona''. The date Roger was appointed to the minster by its patrons, the monks of Durham cathedral priory, has been located as around 1169. His title of 'magister' is evidence that he received an education at one of the greater schools of his day, as is also evident from his considerable literary output. Not long after succeeding his father he came into conflict with the lord of Howden and the surrounding district of Howdenshire, Bishop Hugh du Puiset of Durham. Bishop Hugh had made grants of tithes in Howdenshire to the hospital of Kepier in the city of Durham, ignoring the prior rights of the church of Howden. Roger pushed back with the assistance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aloes
Agarwood, aloeswood, eaglewood, gharuwood or the Wood of Gods, commonly referred to as oud or oudh (from , ), is a fragrant, dark and resinous wood used in incense, perfume, and small hand carvings. It forms in the heartwood of ''Aquilaria'' trees after they become infected with a type of '' Phaeoacremonium'' mold, ''P. parasitica''. The tree defensively secretes a resin to combat the fungal infestation. Prior to becoming infected, the heartwood mostly lacks scent, and is relatively light and pale in colouration. However, as the infection advances and the tree produces its fragrant resin as a final option of defense, the heartwood becomes very dense, dark, and saturated with resin. This product is harvested, and most famously referred to in cosmetics under the scent names of ''oud'', ''oodh'' or ''aguru''; however, it is also called ''aloes'' (not to be confused with the succulent plant genus ''Aloe''), ''agar'' (this name, as well, is not to be confused with the edible, alga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Of Wales
Gerald of Wales (; ; ; ) was a Cambro-Norman priest and historian. As a royal clerk to the king and two archbishops, he travelled widely and wrote extensively. He studied and taught in France and visited Rome several times, meeting the Pope. He was nominated for several bishoprics but turned them down in the hope of becoming Bishop of St Davids, but was unsuccessful despite considerable support. His final post was as Archdeacon of Brecon, from which he retired to academic study for the remainder of his life. Much of his writing survives. Life Early life Born at Manorbier Castle in Pembrokeshire, Wales, Gerald was of mixed Norman and Welsh descent. Gerald was the youngest son of William Fitz Odo de Barry (or Barri), the common ancestor of the De Barry family of Barry, Glamorganshire, who subsequently invaded Ireland, a retainer of Arnulf de Montgomery and Gerald de Windsor, and one of the most powerful Anglo-Norman barons in Wales. His mother was Angharad FitzGerald, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seneschal
The word ''seneschal'' () can have several different meanings, all of which reflect certain types of supervising or administering in a historic context. Most commonly, a seneschal was a senior position filled by a court appointment within a royal, ducal, or noble household during the Middle Ages and early Modern period – historically a steward or majordomo of a medieval great house. In a medieval royal household, a seneschal was in charge of domestic arrangements and the administration of servants, which, in the medieval period particularly, meant the seneschal might oversee hundreds of laborers, servants and their associated responsibilities, and have a great deal of power in the community, at a time when much of the local economy was often based on the wealth and responsibilities of such a household. A second meaning is more specific, and concerns the late medieval and early modern nation of France, wherein the seneschal () was also a royal officer in charge of justice a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip II Of France
Philip II (21 August 1165 – 14 July 1223), also known as Philip Augustus (), was King of France from 1180 to 1223. His predecessors had been known as kings of the Franks (Latin: ''rex Francorum''), but from 1190 onward, Philip became the first French monarch to style himself "King of France" (''rex Francie''). The son of King Louis VII and his third wife, Adela of Champagne, he was originally nicknamed () because he was a first son and born late in his father's life. Philip was given the epithet "Augustus" by the chronicler Rigord for having extended the crown lands of France so remarkably. After decades of conflicts with the House of Plantagenet, Philip succeeded in putting an end to the Angevin Empire by defeating a coalition of his rivals at the Battle of Bouvines in 1214. This victory would have a lasting impact on western European politics: the authority of the French king became unchallenged, while John, King of England, was forced by his barons to assent to Magna C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry The Young King
Henry the Young King (28 February 1155 – 11 June 1183) was the eldest son of Henry II of England and Eleanor of Aquitaine to survive childhood. In 1170, he became titular King of England, Duke of Normandy, Count of Anjou and Maine. Henry the Young King was the only English king since the Norman Conquest to be crowned during his father's reign, but he was frustrated by his father's refusal to grant him meaningful autonomous power. He died aged 28, six years before his father, during the course of a campaign in Limousin against his father and his brother Richard. Early life Little is known of the young Henry before the events associated with his marriage and coronation. His mother's children by her first marriage to Louis VII of France were Marie and Alix. He had one elder brother, William (d. 1156), and his younger siblings included Matilda, Richard, Geoffrey, Eleanor, Joan and John. In June 1170, the fifteen-year-old Henry was crowned king during his father's li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |