|
Gardens De La Palace D'Egmont
The Egmont Palace (, ; ), also sometimes known as the Arenberg Palace (; ), is a Neoclassical architecture, neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally built between 1548 and 1560 for Countess Françoise of Luxembourg and Lamoral, Count of Egmont, Count Lamoral of Egmont, though its appearance was heavily modified in the 18th and 19th centuries. It was partly destroyed by fire in 1892, after which it was once again reconstructed. Nowadays, it is used by the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Belgium), Belgian Ministry of Foreign Affairs for receptions, as a guest house and conference centre. The palace is situated in the Sablon, Brussels, Sablon/Zavel district (south-eastern part of Pentagon (Brussels), Brussels' city centre), between the / and the /. This site is served by Porte de Namur metro station, Porte de Namur/Naamsepoort metro station (on lines Brussels Metro line 2, 2 and Brussels Metro line 6, 6 of the Brussels Metro), as well as the Trams in Brussels, tram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cour D'honneur
A court of honor ( ; ) is the principal and formal approach and forecourt of a large building. It is usually defined by two secondary wings projecting forward from the main central block ('' corps de logis''), sometimes with a fourth side, consisting of a low wing or a railing. The Palace of Versailles (''illustration'') and Blenheim Palace (''plan'') both feature such entrance courts. Definition Technically, the term ''cour d'honneur'' can be used of any large building whether public or residential, ancient or modern, which has a symmetrical courtyard laid out in this way. History Some 16th-century symmetrical Western European country houses built on U-shaped groundplans resulted in a sheltered central door in a main range that was embraced between projecting wings, but the formalized ''cour d'honneur'' is first found in the great palaces and mansions of 17th-century Europe, where it forms the principal approach and ceremonial entrance to the building. Its open courtyard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John IV Of Egmont
John IV of Egmont (or Egmond) (1499, Egmond aan den Hoef – April 1528, near Ferrara) was second Count of Egmont, Lord of Hoogwoud, Aartswoud and Baer, and tenth Free Lord of Purmerend, Purmerland and Ilpendam. He belonged to the House of Egmond. John was the eldest surviving son of John III of Egmont and Magdalena van Werdenburg. In 1516 he succeeded his father as Count of Egmont and was made a Knight in the Order of the Golden Fleece. Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor made him in 1527 head of the light infantry in Naples and Milan. One year later, John died near Ferrara, aged 29. Marriage and Children John married in 1516 in Brussels with (1495–1557), daughter of James II of Luxembourg. They had three children: *Margaretha (1517 – 10 March 1554, Bar-le-Duc), married Nicolas, Duke of Mercœur (1524–1577) and mother of Louise of Lorraine, Queen consort of France and Poland by marriage to Henri III of France Henry III (; ; ; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital (architecture), capital, which have been the subject of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tilman-François Suys
Tilman-François Suys (in French) or Tieleman Frans Suys (in Dutch) (1 July 1783 – 22 July 1864) was a Belgian architect who also worked in the Netherlands. Biography Suys completed his architectural education in Paris, where he studied under Charles Percier and won the Prix de Rome in 1812. During his stay in Rome he became a protégé of King William I of the Netherlands the new king of the Belgian and Dutch provinces unified in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands. In 1817 he settled in Amsterdam and worked as an architect for the Dutch Crown. In this period his style shows the marks of the Empire style created for Napoleon by his teacher Charles Percier and Pierre François Léonard Fontaine. From 1825 onwards, Suys was employed on a series of royal commissions in Brussels, a city that, together with The Hague in the province of Holland, had been given the title of capital of the new established kingdom. His projects in Brussels were more severely neoclassical in c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte (born Napoleone di Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French general and statesman who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led Military career of Napoleon, a series of military campaigns across Europe during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars from 1796 to 1815. He led the French First Republic, French Republic as French Consulate, First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then ruled the First French Empire, French Empire as Emperor of the French from 1804 to 1814, and briefly again in 1815. He was King of Italy, King of Kingdom of Italy (Napoleonic), Italy from 1805 to 1814 and Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine, Protector of the Confederation of the Rhine from 1806 to 1813. Born on the island of Corsica to a family of Italian origin, Napoleon moved to mainland France in 1779 and was commissioned as an officer in the French Royal Army in 1785. He supported the French Rev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrian Netherlands
The Austrian Netherlands was the territory of the Burgundian Circle of the Holy Roman Empire between 1714 and 1797. The period began with the acquisition by the Austrian Habsburg monarchy of the former Spanish Netherlands under the Treaty of Rastatt in 1714. It lasted until Revolutionary France annexation, annexed the territory after the Battle of Sprimont in 1794 and the Peace of Basel in 1795. Austria relinquished its claim on the province in 1797 through the Treaty of Campo Formio. The Netherlands, previously the Burgundian Netherlands, inherited by the Spanish branch of the Habsburgs, having revolted against the absolutism and centralism of Philip II of Spain, their common sovereign, launched a war which led in fact, in 1568, to the formation in the north of the Republic of the United Provinces, a new state whose independence would finally be recognized by the King of Spain in 1648 during the Treaty of Münster (October 1648), Treaty of Münster, and in the south of a group o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rococo
Rococo, less commonly Roccoco ( , ; or ), also known as Late Baroque, is an exceptionally ornamental and dramatic style of architecture, art and decoration which combines asymmetry, scrolling curves, gilding, white and pastel colours, sculpted moulding, and ''trompe-l'œil'' frescoes to create surprise and the illusion of motion and drama. It is often described as the final expression of the Baroque movement. The Rococo style began in France in the 1730s as a reaction against the more formal and geometric Louis XIV style. It was known as the "style Rocaille", or "Rocaille style". It soon spread to other parts of Europe, particularly northern Italy, Austria, southern Germany, Central Europe and Russia. It also came to influence other arts, particularly sculpture, furniture, silverware, glassware, painting, music, theatre, and literature. Although originally a secular style primarily used for interiors of private residences, the Rococo had a spiritual aspect to it which led to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism, also spelled Neo-classicism, emerged as a Western cultural movement in the decorative arts, decorative and visual arts, literature, theatre, music, and architecture that drew inspiration from the art and culture of classical antiquity. Neoclassicism was born in Rome, largely due to the writings of Johann Joachim Winckelmann during the rediscovery of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Its popularity expanded throughout Europe as a generation of European art students finished their Grand Tour and returned from Italy to their home countries with newly rediscovered Greco-Roman ideals. The main Neoclassical movement coincided with the 18th-century Age of Enlightenment, and continued into the early 19th century, eventually competing with Romanticism. In architecture, the style endured throughout the 19th, 20th, and into the 21st century. European Neoclassicism in the visual arts began in opposition to the then-dominant Rococo style. Rococo architecture emphasizes grace, Ornament ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni
Jean-Nicolas Servan, also known as Giovanni Niccolò Servandoni (2 May 1695 – 19 January 1766) was an Italian decorator, architect, scene-painter, firework designer and trompe-l'œil specialist. He was born in Florence, the son of a French carriage driver. Career He was educated as an artist of perspective in Rome and was a pupil of Giovanni Paolo Panini worked in London as a set designer at the recently founded Royal Academy of Music but moved to Paris in 1724, where he became director of decorations (1724 to 1742) at the Paris Opera, at that time situated in the Théâtre du Palais-Royal (rue Saint-Honoré), Théâtre du Palais-Royal. He became a member of the Académie Royale de Peinture et de Sculpture in 1731. His activity was considerable, whether as a painter or as an inventor of scenic contrivances for fêtes at the marriage of royal personages. He decorated public festivals in England, France, and Portugal. During the years 1738–1743 and 1754–1758, Servando ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
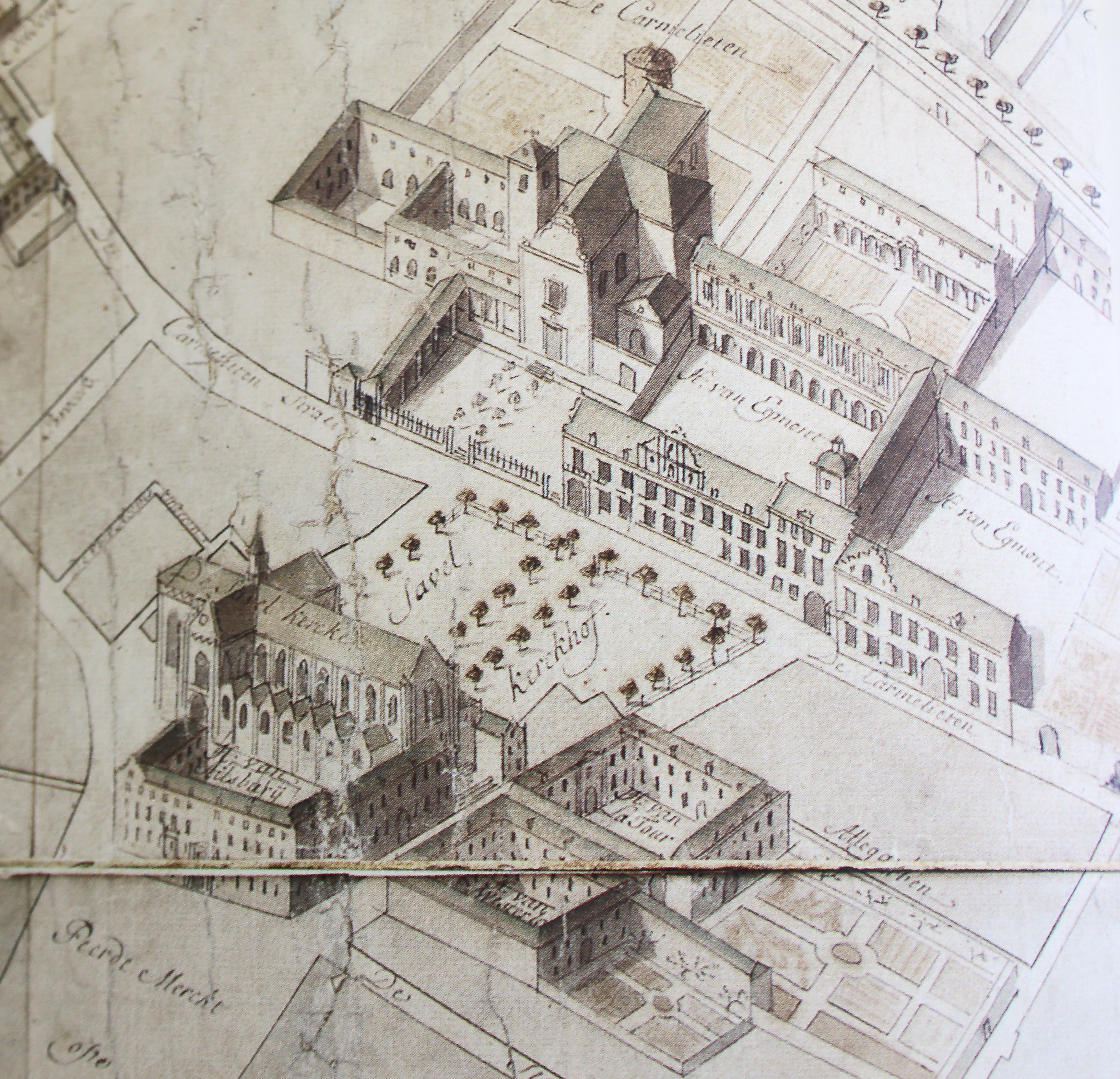
Egmontpaleis 1750
The Egmont Palace (, ; ), also sometimes known as the Arenberg Palace (; ), is a neoclassical palace in Brussels, Belgium. It was originally built between 1548 and 1560 for Countess Françoise of Luxembourg and Count Lamoral of Egmont, though its appearance was heavily modified in the 18th and 19th centuries. It was partly destroyed by fire in 1892, after which it was once again reconstructed. Nowadays, it is used by the Belgian Ministry of Foreign Affairs for receptions, as a guest house and conference centre. The palace is situated in the Sablon/Zavel district (south-eastern part of Brussels' city centre), between the / and the /. This site is served by Porte de Namur/Naamsepoort metro station (on lines 2 and 6 of the Brussels Metro), as well as the tram stop / (on lines 92 and 93). History The Palace of Françoise of Luxembourg The original Egmont Palace was built between 1548 and 1560 as a ''hôtel particulier'' in Flemish Gothic style for , Princess of Gavre and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Arenberg
The House of Arenberg is an aristocratic lineage that is constituted by three successive families that took their name from Arenberg, a small territory of the Holy Roman Empire in the Eifel region. The inheritance of the House of Croÿ, House of Croÿ-Aarschot made the Arenbergs the wealthiest and most influential noble family of the Southern Netherlands, Habsburg Netherlands. The family's Arenberg#1810, Duchy of Arenberg was a Sovereign State until it was German mediatisation, mediatized in 1810. As such, the Arenbergs belong to the small group of families that constitute the . The current head of the house bears the title of Herzog, Duke of Arenberg, while all other members are princes or princesses. They all enjoy the style of Serene Highness. In 1827, Prince Pierre d'Arenberg, third son of the 6th Duke of Arenberg, was granted the French nobility, French noble title of duke by King Charles X of France, Charles X and was made a hereditary peer of France. His descendants form a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |