|
G Major
G major is a major scale based on G (musical note), G, with the pitches G, A (musical note), A, B (musical note), B, C (musical note), C, D (musical note), D, E (musical note), E, and F♯ (musical note), F. Its key signature has one sharp (music), sharp. Its relative key, relative minor is E minor and its parallel key, parallel minor is G minor. The G major scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The G Harmonic major scale, harmonic major and Melodic major scale, melodic major scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of G major are: * Tonic (music), Tonic – G major * Supertonic – A minor * Mediant – B minor * Subdominant – C major * Dominant (music), Dominant – D major * Submediant – E minor * Leading-tone – Diminished triad, F-sharp diminished Notable compositions Baroque period In Baroque music, G major was regarded as the "key of benediction". Of Domen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
E Minor
E minor is a minor scale based on E, consisting of the pitches E, F, G, A, B, C, and D. Its key signature has one sharp, on the F. Its relative major is G major and its parallel major is E major. The E natural minor scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The E harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: Much of the classical guitar repertoire is in E minor, as this is a very natural key for the instrument. In standard tuning (E A D G B E), four of the instrument's six open (un fretted) strings are part of the tonic chord. The key of E minor is also popular in heavy metal music, as its tonic is the lowest note on a standard-tuned guitar. Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of E minor are: * Tonic – E minor * Supertonic – F-sharp diminished * Mediant – G major * Subdominant – A minor * Dominant – B minor * Submediant – C major * Subtonic – D major Nota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
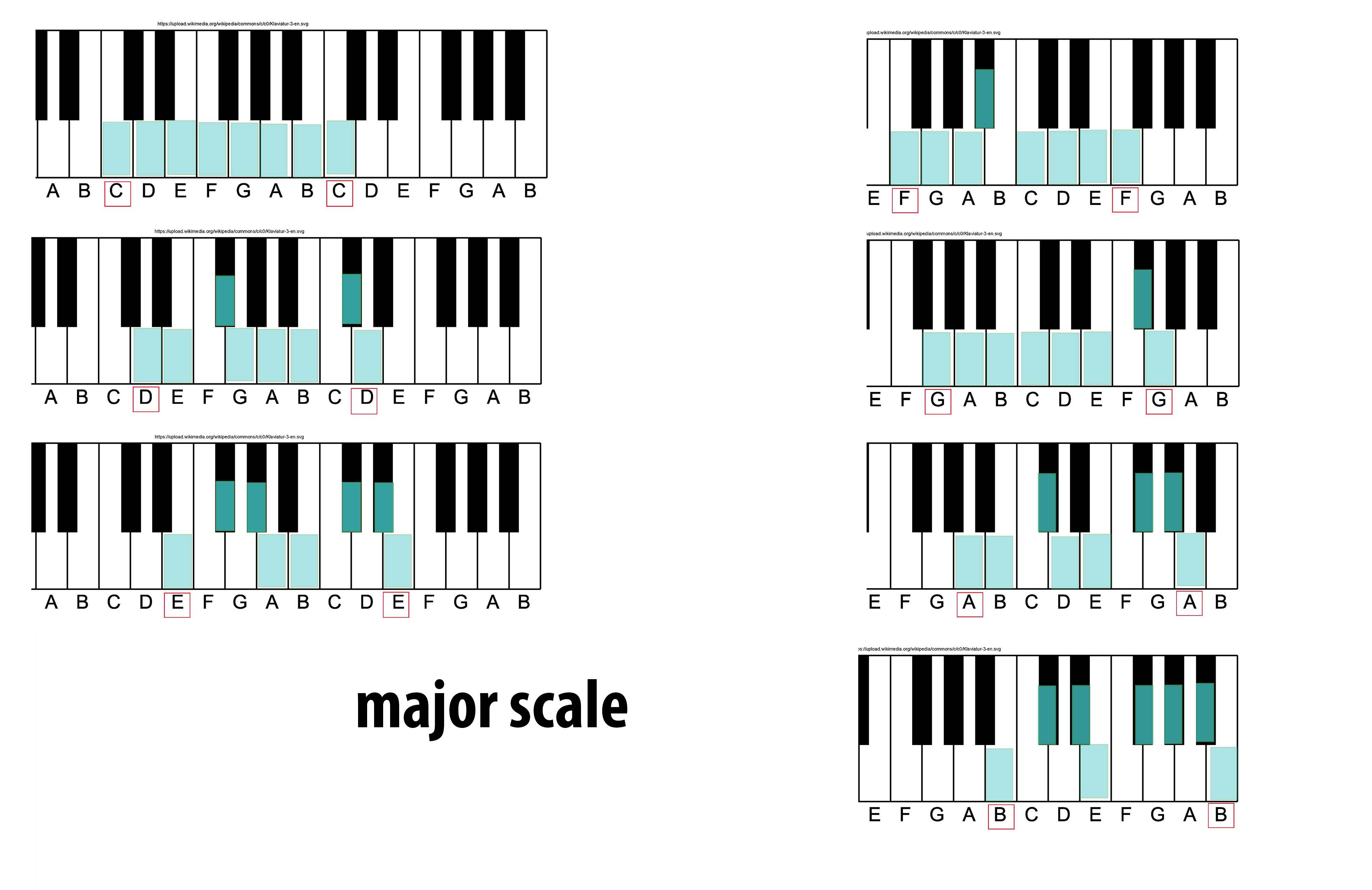
Melodic Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale has a central importance in Western music, particularly that of the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benediction
A benediction (, 'well' + , 'to speak') is a short invocation for divine help, blessing and guidance, usually at the end of worship service. It can also refer to a specific Christian religious service including the exposition of the eucharistic host in the monstrance and the blessing of the people with it. Christianity From the earliest church, Christians adopted ceremonial benedictions into their liturgical worship, particularly at the end of a service. Such benedictions have been regularly practiced both in the Christian East and West. Among the benedictions of the Roman Catholic Church, include thApostolic Benedictionmade by the Pope and his delegates, and th"last blessing"of the dying. The Anglican Church retained the principle of benediction after the Protestant Reformation, and as a result, the benediction or blessing ends most Anglican, as well as Methodist, services of worship. A common form of benediction in Baptist and liturgical Protestant churches is for t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Music
Baroque music ( or ) refers to the period or dominant style of Classical music, Western classical music composed from about 1600 to 1750. The Baroque style followed the Renaissance music, Renaissance period, and was followed in turn by the Classical period (music), Classical period after a short transition (the Galant music, galant style). The Baroque period is divided into three major phases: early, middle, and late. Overlapping in time, they are conventionally dated from 1580 to 1650, from 1630 to 1700, and from 1680 to 1750. Baroque music forms a major portion of the "Western art music, classical music" Western canon, canon, and continues to be widely studied, performed, and listened to. The term "baroque" comes from the Portuguese word ''barroco'', meaning "baroque pearl, misshapen pearl". Key List of Baroque composers, composers of the Baroque era include Johann Sebastian Bach, Antonio Vivaldi, George Frideric Handel, Georg Philipp Telemann, Domenico Scarlatti, Claudio Monte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminished Triad
In music theory, a diminished triad is a triad (music), triad consisting of two minor thirds above the root (chord), root. It is a Minor chord, minor triad with a lowered (flat (music), flattened) Fifth (chord), fifth. When using Chord names and symbols (popular music), chord symbols, it may be indicated by the symbols "dim", "", "m5", or "MI(5)". However, in most popular-music chord books, the symbol "dim" or "" represents a diminished seventh chord (a four-tone chord), which in some modern jazz books and music theory books is represented by the "dim7" or "7" symbols. For example, the diminished triad built on B, written as B, has pitches B-D-F: : The chord can be represented by the Pitch class#Integer notation, integer notation . In the common practice period, the diminished triad is considered Consonance and dissonance, dissonant because of the Tritone, diminished fifth (or tritone). Harmonic function In Major scale, major scales, a diminished triad occurs only on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leading-tone
In music theory, a leading tone (also called subsemitone or leading note in the UK) is a note or pitch which resolves or "leads" to a note one semitone higher or lower, being a lower and upper leading tone, respectively. Typically, leading tone refers to the seventh scale degree of a major scale (), a major seventh above the tonic. In the movable do solfège system, the leading tone is sung as ''si''. A leading-tone triad is a triad built on the seventh scale degree in a major key (vii in Roman numeral analysis), while a leading-tone seventh chord is a seventh chord built on the seventh scale degree (vii7). Walter Piston considers and notates vii as V, an incomplete dominant seventh chord. (For the Roman numeral notation of these chords, see Roman numeral analysis.) Note Seventh scale degree (or lower leading tone) Typically, when people speak of ''the'' leading tone, they mean the seventh scale degree () of the major scale, which has a strong affinity for and leads ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submediant
In music, the submediant is the sixth degree () of a diatonic scale. The submediant ("lower mediant") is named thus because it is halfway between the tonic and the subdominant ("lower dominant") or because its position below the tonic is symmetrical to that of the mediant above. (See the figure in the Degree (music) article.) In the movable do solfège system, the submediant is sung as ''la'' in a major mode, ''le'' or ''lo'' in do-based minor and ''fa'' in la-based minor. It is occasionally called superdominant, as the degree above the dominant. This is its normal name (''sus-dominante'') in French. In Roman numeral analysis, the triad formed on the submediant is typically symbolized by "VI" if it is a major triad (the default in a minor mode) and by "vi" if it is a minor triad (the default in a major mode). The term ''submediant'' may also refer to a relationship of musical keys. For example, relative to the key of C major, the key of A minor is the submediant. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominant (music)
In music Music is the arrangement of sound to create some combination of Musical form, form, harmony, melody, rhythm, or otherwise Musical expression, expressive content. Music is generally agreed to be a cultural universal that is present in all hum ..., the dominant is the fifth degree (music), scale degree () of the diatonic scale. It is called the ''dominant'' because it is second in importance to the first scale degree, the tonic (music), tonic. In the Solfège#Movable do solf%C3%A8ge, movable do solfège system, the dominant note is sung as "So(l)". The Triad (music), triad built on the dominant note is called the dominant chord. This chord is said to have dominant Function (music), function, which means that it creates an instability that requires the tonic (music), tonic for resolution (music), resolution. Dominant triads, Seventh chord, seventh chords, and Ninth chord, ninth chords typically have dominant function. Leading-tone triad, Leading-tone triads and Leadin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subdominant
In music, the subdominant is the fourth tonal degree () of the diatonic scale. It is so called because it is the same distance ''below'' the tonic as the dominant is ''above'' the tonicin other words, the tonic is the dominant of the subdominant. It also happens to be the note one step below the dominant. In the movable do solfège system, the subdominant note is sung as ''fa''. The triad built on the subdominant note is called the subdominant chord. In Roman numeral analysis In music theory, Roman numeral analysis is a type of Harmony, harmonic analysis in which chord (music), chords are represented by Roman numerals, which encode the chord's Degree (music), degree and Function_(music), harmonic function within a given ..., the subdominant chord is typically symbolized by the Roman numeral "IV" in a major key, indicating that the chord is a major triad. In a minor key, it is symbolized by "iv", indicating that the chord is a minor triad. These chords may also appear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
B Minor
B minor is a minor scale based on B, consisting of the pitches B, C, D, E, F, G, and A. Its key signature has two sharps. Its relative major is D major and its parallel major is B major. The B natural minor scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The B harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart (1739–1791) regarded B minor as a key expressing a quiet acceptance of fate and very gentle complaint, something commentators find to be in line with Bach's use of the key in his '' St John Passion''. By the end of the Baroque era, however, conventional academic views of B minor had shifted: Composer-theorist Francesco Galeazzi (1758–1819) opined that B minor was not suitable for music in good taste. Beethoven labelled a B-minor melodic idea in one of his sketchbooks as a "black key". Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of B minor are: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediant
In music, the mediant (''Latin'': "being in the middle") is the third scale degree () of a diatonic scale, being the note halfway between the tonic and the dominant.Benward & Saker (2003), p.32. In the movable do solfège system, the mediant note is sung as ''mi''. While the fifth scale degree is almost always a perfect fifth, the mediant can be a major or minor third. Schenkerian analysts consider the ''mediant'' (third scale degree) as an expansion or extension of the tonic since they are both common tones of the tonic chord. Thus, the third degree of a tonic triad is also the mediant iii note; furthermore, the 5th degree of the submediant chord vi is also the mediant iii note. On the other hand, in German theory derived from Hugo Riemann the mediant in major is considered the dominant parallel, Dp, and in minor the tonic parallel, tP. In Roman numeral analysis, the mediant chord can take several forms. In major scales, the mediant chord is a minor triad and is symboli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Minor
A minor is a minor scale based on A, B, C, D, E, F, and G. Its key signature has no flats or sharps. Its relative major is C major and its parallel major is A major. The A natural minor scale is: Changes needed for the melodic and harmonic versions of the scale are written in with accidentals as necessary. The A harmonic minor and melodic minor scales are: Scale degree chords The scale degree chords of A minor are: * Tonic – A minor * Supertonic – B diminished * Mediant – C major * Subdominant – D minor * Dominant – E minor * Submediant – F major * Subtonic – G major Well-known compositions in A minor *Johann Sebastian Bach ** English Suite No. 2, BWV 807 ** Sonata No. 2 in A minor, BWV 1003 ** Partita in A minor, BWV 1013 ** Violin Concerto in A minor, BWV 1041 ** Allein zu dir, Herr Jesu Christ, BWV 33 *Ludwig van Beethoven ** Violin Sonata No. 4, Op. 23 ** String Quartet No. 15, Op. 132 ** Bagatelle in A minor, "Für Elise" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |