|
GUS Reporter System
The GUS reporter system (''GUS'': β-glucuronidase) is a reporter gene system, particularly useful in plant molecular biology and microbiology. Several kinds of GUS reporter gene assay are available, depending on the substrate used. The term GUS staining refers to the most common of these, a Immunohistochemistry, histochemical technique. Purpose The purpose of this technique is to analyze the activity of a gene transcription Promoter (biology), promoter (in terms of gene expression, expression of a so-called reporter gene under the regulatory control of that promoter) either in a quantitative manner, involving some measure of activity, or qualitatively (on versus off) through visualization of its activity in different cells, Tissue (biology), tissues, or organs. The technique utilizes the uidA gene of ''Escherichia coli'', which codes for the enzyme, β-glucuronidase; this enzyme, when incubated with specific colorless or non-fluorescent Substrate (biology), substrates, can convert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorimeter
A fluorometer, fluorimeter or fluormeter is a device used to measure parameters of visible spectrum fluorescence: its luminous intensity, intensity and wavelength distribution of emission spectrum after Excitation spectrum, excitation by a certain spectrum, spectrum of light. These parameters are used to identify the presence and the amount of specific molecules in a medium. Modern fluorometers are capable of detecting fluorescent molecule concentrations as low as 1 part per trillion. Fluorescence analysis can be orders of magnitude more sensitive than other techniques. Applications include chemistry/biochemistry, medicine, environmental monitoring. For instance, they are used to measure chlorophyll fluorescence to investigate plant physiology. Components and design Typically fluorometers utilize a double beam. These two beams work in tandem to decrease the noise created from radiant power fluctuations. The upper beam is passed through a filter or monochromator and passes throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moss
Mosses are small, non-vascular plant, non-vascular flowerless plants in the taxonomic phylum, division Bryophyta (, ) ''sensu stricto''. Bryophyta (''sensu lato'', Wilhelm Philippe Schimper, Schimp. 1879) may also refer to the parent group bryophytes, which comprise Marchantiophyta, liverworts, mosses, and hornworts. Mosses typically form dense green clumps or mats, often in damp or shady locations. The individual plants are usually composed of simple leaf, leaves that are generally only one cell thick, attached to a plant stem, stem that may be branched or unbranched and has only a limited role in conducting water and nutrients. Although some species have conducting tissues, these are generally poorly developed and structurally different from similar tissue found in vascular plants. Mosses do not have seeds and after fertilisation develop sporophytes with unbranched stalks topped with single capsules containing sporangium, spores. They are typically tall, though some species ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatophyte
A seed plant or spermatophyte (; New Latin ''spermat-'' and Greek ' (phytón), plant), also known as a phanerogam (taxon Phanerogamae) or a phaenogam (taxon Phaenogamae), is any plant that produces seeds. It is a category of embryophyte (i.e. land plant) that includes most of the familiar land plants, including the flowering plants and the gymnosperms, but not ferns, mosses, or algae. The term ''phanerogam'' or ''phanerogamae'' is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek (), meaning "visible", in contrast to the term "cryptogam" or "cryptogamae" (, and (), 'to marry'). These terms distinguish those plants with hidden sexual organs (cryptogamae) from those with visible ones (phanerogamae). Description The extant spermatophytes form five divisions, the first four of which are classified as gymnosperms, plants that have unenclosed, "naked seeds": * Cycadophyta, the cycads, a subtropical and tropical group of plants, * Ginkgophyta, which includes a single living species of tree in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molluscs
Mollusca is a phylum of protostome, protostomic invertebrate animals, whose members are known as molluscs or mollusks (). Around 76,000 extant taxon, extant species of molluscs are recognized, making it the second-largest animal phylum after Arthropoda. The number of additional fossil species is estimated between 60,000 and 100,000, and the proportion of undescribed species is very high. Many taxa remain poorly studied. Molluscs are the largest marine biology, marine phylum, comprising about 23% of all the named marine organisms. They are highly diverse, not just in size and anatomical structure, but also in behaviour and habitat, as numerous groups are freshwater mollusc, freshwater and even terrestrial molluscs, terrestrial species. The phylum is typically divided into 7 or 8 taxonomy (biology), taxonomic class (biology), classes, of which two are entirely extinct. Cephalopod molluscs, such as squid, cuttlefish, and octopuses, are among the most neurobiology, neurologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain. The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebrata with some 65,000 species, by far the largest ranked grouping in the phylum Chordata. The vertebrates include mammals, birds, amphibians, and various classes of fish and reptiles. The fish include the jawless Agnatha, and the jawed Gnathostomata. The jawed fish include both the Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous fish and the Osteichthyes, bony fish. Bony fish include the Sarcopterygii, lobe-finned fish, which gave rise to the tetrapods, the animals with four limbs. Despite their success, vertebrates still only make up less than five percent of all described animal species. The first vertebrates appeared in the Cambrian explosion some 518 million years ago. Jawed vertebrates evolved in the Ordovician, followed by bony fishes in the Devonian. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rice Embryo
Rice is a cereal grain and in its domesticated form is the staple food of over half of the world's population, particularly in Asia and Africa. Rice is the seed of the grass species ''Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice)—or, much less commonly, ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). Asian rice was domesticated in China some 13,500 to 8,200 years ago; African rice was domesticated in Africa about 3,000 years ago. Rice has become commonplace in many cultures worldwide; in 2023, 800 million tons were produced, placing it third after sugarcane and maize. Only some 8% of rice is traded internationally. China, India, and Indonesia are the largest consumers of rice. A substantial amount of the rice produced in developing nations is lost after harvest through factors such as poor transport and storage. Rice yields can be reduced by pests including insects, rodents, and birds, as well as by weeds, and by diseases such as rice blast. Traditional rice polycultures such as rice-duck farming, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
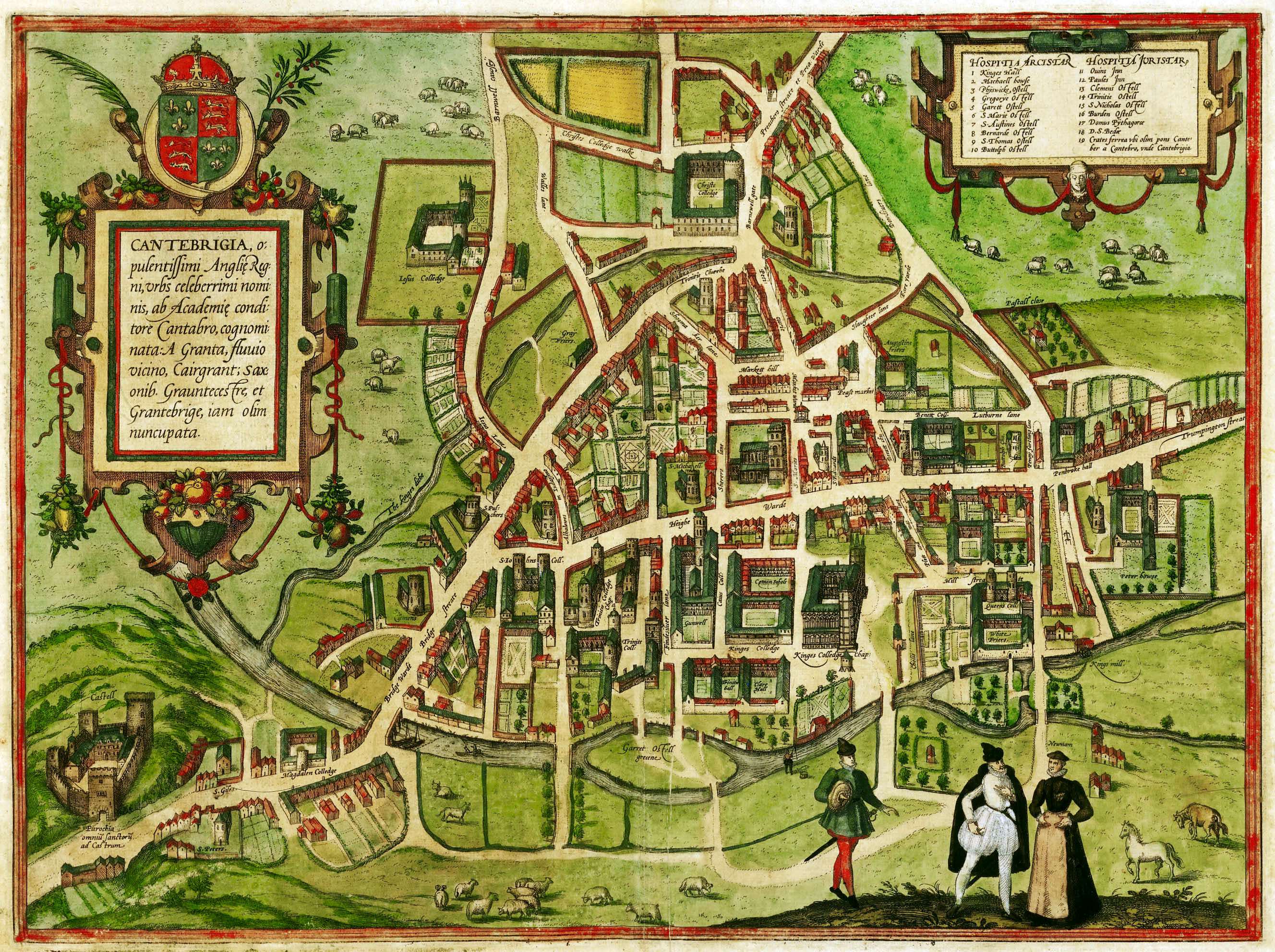
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
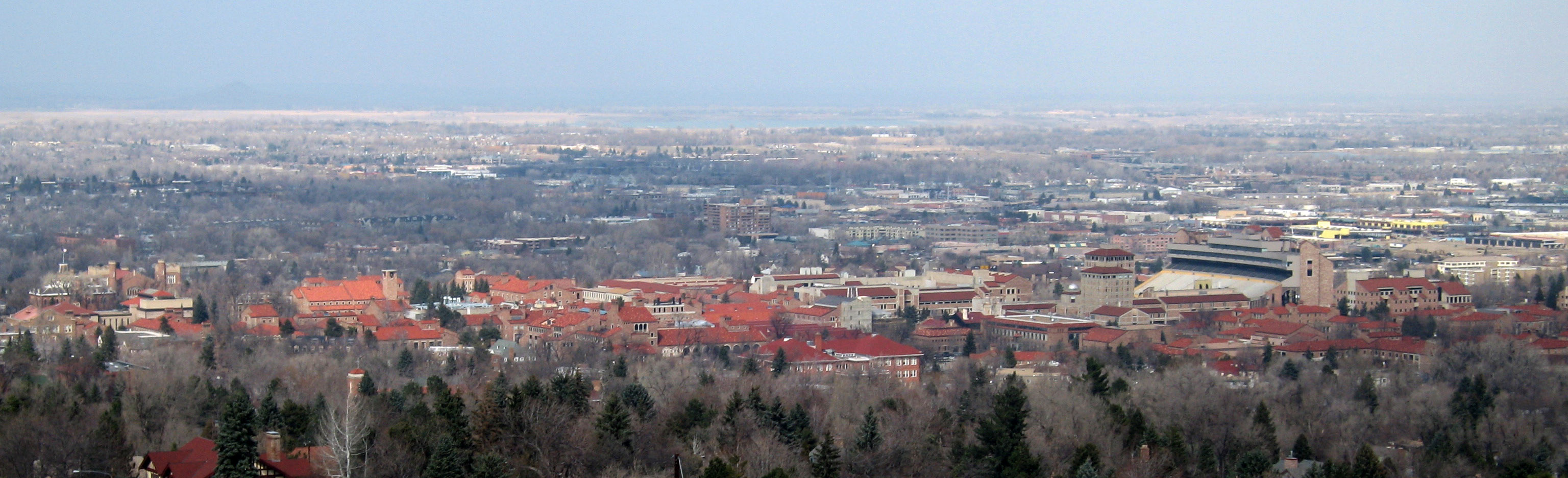
University Of Colorado At Boulder
The University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder, CU, or Colorado) is a Public university, public research university in Boulder, Colorado, United States. Founded in 1876, five months before Colorado became a Federated state, state, it is the flagship university of the University of Colorado system. CU Boulder is a member of the Association of American Universities, considered a Public Ivy and is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity. The university consists of nine colleges and schools and offers over 150 academic programs, enrolling more than 35,000 students as of January 2022. In 2021, the university attracted the support of over $634 million for research and spent $536 million on research and development according to the National Science Foundation, ranking it 50th in the nation. It receives the most NASA astrophysics technology grants of all academic institutions and is the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Anthony Jefferson
Richard Anthony Jefferson (born 1956) is an American-born molecular biologist and social entrepreneur who developed the widely used reporter gene system GUS, conducted the world's first biotech crop release, proposed the Hologenome theory of evolution, pioneered Biological Open Source and founded The Lens. He is founder of the social enterprise Cambia and a professor of Biological Innovation at the Queensland University of Technology. In 2003, he was named by Scientific American as one of the world's 50 most influential technologists, and is renowned for his work on making science-enabled innovation more widely accessible. He was profiled in 'Open & Shut: The Basement Interviews', and other major media, including in an Economist Feature 'Grassroots Innovator' in 2001. Education Born in Santa Cruz, California, Jefferson studied at the University of California, Santa Barbara at the College of Creative Studies, and obtained his BA (Molecular Genetics) in 1978. He then moved to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-gal
X-gal (also abbreviated BCIG for 5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-β--galactopyranoside) is an organic compound consisting of galactose linked to a substituted indole. The compound was synthesized by Jerome Horwitz and collaborators in 1964. The formal chemical name is often shortened to less accurate but also less cumbersome phrases such as bromochloroindoxyl galactoside. The X from indoxyl may be the source of the X in the X-gal contraction. X-gal is often used in molecular biology to test for the presence of an enzyme, β-galactosidase, in the place of its usual target, a β-galactoside. It is also used to detect activity of this enzyme in histochemistry and bacteriology. X-gal is one of many indoxyl glycosides and esters that yield insoluble blue compounds similar to indigo dye as a result of enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis. A less often used but very similar (chiral) compound is X-\alpha-gal (Xαgal, X-alpha-gal), or 5-Bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl-α-D-galactopyranoside, which is hydrolyze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |