|
Four-toed Jerboa
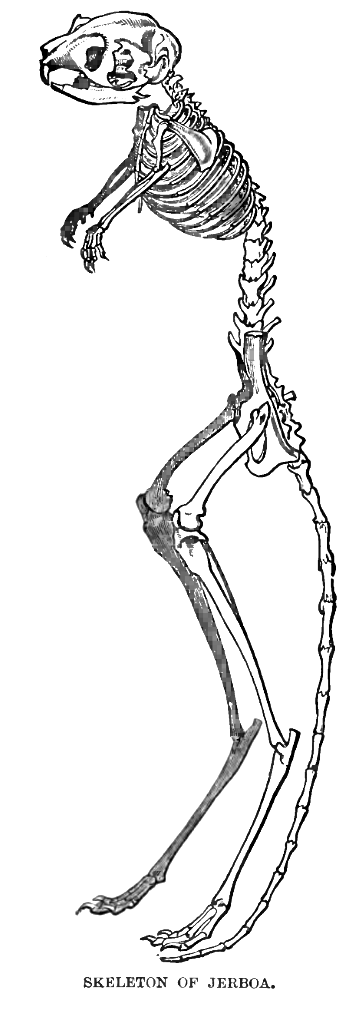
The four-toed jerboa (''Allactaga tetradactyla'') is a rodent of the family Dipodidae and genus '' Allactaga'' that has four digits. It is the sole species in the subgenus ''Scarturus''. Four-toed jerboas are native to Egypt and Libya. They live in coastal salt marshes and dry deserts. Physical appearance Similar to the other jerboas in the genus '' Allactaga'', the four-toed jerboa are small hopping rodents with large ears and a long tail, with a black band near the white, feathery tip. The tail assists and serves as support when the jerboa is standing upright. They have long hind feet and short forelegs. The pelt of the four-toed jerboa is velvety in texture and the upper-parts are speckled black and orange, the rump orange, and the sides gray. The four-toed jerboa hind-limbs have an extra digit compared to other jerboas in the genus '' Allactaga''. The extra digit is smaller in size and nonfunctional compared to the other three digits. Nutrition Emerging at night, the four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Lichtenstein
Martin Hinrich Carl Lichtenstein (10 January 1780 – 2 September 1857) was a German physician, explorer, botanist and zoologist. Biography Born in Hamburg, Lichtenstein was the son of Anton August Heinrich Lichtenstein. He studied medicine at Jena and Helmstedt. Between 1802 and 1806 he travelled in southern Africa, becoming the personal physician of the Governor of the Cape of Good Hope. In 1811 he published ''Reisen im südlichen Afrika : in den Jahren 1803, 1804, 1805, und 1806''; as a result, he was appointed professor of zoology at the University of Berlin in 1811, and appointed director of the Berlin Zoological Museum in 1813. In 1829, he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. He died after he had a stroke at sea travelling aboard a steamer from Korsør to Kiel. Legacy Lichtenstein was responsible for the creation of Berlin's Zoological Gardens in 1841, when he persuaded King Frederick William IV of Prussia to donate the ground ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipodidae
Jerboas (from ar, جربوع ') are hopping desert rodents found throughout North Africa and Asia, and are members of the family Dipodidae. They tend to live in hot deserts. When chased, jerboas can run at up to . Some species are preyed on by little owls (''Athene noctua'') in central Asia. Most species of jerboas have excellent hearing that they use to avoid becoming the prey of nocturnal predators. The typical lifespan of a jerboa is around 6 years. Taxonomy Jerboas, as previously defined, were thought to be paraphyletic, with the jumping mice (Zapodidae) and birch mice (Sminthidae) also classified in the family Dipodidae. However, phylogenetic analysis split all three as distinct families, leaving just the jerboas in Dipodidae and revealing them to be a monophyletic group. Anatomy and body features Jerboas look somewhat like miniature kangaroos, and have some external similarities. Both have long hind legs, short forelegs, and long tails. Jerboas move around in a similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allactaga
The genus ''Allactaga'' contains the four and five-toed jerboas of Asia. They are small mammals belonging to the order of rodents. They are characteristically known as the hopping rodents of the desert and semi-arid regions. They have long hind feet, short forelimbs, and walk upright. They have large ears in comparison to their body size and a large tail. The tail assists and serves as support when the jerboa is standing upright. The jerboa body length ranges from 5–15 cm and has a tail ranging from 7–25 cm."Jerboa (rodent)" ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 2013. Web. 12 October 2013. The "forelimbs of the jerboa serve as a pair of hands for feeding, grooming, etc."Kirmiz, John P. ''Adaptation to Desert Environment; A Study on the Jerboa, Rat and Man''. Lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
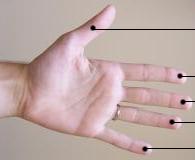
Digit (anatomy)
A digit is one of several most distal parts of a limb, such as fingers or toes, present in many vertebrates. Names Some languages have different names for hand and foot digits (English: respectively " finger" and "toe", German: "Finger" and "Zeh", French: "doigt" and "orteil"). In other languages, e.g. Arabic, Russian, Polish, Spanish, Portuguese, Italian, Czech, Tagalog, Turkish, Bulgarian, and Persian, there are no specific one-word names for fingers and toes; these are called "digit of the hand" or "digit of the foot" instead. In Japanese, yubi (指) can mean either, depending on context. Human digits Humans normally have five digits on each extremity. Each digit is formed by several bones called phalanges, surrounded by soft tissue. Human fingers normally have a nail at the distal phalanx. The phenomenon of polydactyly occurs when extra digits are present; fewer digits than normal are also possible, for instance in ectrodactyly. Whether such a mutation can be s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad to the south, Niger to the southwest, Algeria to the west, and Tunisia to the northwest. Libya is made of three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica. With an area of almost 700,000 square miles (1.8 million km2), it is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the 16th-largest in the world. Libya has the 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. The largest city and capital, Tripoli, is located in western Libya and contains over three million of Libya's seven million people. Libya has been inhabited by Berbers since the late Bronze Age as descendants from Iberomaurusian and Capsian cultures. In ancient times, the Phoenicians established city-states and tradin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Marsh
A salt marsh or saltmarsh, also known as a coastal salt marsh or a tidal marsh, is a coastal ecosystem in the upper coastal intertidal zone between land and open saltwater or brackish water that is regularly flooded by the tides. It is dominated by dense stands of salt-tolerant plants such as herbs, grasses, or low shrubs. These plants are terrestrial in origin and are essential to the stability of the salt marsh in trapping and binding sediments. Salt marshes play a large role in the aquatic food web and the delivery of nutrients to coastal waters. They also support terrestrial animals and provide coastal protection. Salt marshes have historically been endangered by poorly implemented coastal management practices, with land reclaimed for human uses or polluted by upstream agriculture or other industrial coastal uses. Additionally, sea level rise caused by climate change is endangering other marshes, through erosion and submersion of otherwise tidal marshes. However, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About one-third of the land surface of the Earth is arid or semi-arid. This includes much of the polar regions, where little precipitation occurs, and which are sometimes called polar deserts or "cold deserts". Deserts can be classified by the amount of precipitation that falls, by the temperature that prevails, by the causes of desertification or by their geographical location. Deserts are formed by weathering processes as large variations in temperature between day and night put strains on the rocks, which consequently break in pieces. Although rain seldom occurs in deserts, there are occasional downpours that can result in flash floods. Rain falling on hot rocks can cause them to shatter, and the resulting fragments and rubble strewn over t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
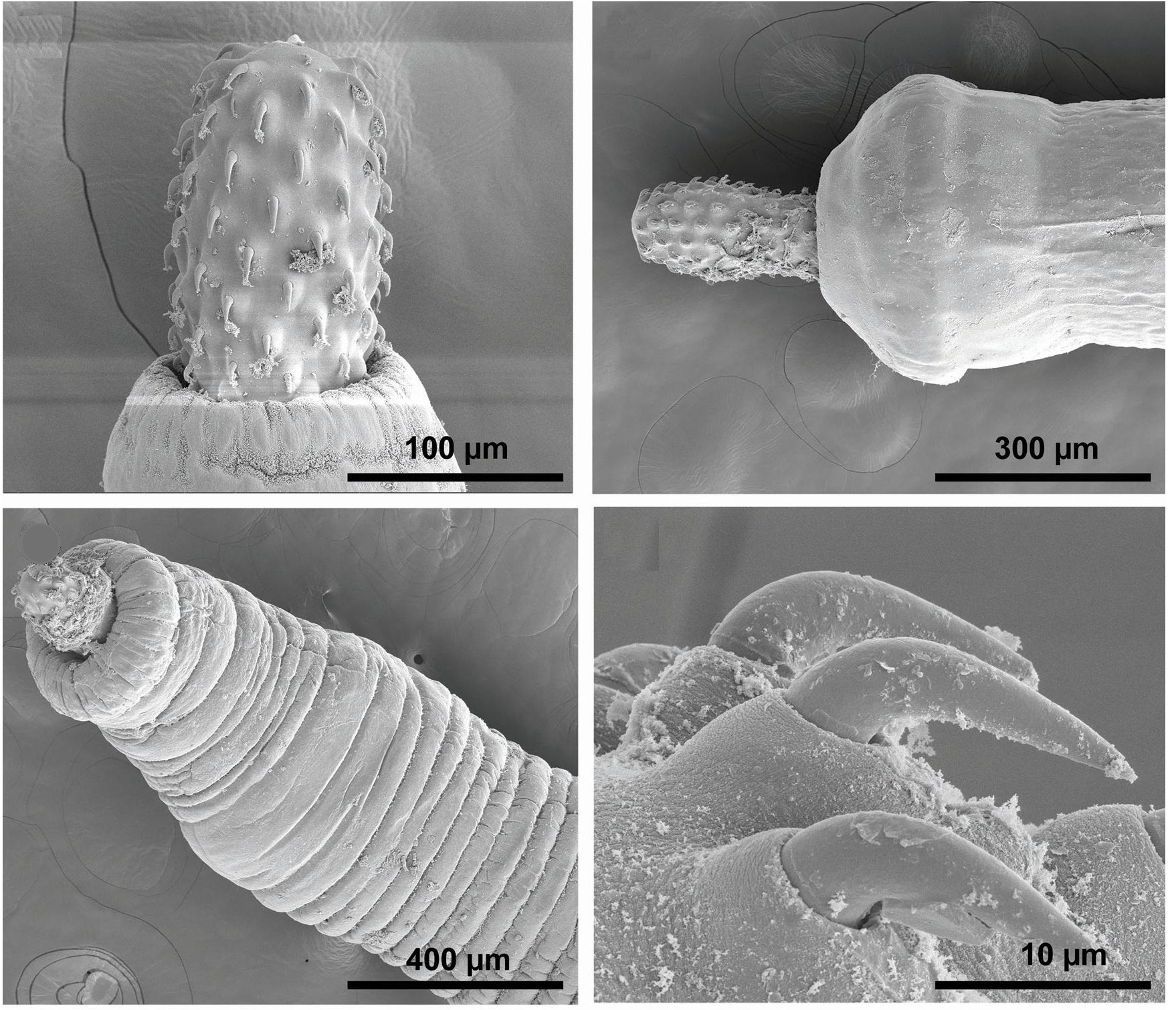
Acanthocephala
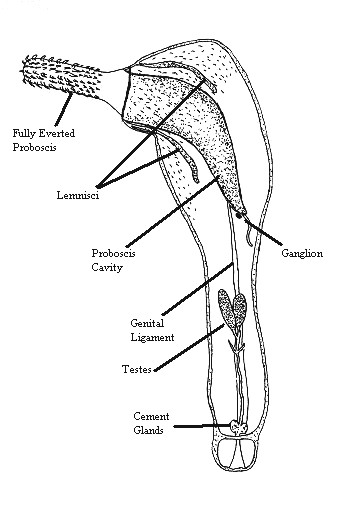
Acanthocephala (Greek , ', thorn + , ', head) is a phylum of parasitic worms known as acanthocephalans, thorny-headed worms, or spiny-headed worms, characterized by the presence of an eversible proboscis, armed with spines, which it uses to pierce and hold the gut wall of its host. Acanthocephalans have complex life cycles, involving at least two hosts, which may include invertebrates, fish, amphibians, birds, and mammals. About 1420 species have been described. The Acanthocephala were thought to be a discrete phylum. Recent genome analysis has shown that they are descended from, and should be considered as, highly modified rotifers. This unified taxon is known as Syndermata. History The earliest recognisable description of Acanthocephala – a worm with a proboscis armed with hooks – was made by Italian author Francesco Redi (1684).Crompton 1985, p. 27 In 1771, Joseph Koelreuter proposed the name Acanthocephala. Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller independently called t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moniliformis Aegyptiacus
Moniliformidae is a family of parasitic spiny-headed (or thorny-headed) worms. It is the only family in the Moniliformida order and contains three genera: ''Australiformis'' containing a single species, ''Moniliformis'' containing eighteen species and ''Promoniliformis'' containing a single species. Genetic analysis have determined that the clade is monophyletic despite being distributed globally. These worms primarily parasitize mammals, including humans in the case of ''Moniliformis moniliformis'', and occasionally birds by attaching themselves into the intestinal wall using their hook-covered proboscis. The intermediate hosts are mostly cockroaches. The distinguishing features of this order among archiacanthocephalans is the presence of a cylindrical proboscis with long rows of hooks with posteriorly directed roots and proboscis retractor muscles that pierce both the posterior and ventral end or just posterior end of the receptacle. Infestation with Monoliformida species ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and invasive species. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List lists the global conservation status of many species, and various other agencies assess the status of species within particular areas. Many nations have laws that protect conservation-reliant species which, for example, forbid hunting, restrict land development, or create protected areas. Some endangered species are the target of extensive conservation efforts such as captive breeding and habitat restoration. Human activity is a significant cause in causing some species to become endangered. Conservation status The conservation status of a species indicates the likelihood that it will become extinct. Multiple factors are considered when assessing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |