|
FluoProbes
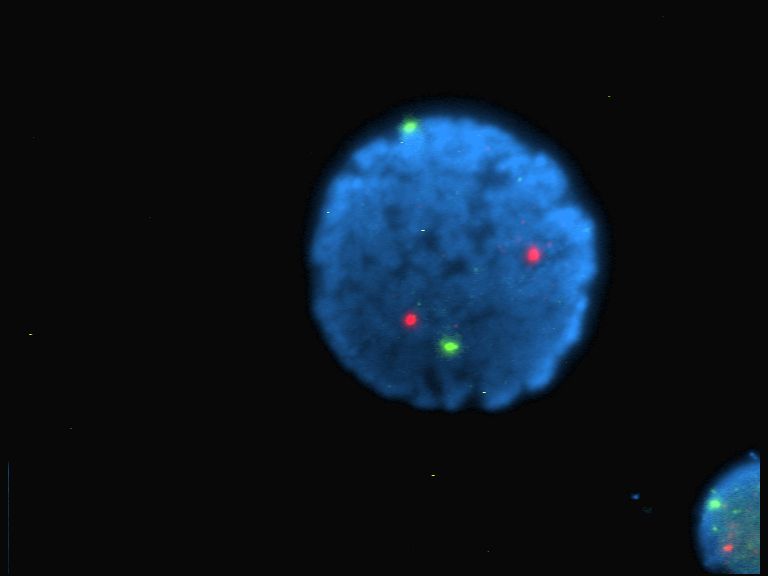
The FluoProbes series of fluorescent dyes were developed by Interchim to improve performances of standard fluorophores. They are designed for labeling biomolecules, cells, tissues or beads in advanced fluorescent detection techniques. * FluoProbes dyes are typically used to label proteins or nucleic acids (ultrafast -3 minutes- labeling of antibodies employs Lightning technology). Labeled products can be used for multiparameter detections, life time resolved fluorescence (TRF), polarisation anisotropy fluorescence, FRET, Quenching, FRAP. They are typically used in biotechnology and research applications as fluorescence microscopy, cell biology or molecular biology, as well as infrared imaging. Derivatives with Amine and Carboxyl suit peptide and nucleic acid synthesis, while reactive ones (with succinimidyl, maleimide and hydrazide) suit conjugation by conventional chemistry, while FluoProbes labeled antibodies and cellular probes (i.e. Phalloidin) suit direct use in immun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyanine
Cyanines, also referred to as tetramethylindo(di)-carbocyanines are a synthetic dye family belonging to the polymethine group. Although the name derives etymologically from terms for shades of blue, the cyanine family covers the electromagnetic spectrum from near IR to UV. Chemically, cyanines are a conjugated system between two nitrogen atoms; in each resonance structure, exactly one nitrogen atom is oxidized to an iminium. Typically, they form part of a nitrogenous heterocyclic system. The main application for cyanine dyes is in biological labeling. Nevertheless, there is a wide literature on both their synthesis and uses, and cyanines are common in some CD and DVD media. Structure Cyanines have been classified in many ways: * ''Streptocyanines'' or ''open chain cyanines'': : R2N+=CH H=CH'n''-NR2 (I) * ''Hemicyanines'': : Aryl=N+=CH H=CH'n''-NR2 (II) * ''Closed chain cyanines'': :Aryl=N+=CH H=CH'n''-N=Aryl (III) Additionally, these classes are recognized: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interchim
Interchim is a privately owned French company specialized in manufacturing and distribution of reagents, consumables and dedicated instruments for the R&D and industry laboratory in the fields of fine chemistry, chromatography and bio-analysis. It has become a provider of reference methods, products for analytics (analytical chemistry and bioassays) serving research and quality control in the biomedical field, pharmaceutical industry, but also cosmetics and environment. History Interchim was founded by Boch Jean (formerly chemical engineer at Rhone-Poulenc) and Boch Colette in 1970. Their initial activity started with distribution of fine chemicals, then chromatography and Biology. Production was developed as well, in each fields. Affiliate companies were created for production and commercial activities in France, UK (2003), USA (2007) and Instrumentation business (2010). Interchim has now major activity in fine chromatography, fine chemistry and bio-analysis. Leadership in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorophore
A fluorophore (or fluorochrome, similarly to a chromophore) is a fluorescent chemical compound that can re-emit light upon light excitation. Fluorophores typically contain several combined aromatic groups, or planar or cyclic molecules with several π bonds. Fluorophores are sometimes used alone, as a tracer in fluids, as a dye for staining of certain structures, as a substrate of enzymes, or as a probe or indicator (when its fluorescence is affected by environmental aspects such as polarity or ions). More generally they are covalently bonded to a macromolecule, serving as a marker (or dye, or tag, or reporter) for affine or bioactive reagents ( antibodies, peptides, nucleic acids). Fluorophores are notably used to stain tissues, cells, or materials in a variety of analytical methods, i.e., fluorescent imaging and spectroscopy. Fluorescein, via its amine-reactive isothiocyanate derivative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC), has been one of the most popular fluorophores. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescence
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, than the absorbed radiation. A perceptible example of fluorescence occurs when the absorbed radiation is in the ultraviolet region of the electromagnetic spectrum (invisible to the human eye), while the emitted light is in the visible region; this gives the fluorescent substance a distinct color that can only be seen when the substance has been exposed to UV light. Fluorescent materials cease to glow nearly immediately when the radiation source stops, unlike phosphorescent materials, which continue to emit light for some time after. Fluorescence has many practical applications, including mineralogy, gemology, medicine, chemical sensors (fluorescence spectroscopy), fluorescent labelling, dyes, biological detectors, cosmic-ray detection, vac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore H. Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles Hard Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light which is ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling applications such as laser cutting and lithography. Spatial coherence also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimation), enabling applications such as laser pointers and lidar (light detection and ranging). Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which allows them to emit light with a very narrow spectrum. Alternatively, temporal coherence can be used to produce ultrashort pulses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulforhodamine 101
Sulforhodamine 101 (SR101) is a red fluorescent dye. In neurophysiological experiments which comprise calcium imaging methods, it can be used for a counterstaining of astrocytes to be able to analyze data from neurons separately. However, in addition to labeling astrocytes, SR101 labels myelinating oligodendrocytes. SR101 has been reported to affect excitability of neurons and should therefore be used with caution. A sulfonyl chloride In inorganic chemistry, sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl () functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula , where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides ... derivative of sulforhodamine 101, known as Texas Red, is used for conjugation to a number of functional groups, especially primary amines. References {{Reflist Benzenesulfonates Rhodamine dyes Nitrogen heterocycles Oxygen heterocycles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TRITC
Rhodamine is a family of related dyes, a subset of the triarylmethane dyes. They are derivatives of xanthene. Important members of the rhodamine family are Rhodamine 6G, Rhodamine 123, and Rhodamine B. They are mainly used to dye paper and inks, but they lack the lightfastness for fabric dyeing. Use Aside from their major applications, they are often used as a tracer dye, e.g. to determine the rate and direction of flow and transport of water. Rhodamine dyes fluoresce and can thus be detected easily and inexpensively with instruments called fluorometers. Rhodamine dyes are used extensively in biotechnology applications such as fluorescence microscopy, flow cytometry, fluorescence correlation spectroscopy and ELISA. Rhodamine 123 is used in biochemistry to inhibit mitochondrion function. Rhodamine 123 appears to bind to the mitochondrial membranes and inhibit transport processes, especially the electron transport chain, thus slowing down cellular respiration. It is a substra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helium–neon Laser
A helium–neon laser or He-Ne laser, is a type of gas laser whose high energetic medium gain medium consists of a mixture of 10:1 ratio of helium and neon at a total pressure of about 1 torr inside of a small electrical discharge. The best-known and most widely used He-Ne laser operates at a wavelength of 632.8 nm, in the red part of the visible spectrum. History of He-Ne laser development The first He-Ne lasers emitted infrared at 1150 nm, and were the first gas lasers and the first lasers with continuous wave output. However, a laser that operated at visible wavelengths was much more in demand, and a number of other neon transitions were investigated to identify ones in which a population inversion can be achieved. The 633 nm line was found to have the highest gain in the visible spectrum, making this the wavelength of choice for most He-Ne lasers. However, other visible and infrared stimulated-emission wavelengths are possible, and by using mirror coating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ion Laser
An ion laser is a gas laser that uses an ionized gas as its lasing medium. Like other gas lasers, ion lasers feature a sealed cavity containing the laser medium and mirrors forming a Fabry–Pérot resonator. Unlike helium–neon lasers, the energy level transitions that contribute to laser action come from ions. Because of the large amount of energy required to excite the ionic transitions used in ion lasers, the required current is much greater, and as a result all but the smallest ion lasers are water-cooled. A small air-cooled ion laser might produce, for example, 130 milliwatts of output light with a tube current of about 10 amperes and a voltage of 105 volts. Since one ampere times one volt is one watt, this is an electrical power input of about one kilowatt. Subtracting the (desirable) light output of 130 mW from power input, this leaves the large amount of waste heat of nearly one kW. This has to be dissipated by the cooling system. In other words, the power efficiency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorescein Isothiocyanate
Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) is a derivative of fluorescein used in wide-ranging applications including flow cytometry. First described in 1942, FITC is the original fluorescein molecule functionalized with an isothiocyanate reactive group (−N=C=S), replacing a hydrogen atom on the bottom ring of the structure. It is typically available as a mixture of isomers, fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate (5-FITC) and fluorescein 6-isothiocyanate (6-FITC). FITC is reactive towards nucleophiles including amine and sulfhydryl groups on proteins. It was synthesized by Robert Seiwald and Joseph Burckhalter in 1958. A succinimidyl-ester functional group attached to the fluorescein core, creating "NHS-fluorescein", forms another common amine reactive derivative that has much greater specificity toward primary amines in the presence of other nucleophiles. FITC has excitation and emission spectrum peak wavelengths of approximately 495 nm and 519 nm, giving it a green color. Like mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Diode
The laser diode chip removed and placed on the eye of a needle for scale A laser diode (LD, also injection laser diode or ILD, or diode laser) is a semiconductor device similar to a light-emitting diode in which a diode pumped directly with electrical current can create lasing conditions at the diode's junction. Driven by voltage, the doped p–n-transition allows for recombination of an electron with a hole. Due to the drop of the electron from a higher energy level to a lower one, radiation, in the form of an emitted photon is generated. This is spontaneous emission. Stimulated emission can be produced when the process is continued and further generates light with the same phase, coherence and wavelength. The choice of the semiconductor material determines the wavelength of the emitted beam, which in today's laser diodes range from infra-red to the UV spectrum. Laser diodes are the most common type of lasers produced, with a wide range of uses that include fiber optic c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confocal Microscopy
Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser confocal scanning microscopy (LCSM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation. Capturing multiple two-dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures (a process known as optical sectioning) within an object. This technique is used extensively in the scientific and industrial communities and typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science. Light travels through the sample under a conventional microscope as far into the specimen as it can penetrate, while a confocal microscope only focuses a smaller beam of light at one narrow depth level at a time. The CLSM achieves a controlled and highly limited depth of field. Basic concept The principle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |