|
Fibular Artery
In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The fibular artery arises from the bifurcation of tibial-fibular trunk into the fibular and posterior tibial arteries in the upper part of the leg proper, just below the knee. It runs towards the foot in the deep posterior compartment of the leg, just medial to the fibula. It supplies a perforating branch to both the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg; it also provides a nutrient artery to the fibula. Some sources claim that the fibular artery arises directly from the posterior tibial artery, but vascular and plastic surgeons note the clinical significance of the tibial-fibular trunk. The fibular artery is accompanied by small veins (venae comitantes) known as fibular veins. Branches Communication branch to posterior tibial artery. Perforating branch to anterior lateral malleolar artery. A calcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibial-fibular Trunk
Tibiofibular trunk (or tibioperoneal trunk) is an arterial trunk representing the direct continuation of the popliteal artery distal to where the anterior tibial artery (the first branch of the popliteal artery) branches off from it. The tibiofibular trunk terminates by bifurcating into two terminal branches: the posterior tibial artery, and the fibular artery In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The fibular artery arises from the bifurcation of tibial-fibular trunk .... This is the most common configuration of the origins of these arteries, however, many other anatomical variations exist. The vessel here described as the tibiofibular trunk may alternately be regarded as the initial portion of the posterior tibial artery, with the fibular artery instead regarded as its branch. References External links * http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
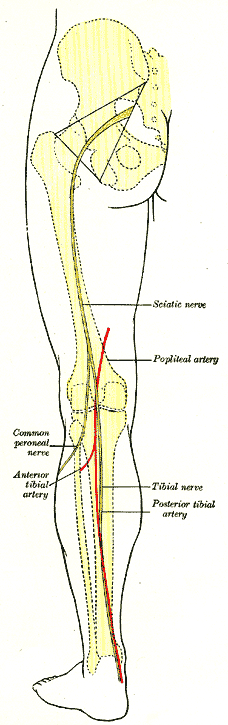
Popliteal Artery
The popliteal artery is a deeply placed continuation of the femoral artery opening in the distal portion of the adductor magnus muscle. It courses through the popliteal fossa and ends at the lower border of the popliteus muscle, where it branches into the anterior tibial artery, anterior and Posterior tibial artery, posterior tibial arteries. The deepest (most anterior) structure in the fossa, the popliteal artery runs close to the joint capsule of the knee as it spans the Intercondylar fossa of femur, intercondylar fossa. Five genicular branches of the popliteal artery supply the capsule and ligaments of the knee joint. The genicular arteries are the superior lateral, superior medial, middle, inferior lateral, and inferior medial genicular arteries. They participate in the formation of the periarticular genicular anastomosis, a network of vessels surrounding the knee that provides collateral circulation capable of maintaining blood supply to the leg during full knee flexion, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Tibial Artery
The anterior tibial artery is an artery of the leg. It carries blood to the anterior compartment of the leg and dorsum (biology), dorsal surface of the foot, from the popliteal artery. Structure Course The anterior tibial artery is a branch of the popliteal artery. It originates at the distal end of the popliteus muscle posterior to the tibia. The artery typically passes anterior to the popliteus muscle prior to passing between the tibia and fibula through an oval opening at the superior aspect of the interosseus membrane. The artery then descends between the tibialis anterior and extensor digitorum longus muscles. It is accompanied by the anterior tibial vein, and the deep peroneal nerve, along its course. It crosses the anterior aspect of the ankle joint, at which point it becomes the dorsalis pedis artery. Branches The branches of the anterior tibial artery are: *posterior tibial recurrent artery *anterior tibial recurrent artery *muscular branches *anterior medial malleo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Posterior Tibial Artery
The posterior tibial artery of the lower limb is an artery that carries blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and plantar surface of the foot. It branches from the popliteal artery via the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The posterior tibial artery arises from the popliteal artery in the popliteal fossa. It is accompanied by a deep vein, the posterior tibial vein, along its course. It passes just posterior to the medial malleolus of the tibia, but anterior to the Achilles tendon. It passes into the foot deep to the flexor retinaculum of the foot. It runs through the tarsal tunnel. Branches The posterior tibial artery gives rise to: * medial plantar artery. * lateral plantar artery. * fibular artery, which is said to rise from the bifurcation of the tibial-fibular trunk and the posterior tibial artery. * calcaneal branch to the medial aspect of the calcaneus. Function The posterior tibial artery supplies oxygenated blood to the posterior compartment of the leg and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Vein
In anatomy, the fibular veins (also known as peroneal veins) are accompanying veins (venae comitantes) of the fibular artery. Structure The fibular veins are deep veins that help carry blood from the lateral compartment of the leg. They drain into the posterior tibial veins, which in turn drain into the popliteal vein. The fibular veins accompany the fibular artery. See also * Fibular artery * Common fibular nerve * Venae comitantes Additional images File:Gray440_color.png, Cross-section through middle of leg. File:Ultrasonography of thrombosis of the fibular veins, coronal plane, annotated.jpg, Coronal plane The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal and transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a longit ... (seen from medial side of lower leg) ultrasonography of deep vein thrombosis of the fibular veins, seen as hyperechoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Compartment Of The Leg
The lateral compartment of the leg is a fascial compartment of the lower leg. It contains muscles which make eversion and plantarflexion of the foot. Muscles The lateral compartment of the leg contains: * Fibularis longus * Fibularis brevis Action * Foot evertors * Foot plantarflexion Nerve Supply The lateral compartment of the leg is supplied by the superficial fibular nerve (superficial peroneal nerve). Blood Supply Its proximal and distal arterial supply consists of perforating branches of the anterior tibial artery and fibular artery. Additional images File:Lateral compartment of leg - animation.gif, Animation. Fibularis longus (blue) and fibularis brevis (red). See also *Fascial compartments of leg The fascial compartments of the leg are the four fascial compartments that separate and contain the muscles of the lower leg (from the knee to the ankle). The compartments are divided by septa formed from the fascia. The compartments usually hav ... Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function (biology), function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic research, basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic scale, macroscopic and microscopic scale, microscopic. Gross anatomy, Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venae Comitantes
Vena comitans is Latin for accompanying vein. It refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. They are found in close proximity to arteries so that the pulsations of the artery aid venous return. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes. Venae comitantes are usually found with certain smaller arteries, especially those in the extremities. Larger arteries, on the other hand, generally do not have venae comitantes. They usually have a single, similarly sized vein which is not as intimately associated with the artery. Examples of arteries and their venae comitantes: * Radial artery and radial veins * Ulnar artery and ulnar veins * Brachial artery and brachial veins * Anterior tibial artery and anterior tibial veins * Posterior tibial artery and Posterior tibial veins * Fibular artery and Fibular veins Examples of arteries that do not have venae comitantes (i.e. thos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Veins
In anatomy, the fibular veins (also known as peroneal veins) are accompanying veins (venae comitantes) of the fibular artery. Structure The fibular veins are deep veins that help carry blood from the lateral compartment of the leg. They drain into the posterior tibial veins, which in turn drain into the popliteal vein. The fibular veins accompany the fibular artery. See also * Fibular artery * Common fibular nerve * Venae comitantes Additional images File:Gray440_color.png, Cross-section through middle of leg. File:Ultrasonography of thrombosis of the fibular veins, coronal plane, annotated.jpg, Coronal plane The coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is an anatomical plane that divides the body into dorsal and ventral sections. It is perpendicular to the sagittal and transverse planes. Details The coronal plane is an example of a longitud ... (seen from medial side of lower leg) ultrasonography of deep vein thrombosis of the fibular veins, seen as hyperechoic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anterior Lateral Malleolar Artery
The anterior lateral malleolar artery (lateral anterior malleolar artery, external malleolar artery) is an artery in the ankle. The anterior lateral malleolar artery is a branch of the anterior tibial artery. It passes beneath the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus and fibularis tertius and supplies the lateral side of the ankle. It forms anastomoses with the perforating branch of the fibular artery In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The fibular artery arises from the bifurcation of tibial-fibular trunk ..., and with ascending twigs from the lateral tarsal artery. References External links * http://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/figures/chapter_17/17-3.HTM Arteries of the lower limb {{circulatory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubecle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the abductor hallucis and abductor digiti minimi). The Achilles tendon is inserted into a roughened area on its superio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |