|
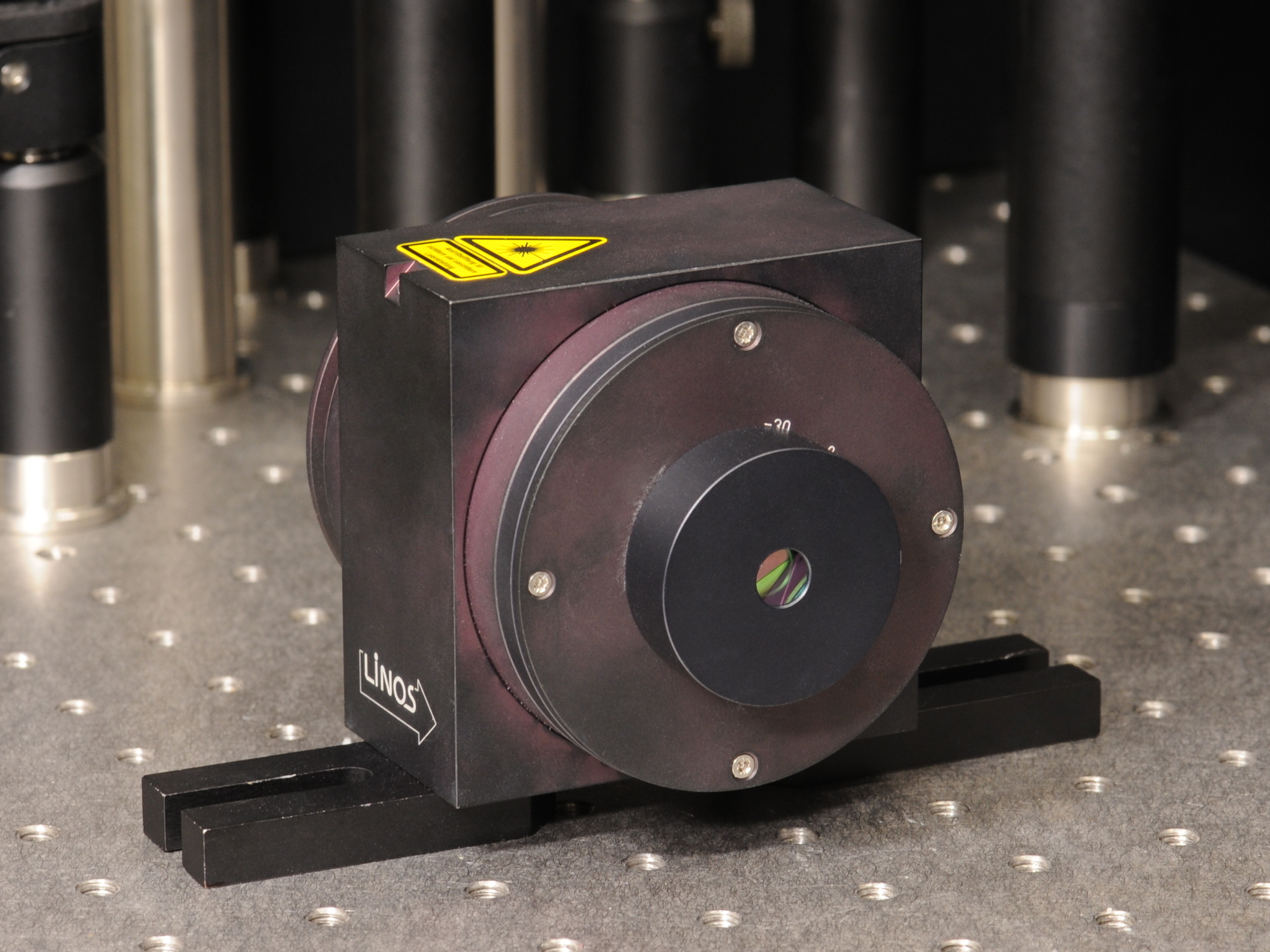
Faraday Rotator
A Faraday rotator is a polarization rotator based on the Faraday effect, a magneto-optic effect involving transmission of light through a material when a longitudinal static magnetic field is present. The state of polarization (such as the axis of linear polarization or the orientation of elliptical polarization) is rotated as the wave traverses the device, which is explained by a slight difference in the phase velocity between the left and right circular polarizations. Thus it is an example of ''circular birefringence'', as is optical activity, but involves a material only having this property in the presence of a magnetic field. Circular birefringence, involving a difference in propagation between opposite ''circular'' polarizations, is distinct from ''linear birefringence'' (or simply birefringence, when the term is not further specified) which also transforms a wave's polarization but not through a simple rotation. The polarization state is rotated in proportion to the appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radian
The radian, denoted by the symbol rad, is the unit of angle in the International System of Units (SI) and is the standard unit of angular measure used in many areas of mathematics. The unit was formerly an SI supplementary unit (before that category was abolished in 1995). The radian is defined in the SI as being a dimensionless unit, with 1 rad = 1. Its symbol is accordingly often omitted, especially in mathematical writing. Definition One radian is defined as the angle subtended from the center of a circle which intercepts an arc equal in length to the radius of the circle. More generally, the magnitude in radians of a subtended angle is equal to the ratio of the arc length to the radius of the circle; that is, \theta = \frac, where is the subtended angle in radians, is arc length, and is radius. A right angle is exactly \frac radians. The rotation angle (360°) corresponding to one complete revolution is the length of the circumference divided by the radius, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Devices
An optical instrument (or "optic" for short) is a device that processes light waves (or photons), either to enhance an image for viewing or to analyze and determine their characteristic properties. Common examples include periscopes, microscopes, telescopes, and cameras. Image enhancement The first optical instruments were telescopes used for magnification of distant images, and microscopes used for magnifying very tiny images. Since the days of Galileo and Van Leeuwenhoek, these instruments have been greatly improved and extended into other portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The binocular device is a generally compact instrument for both eyes designed for mobile use. A camera could be considered a type of optical instrument, with the pinhole camera and camera obscura being very simple examples of such devices. Analysis Another class of optical instrument is used to analyze the properties of light or optical materials. They include: *Interferometer for measuring the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atomic Line Filter
An atomic line filter (ALF) is a more effective optical band-pass filter used in the physical sciences for filtering electromagnetic radiation with precision, accuracy, and minimal signal strength loss. Atomic line filters work via the absorption or resonance lines of atomic vapors and so may also be designated an atomic resonance filter (ARF). The three major types of atomic line filters are absorption-re-emission ALFs, Faraday filters and Voigt filters. Absorption-re-emission filters were the first type developed, and so are commonly called simply "atomic line filters"; the other two types are usually referred to specifically as "Faraday filters" or "Voigt filters". Atomic line filters use different mechanisms and designs for different applications, but the same basic strategy is always employed: by taking advantage of the narrow lines of absorption or resonance in a metallic vapor, a specific frequency of light bypasses a series of filters that block all other light. Atomic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Isolator
An optical isolator, or optical diode, is an optical component which allows the transmission of light in only one direction. It is typically used to prevent unwanted feedback into an optical oscillator, such as a laser cavity. The operation of ome ofthe devices depends on the Faraday effect (which in turn is produced by magneto-optic effect), which is used in the main component, the Faraday rotator. Theory The main component of the optical isolator is the Faraday rotator. The magnetic field, B, applied to the Faraday rotator causes a rotation in the polarization of the light due to the Faraday effect. The angle of rotation, \beta, is given by, :\beta=\nu B d\,, where, \nu is the Verdet constant of the material (amorphous or crystalline solid, or liquid, or crystalline liquid, or vaprous, or gaseous) of which the rotator is made, and d is the length of the rotator. This is shown in Figure 2. Specifically for an optical isolator, the values are chosen to give a rotation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Isolator
An optical isolator, or optical diode, is an optical component which allows the transmission of light in only one direction. It is typically used to prevent unwanted feedback into an optical oscillator, such as a laser cavity. The operation of ome ofthe devices depends on the Faraday effect (which in turn is produced by magneto-optic effect), which is used in the main component, the Faraday rotator. Theory The main component of the optical isolator is the Faraday rotator. The magnetic field, B, applied to the Faraday rotator causes a rotation in the polarization of the light due to the Faraday effect. The angle of rotation, \beta, is given by, :\beta=\nu B d\,, where, \nu is the Verdet constant of the material (amorphous or crystalline solid, or liquid, or crystalline liquid, or vaprous, or gaseous) of which the rotator is made, and d is the length of the rotator. This is shown in Figure 2. Specifically for an optical isolator, the values are chosen to give a rotation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polarizer
A polarizer or polariser is an optical filter that lets light waves of a specific polarization pass through while blocking light waves of other polarizations. It can filter a beam of light of undefined or mixed polarization into a beam of well-defined polarization, that is polarized light. The common types of polarizers are linear polarizers and circular polarizers. Polarizers are used in many optical techniques and instruments, and polarizing filters find applications in photography and LCD technology. Polarizers can also be made for other types of electromagnetic waves besides visible light, such as radio waves, microwaves, and X-rays. Linear polarizers ''Linear polarizers'' can be divided into two general categories: absorptive polarizers, where the unwanted polarization states are absorbed by the device, and beam-splitting polarizers, where the unpolarized beam is split into two beams with opposite polarization states. Polarizers which maintain the same axes of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetics
In physics, electromagnetism is an interaction that occurs between particles with electric charge. It is the second-strongest of the four fundamental interactions, after the strong force, and it is the dominant force in the interactions of atoms and molecules. Electromagnetism can be thought of as a combination of electricity and magnetism, two distinct but closely intertwined phenomena. In essence, electric forces occur between any two charged particles, causing an attraction between particles with opposite charges and repulsion between particles with the same charge, while magnetism is an interaction that occurs exclusively between ''moving'' charged particles. These two effects combine to create electromagnetic fields in the vicinity of charge particles, which can exert influence on other particles via the Lorentz force. At high energy, the weak force and electromagnetic force are unified as a single electroweak force. The electromagnetic force is responsible for many o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reciprocity (electromagnetism)
In classical electromagnetism, reciprocity refers to a variety of related theorems involving the interchange of time-harmonic electric current densities (sources) and the resulting electromagnetic fields in Maxwell's equations for time-invariant linear media under certain constraints. Reciprocity is closely related to the concept of symmetric operators from linear algebra, applied to electromagnetism. Perhaps the most common and general such theorem is Lorentz reciprocity (and its various special cases such as Rayleigh-Carson reciprocity), named after work by Hendrik Lorentz in 1896 following analogous results regarding sound by Lord Rayleigh and light by Helmholtz (Potton, 2004). Loosely, it states that the relationship between an oscillating current and the resulting electric field is unchanged if one interchanges the points where the current is placed and where the field is measured. For the specific case of an electrical network, it is sometimes phrased as the statement tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verdet Constant
The Verdet constant is an optical property named after the French physicist Émile Verdet. It describes the strength of the Faraday effect for a particular material. For a constant magnetic field parallel to the path of the light, it can be calculated by: :\theta=V B L Where \theta is the angle between the starting and ending polarizations, V is the Verdet constant, B is the strength of the magnetic flux density, and L is the path length in the material. The Verdet constant of a material is wavelength dependent and for most materials is extremely small. It is strongest in substances containing paramagnetic ions such as terbium. The highest Verdet constants in bulk media are found in terbium doped dense flint glasses or in crystals of terbium gallium garnet (TGG). These materials have excellent transparency properties and high damage thresholds for laser radiation. Atomic vapours, however, can have Verdet constants which are orders of magnitude larger than TGG, but only ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tesla (unit)
The tesla (symbol: T) is the unit of magnetic flux density (also called magnetic B-field strength) in the International System of Units (SI). One tesla is equal to one weber per square metre. The unit was announced during the General Conference on Weights and Measures in 1960 and is named in honour of Serbian-American electrical and mechanical engineer Nikola Tesla, upon the proposal of the Slovenian electrical engineer France Avčin. Definition A particle, carrying a charge of one coulomb (C), and moving perpendicularly through a magnetic field of one tesla, at a speed of one metre per second (m/s), experiences a force with magnitude one newton (N), according to the Lorentz force law. That is, : \text = \dfrac. As an SI derived unit, the tesla can also be expressed in terms of other units. For example, a magnetic flux of 1 weber (Wb) through a surface of one square meter is equal to a magnetic flux density of 1 tesla.''The International System of Units (SI), 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |