|
Fall Line (topography)
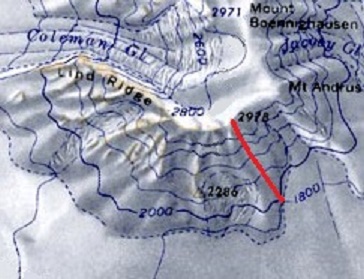
A fall line refers to the line down a mountain or hill which is most directly downhill; that is, the direction a ball or other body would accelerate if it were free to move on the slope under gravity. Mathematically the fall line, the line of greatest slope, is the negative of the gradient (which points uphill) and perpendicular to the contour lines. In mountain biking, a trail follows the "fall line" if it generally descends in the most downward direction, rather than traversing in a sideways direction. A skier is said to be "skiing the fall line" if they are moving generally down, making turns either side of the fall line, rather than moving across the slope. See also * Glossary of cycling * Ridge line * Topography * Topographic profile A topographic profile or topographic cut is a representation of the relief of the terrain that is obtained by cutting transversely the lines of a topographic map. Each contour line can be defined as a closed line joining relief points at eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fall Line
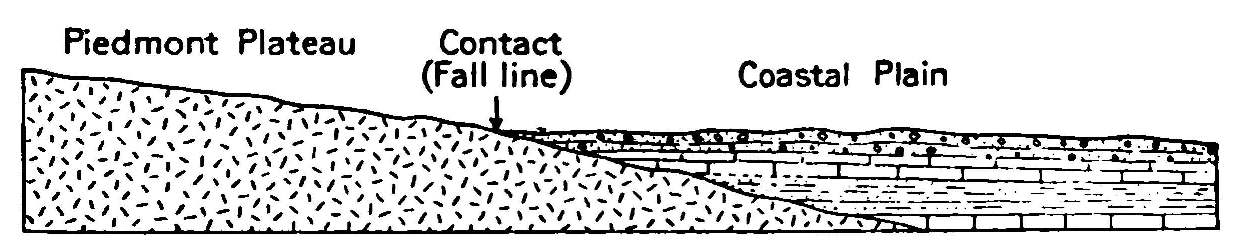
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is typically prominent where rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the coastal plain is softer sedimentary rock. A fall line often will recede upstream as the river cuts out the uphill dense material, forming "c"-shaped waterfalls and exposing bedrock shoals. Because of these features, riverboats typically cannot travel any farther inland without portaging, unless locks are built. The rapid change in elevation of the water and resulting energy release make the fall line a good location for water mills, grist mills, and sawmills. Seeking a head of navigation with a ready supply of water power, people have long made settlements where rivers cross a fall line. Geography The slope of fall zones on rivers played a role in settlement patterns. For example, the fall line represents the inland limit of navigation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Track (mountain Biking)
Singletrack (or single track) describes a type of mountain biking trail that is approximately the width of the bike. It contrasts with double-track or fire road which is wide enough for four-wheeled off-road vehicles. It is often smooth and flowing, but may also feature technical rocky sections, go over tree roots, and include berms, banked turns, switch-backs, hills, drops, jumps, and so forth. Singletrack which descends significantly, and in the most downward direction, is said to be following the fall line. Many mountain bike riders prefer singletrack over other types of trails, as singletrack is usually designed specifically for the sport, and therefore can have elements which highlight features of the sport (whereas other trail types will usually be more straight, and not exhibit as many hills and other special features).https://www.trailforks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Skiing
Alpine skiing, or downhill skiing, is the pastime of sliding down snow-covered slopes on skis with fixed-heel bindings, unlike other types of skiing ( cross-country, Telemark, or ski jumping), which use skis with free-heel bindings. Whether for recreation or for sport, it is typically practiced at ski resorts, which provide such services as ski lifts, artificial snow making, snow grooming, restaurants, and ski patrol. "Off-piste" skiers—those skiing outside ski area boundaries—may employ snowmobiles, helicopters or snowcats to deliver them to the top of a slope. Back-country skiers may use specialized equipment with a free-heel mode, including 'sticky' skins on the bottoms of the skis to stop them sliding backwards during an ascent, then locking the heel and removing the skins for their descent. Alpine skiing has been an event at the Winter Olympic Games since 1936. A competition corresponding to modern slalom was introduced in Oslo in 1886. Participants and venues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain, such as air or coil-sprung shocks used as suspension, larger and wider wheels and tires, stronger frame materials, and mechanically or hydraulically actuated disc brakes. Mountain biking can generally be broken down into five distinct categories: cross country, trail riding, all mountain (also referred to as "Enduro"), downhill, and freeride. This sport requires endurance, core strength and balance, bike handling skills, and self-reliance. Advanced riders pursue both steep technical descents and high incline climbs. In the case of freeride, downhill, and dirt jumping, aerial maneuvers are performed off both natural features and specially constructed jumps and ramps. Mountain bikers ride on off-road trails su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topographic Profile
A topographic profile or topographic cut is a representation of the relief of the terrain that is obtained by cross section (geometry), cutting transversely the lines of a topographic map. Each contour line can be defined as a closed line joining relief points at equal height above sea level. It is usually drawn on the same horizontal scale as the map, but the use of an exaggerated vertical scale is advisable to underline the elements of the relief. This can vary according to the slope and amplitude of the Terrain, terrestrial relief, but is usually three to five times the horizontal scale. A series of parallel profiles, taken at regular intervals on a map, can be combined to provide a more complete three-dimensional view of the area that appears on the topographic map. It is evident that, thanks to computer science, more sophisticated three-dimensional models of the landscape can be made from digital terrain data. The line of the plane defined by the points that limit the profile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically ''relief'', even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form (DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridge Line
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The lines along the crest formed by the highest points, with the terrain dropping down on either side, are called the ridgelines. Ridges are usually termed hills or mountains as well, depending on size. Smaller ridges, especially those leaving a larger ridge, are often referred to as spurs. Types There are several main types of ridges: ;Dendritic ridge: In typical dissected plateau terrain, the stream drainage valleys will leave intervening ridges. These are by far the most common ridges. These ridges usually represent slightly more erosion resistant rock, but not always – they often remain because there were more joints where the valleys formed or other chance occurrences. This type of ridge is generally somewhat random in orientation, often ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Cycling
This is a glossary of terms and jargon used in cycling, mountain biking, and cycle sport. For ''parts of a bicycle'', see List of bicycle parts. 0–9 ; 27.5 Mountain bike: A mountain bike with wheels that are approximately in diameter and are based on ISO 584 mm (650B) rims. ; 29er (bicycle):A mountain bike with wheels that are approximately in diameter and are based on ISO 622 mm (700C) rims. ;3:1 rule : A UCI rule stating the depth and breadth (in cross-section) of the bicycle frame tubes cannot exceed the ratio of 3:1. A ; À bloc: Going ''À bloc'' means riding as hard as one possibly can, which can be risky as it leaves one in a state where recovery is needed, and therefore vulnerable to being attacked. ; Aero bars: Extension of the handlebars usually allowing the rider to rest their elbows and benefit from improved aerodynamics. Often found on Time trial bicycles. ; Aero racing bicycle: A type of racing bike that combines the aerodynamic features of a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountain Biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and performance in rough terrain, such as air or coil-sprung shocks used as suspension, larger and wider wheels and tires, stronger frame materials, and mechanically or hydraulically actuated disc brakes. Mountain biking can generally be broken down into five distinct categories: cross country, trail riding, all mountain (also referred to as "Enduro"), downhill, and freeride. This sport requires endurance, core strength and balance, bike handling skills, and self-reliance. Advanced riders pursue both steep technical descents and high incline climbs. In the case of freeride, downhill, and dirt jumping, aerial maneuvers are performed off both natural features and specially constructed jumps and ramps. Mountain bikers ride on off-road trails su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contour Map With An Example Fall Line , a type of Brit ...
Contour may refer to: * Contour (linguistics), a phonetic sound * Pitch contour * Contour (camera system), a 3D digital camera system * Contour, the KDE Plasma 4 interface for tablet devices * Contour line, a curve along which the function has a constant value * Contour drawing, an artistic technique * A closed path in the mathematical method of contour integration * Boundary (topology) of a set Contours may refer to: * ''Contours'' (album), by Sam Rivers * The Contours, a soul music group Contouring may refer to: * The makeup technique contouring Other uses * Ford Contour, a motor car * CONTOUR, a failed NASA space probe * Contour, a North Wing Apache ultralight aircraft variant See also * Contour fort Hillforts in Britain refers to the various hillforts within the island of Great Britain. Although the earliest such constructs fitting this description come from the Neolithic British Isles, with a few also dating to later Bronze Age Britain, Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contour Line
A contour line (also isoline, isopleth, or isarithm) of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value, so that the curve joins points of equal value. It is a plane section of the three-dimensional graph of the function f(x,y) parallel to the (x,y)-plane. More generally, a contour line for a function of two variables is a curve connecting points where the function has the same particular value. In cartography, a contour line (often just called a "contour") joins points of equal elevation (height) above a given level, such as mean sea level. A contour map is a map illustrated with contour lines, for example a topographic map, which thus shows valleys and hills, and the steepness or gentleness of slopes. The contour interval of a contour map is the difference in elevation between successive contour lines. The gradient of the function is always perpendicular to the contour lines. When the lines are close together the magnitude of the grad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |