|
Fungal Effectors
Fungal effectors are proteins or non-proteinaceous molecules (such as RNAs or small molecules) secreted by pathogenic fungi into a host organism in order to modulate the host's immune response. Plant pathogenic fungi In the first stages of infection, conserved molecules from the fungal pathogen's cell wall, such as polysaccharides and chitin, are recognised by membrane-localised pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on the plant host's side. Such conserved molecules are generally described as pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or microbe-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs) and the initial innate immune response that their recognition triggers is known as PAMP-triggered immunity (PTI). In order to counteract PTI, fungal pathogens secrete effector proteins into the host, some of which may directly inhibit components of the innate immune response cascade. One example is the conserved effector NIS1, present in fungal pathogens from the Ascomycota and Basidiomycota phyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusarium Oxysporum F
''Fusarium'' is a large genus of filamentous fungi, part of a group often referred to as hyphomycetes, widely distributed in soil and associated with plants. Most species are harmless saprobes, and are relatively abundant members of the soil microbial community. Some species produce mycotoxins in cereal crops that can affect human and animal health if they enter the food chain. The main toxins produced by these ''Fusarium'' species are fumonisins and trichothecenes. Despite most species apparently being harmless (some existing on the skin as commensal members of the skin flora), some ''Fusarium'' species and subspecific groups are among the most important fungal pathogens of plants and animals. The name of ''Fusarium'' comes from Latin ''fusus'', meaning a spindle. Taxonomy The taxonomy of the genus is complex. A number of different schemes have been used, and up to 1,000 species have been identified at times, with approaches varying between wide and narrow concepts of spe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hevea Brasiliensis
''Hevea brasiliensis'', the Pará rubber tree, ''sharinga'' tree, seringueira, or most commonly, rubber tree or rubber plant, is a flowering plant belonging to the spurge family Euphorbiaceae originally native to the Amazon basin, but is now pantropical in distribution due to introductions. It is the most economically important member of the genus ''Hevea'' because the milky latex extracted from the tree is the primary source of natural rubber. Description ''H. brasiliensis'' is a tall deciduous tree growing to a height of up to in the wild, but cultivated trees are usually much smaller because drawing off the latex restricts the growth of the tree. The trunk is cylindrical and may have a swollen, bottle-shaped base. The bark is some shade of brown, and the inner bark oozes latex when damaged. The leaves have three leaflets and are spirally arranged. The inflorescence include separate male and female flowers. The flowers are pungent, creamy-yellow and have no petals. The frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
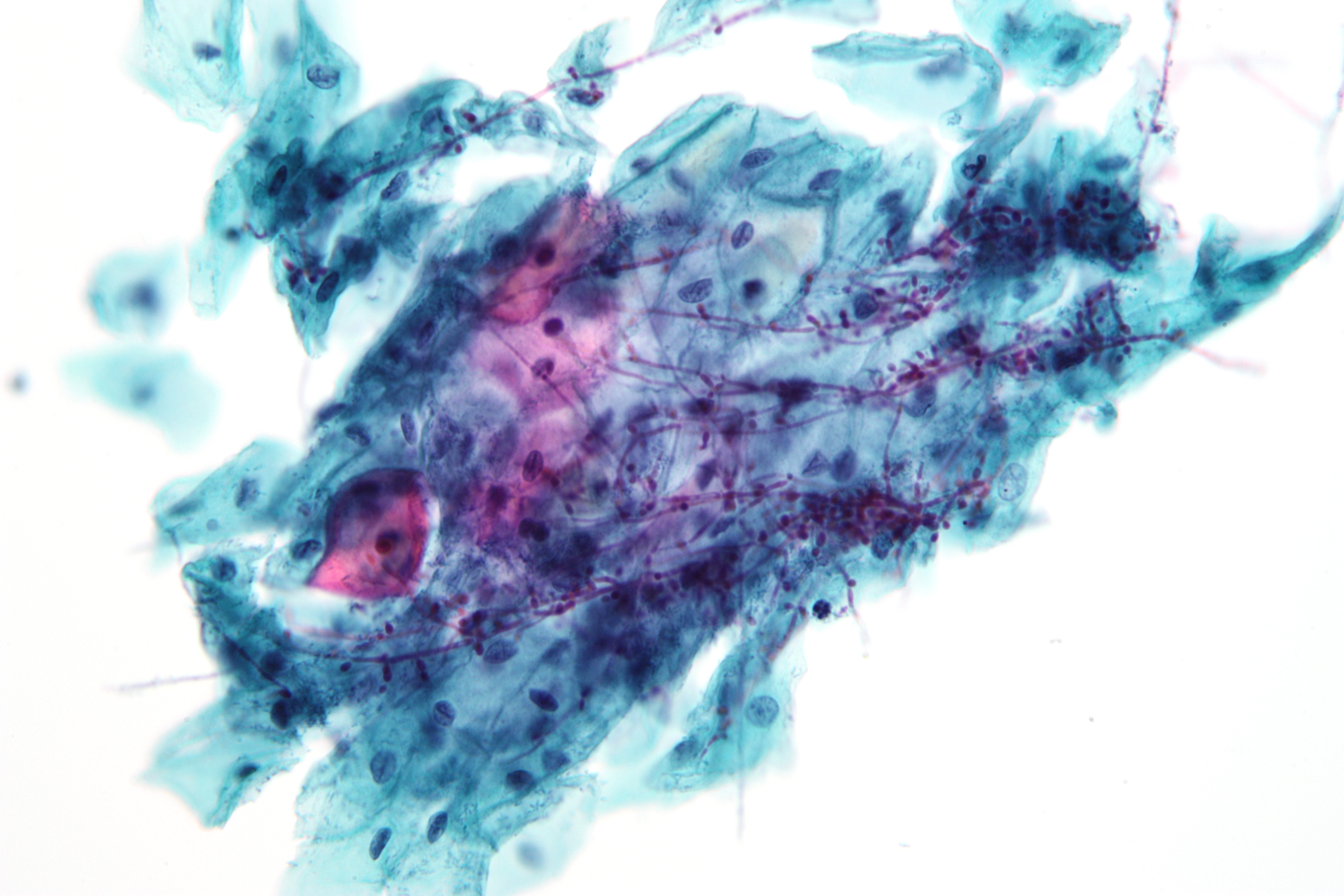
Corynespora Cassiicola
''Corynespora cassiicola'' is a species of fungus well known as a plant pathogen. It is a sac fungus in the family Corynesporascaceae. It is the type species of the genus ''Corynespora''.Dixon, L. J., et al. (2009)Host specialization and phylogenetic diversity of ''Corynespora cassiicola''.''Phytopathology'' 99(9) 1015–27. Hosts This fungus infects over 530 species of plants in 53 families. USDA National Institute of Food and Agriculture.In the tropics and subtropics, it is most common. It has also been isolated from s and from human skin. The fungus is known as a pathogen of many agricultural crop plants, especially [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochliobolus Sativus
The fungus ''Cochliobolus sativus'' is the teleomorph (sexual stage) of ''Bipolaris sorokiniana'' (anamorph) which is the causal agent of a wide variety of cereal diseases. The pathogen can infect and cause disease on roots (where it is known as common root rot), leaf and stem, and head tissue. ''C. sativus'' is extremely rare in nature and thus it is the asexual or anamorphic stage which causes infections. The two most common diseases caused by ''B. sorokiniana'' are spot blotch and common root rot, mainly on wheat and barley crops. Identification The mycelium of ''B. sorokiniana'' is usually deep olive-brown. New cultures produce abundant simple conidiophores, which may be single or clustered and measure 6–10 x 110–220 μm with septations. Conidia develop laterally from pores beneath each conidiophore septum. Conidia are olive-brown and ovate to oblong, with rounded ends and a prominent basal scar. They measure 15–28 x 40–120 μm and are 3- to 10-septate. Some may be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochliobolus Heterostrophus
''Cochliobolus heterostrophus'' is a fungal plant pathogen. It can cause southern corn leaf blight in maize Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. Th .... ''Cochliobolus heterostrophus'' is found in many tropical regions and in the southern part of the US. ''Cochliobolus'', although not currently the most economically serious disease, can be a very serious crop disease. ''C. heterostrophus'' (race O) was considered a mild pathogen of corn, and was of little worry to those growing maize crops. It was not until the 1970s that ''C. heterostrophus'' (race T) destroyed more than 15% of the U.S. corn crop. Race T differed from race O in the sense that it produced T-toxin (host-selective toxin). The corn planted in the 1970s carried T-cms; T-cms was particularly susceptible to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenophora Tritici-repentis
''Pyrenophora tritici-repentis'' ( teleomorph) and ''Drechslera tritici-repentis'' (anamorph) is a necrotrophic plant pathogen of fungal origin, phylum Ascomycota. The pathogen causes a disease originally named yellow spot but now commonly called tan spot, yellow leaf spot, yellow leaf blotch or helminthosporiosis. CABI ISCbr>20001003003 At least eight races of the pathogen are known to occur based on their virulence on a wheat differential set. The tan (yellow) spot fungus was first described by Nisikado in 1923 in Japan. and was later identified in Europe, Australia and the USA, in the mid 1900s. The disease is one of the most important fungal disease on wheat and the fungal pathogen is found to infect in all parts of the world wherever wheat and other susceptible host crops are found. ''P. tritici-repentis'' overwinters on stubble, and due to recent heavily no-till/residue retention cultural practices, increased incidence and yield loss of up to 49% has been witnessed if idea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
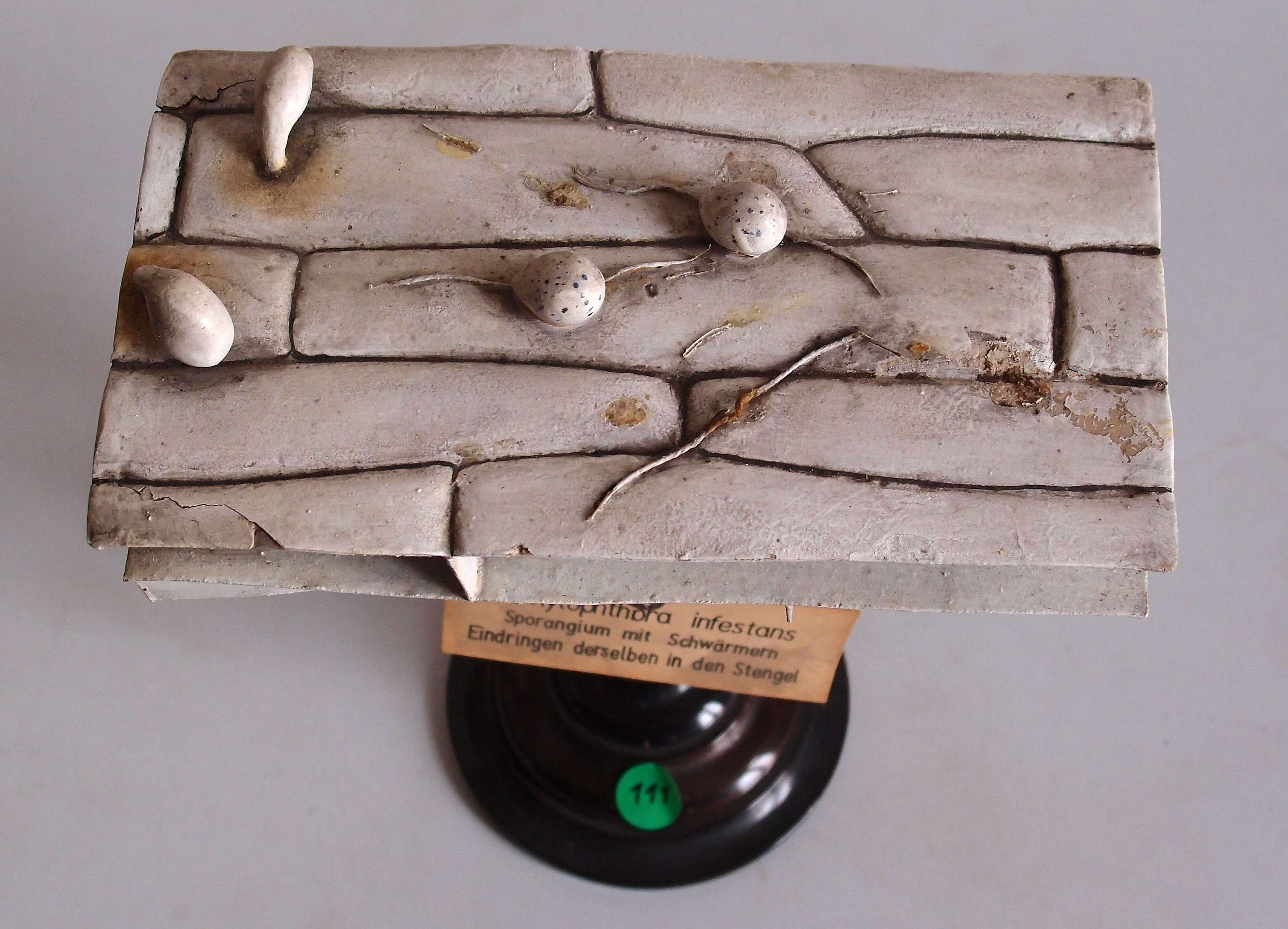
Phytophthora Infestans
''Phytophthora infestans'' is an oomycete or water mold, a fungus-like microorganism that causes the serious potato and tomato disease known as late blight or potato blight. Early blight, caused by '' Alternaria solani'', is also often called "potato blight". Late blight was a major culprit in the 1840s European, the 1845–1852 Irish, and the 1846 Highland potato famines. The organism can also infect some other members of the Solanaceae. The pathogen is favored by moist, cool environments: sporulation is optimal at in water-saturated or nearly saturated environments, and zoospore production is favored at temperatures below . Lesion growth rates are typically optimal at a slightly warmer temperature range of . Etymology The genus name ''Phytophthora'' comes from the Greek –(), meaning : "plant" – plus the Greek (), meaning : "decay, ruin, perish". The species name ''infestans'' is the present participle of the Latin verb , meaning : "attacking, destroying", from whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leptosphaeria Maculans
''Leptosphaeria maculans'' (anamorph ''Phoma lingam'') is a fungal pathogen of the phylum Ascomycota that is the causal agent of blackleg disease on '' Brassica'' crops. Its genome has been sequenced, and ''L. maculans'' is a well-studied model phytopathogenic fungus. Symptoms of blackleg generally include basal stem cankers, small grey lesions on leaves, and root rot. The major yield loss is due to stem canker. The fungus is dispersed by the wind as ascospores or rain splash in the case of the conidia. ''L. maculans'' grows best in wet conditions and a temperature range of 5–20 degrees Celsius. Rotation of crops, removal of stubble, application of fungicide, and crop resistance are all used to manage blackleg. The fungus is an important pathogen of ''Brassica napus'' ( canola) crops. Host and symptoms ''Leptosphaeria maculans'' causes phoma stem canker or blackleg. Symptoms generally include basal stem cankers, small grey oval lesions on the leaf tissue and root rot (as the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
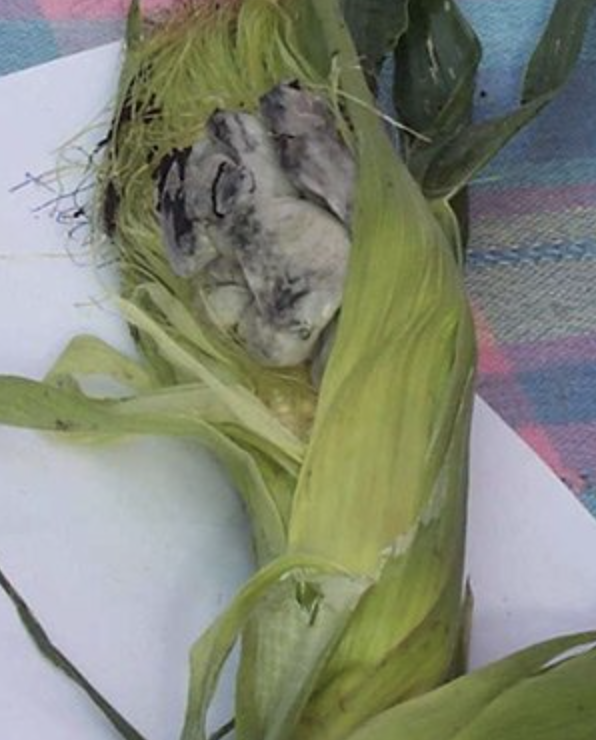
Ustilago Maydis
Corn smut is a plant disease caused by the pathogenic fungus ''Ustilago maydis'' that causes smut on maize and teosinte. The fungus forms galls on all above-ground parts of corn species. It is edible, and is known in Mexico as the delicacy ''huitlacoche''; which is eaten, usually as a filling, in quesadillas and other tortilla-based foods, and in soups. Etymology In Mexico, corn smut is known as ''huitlacoche'' (, sometimes spelled ''cuitlacoche''). This word entered Spanish in Mexico from Classical Nahuatl, though the Nahuatl words from which huitlacoche is derived are debated. In modern Nahuatl, the word for ''huitlacoche'' is ''cuitlacochin'' (), and some sources deem ''cuitlacochi'' to be the classical form.Guido Gómez de Silva, "Diccionario breve de mexicanismos", Fondo de Cultura Económica, Mexico 2001. Entries for "huitlacoche" and "cuicacoche o cuiltacoche". Some sources wrongly give the etymology as coming from the Nahuatl words ''cuitlatl'' ("excrement" or "rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenic Fungus
Pathogenic fungi are fungi that cause disease in humans or other organisms. Approximately 300 fungi are known to be pathogenic to humans. Markedly more fungi are known to be pathogenic to plant life than those of the animal kingdom. The study of fungi pathogenic to humans is called "medical mycology". Although fungi are eukaryotic, many pathogenic fungi are microorganisms. The study of fungi and other organisms pathogenic to plants is called plant pathology. ''Candida'' ''Candida'' species cause infections in individuals with deficient immune systems. Th1-type cell-mediated immunity (CMI) is required for clearance of a fungal infection. ''Candida albicans'' is a kind of diploid yeast that commonly occurs among the human gut microflora. ''C. albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogen in humans. Abnormal over-growth of this fungus can occur, particularly in immunocompromised individuals. ''C. albicans'' has a parasexual cycle that appears to be stimulated by environmental stress ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |