|
Fumal
Fumal () is a village and district of the municipality of Braives, located in the province of Liège in Wallonia, Belgium. The village developed around the castle, which was the centre of a fief since the 12th century. During much of its history, the village was divided with some parts belonging to the County of Namur and some to the Prince-Bishopric of Liège The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was a Roman Catholic ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. It was an Imperial Estate, so the bishop of Liège, as .... The castle of Fumal has been rebuilt and altered continuously since the 16th century. Its oldest part is the square tower. Other historical buildings in the village includes the church, dedicated to Saint Martin and the former castle farm, dating from the 16th century. References External links * {{Liege-geo-stub Populated places in Liège Province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braives
Braives (; ) is a municipality of Wallonia located in the province of Liège, Belgium. On January 1, 2006, Braives had a total population of 5,579. The total area is 44.00 km² which gives a population density of 127 inhabitants per km². , German-language, retrieved 2007-09-04 The municipality consists of the following districts: Avennes, Braives, Ciplet, Fallais, Fumal, Latinne, Tourinne, and < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communities, Regions And Language Areas Of Belgium
Belgium is a federation, federal state comprising three communities and three regions that are based on four language areas. For each of these subdivision types, the subdivisions together make up the entire country; in other words, the types overlap. The language areas were established by the History of Belgium#The rise of the federal state, Second Gilson Act, which entered into force on 2 August 1963. The division into language areas was included in the Constitution of Belgium, Belgian Constitution in 1970. Through state reform in Belgium, constitutional reforms in the 1970s and 1980s, regionalism (politics), regionalisation of the unitary state led to a three-tiered federation: federalism, federal, regional, and community governments were created, a compromise designed to minimize linguistic, cultural, social, and economic tensions. Schematic overview This is a schematic overview of the basic federal structure of Belgium as defined by Title I of the Belgian Constitution. Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
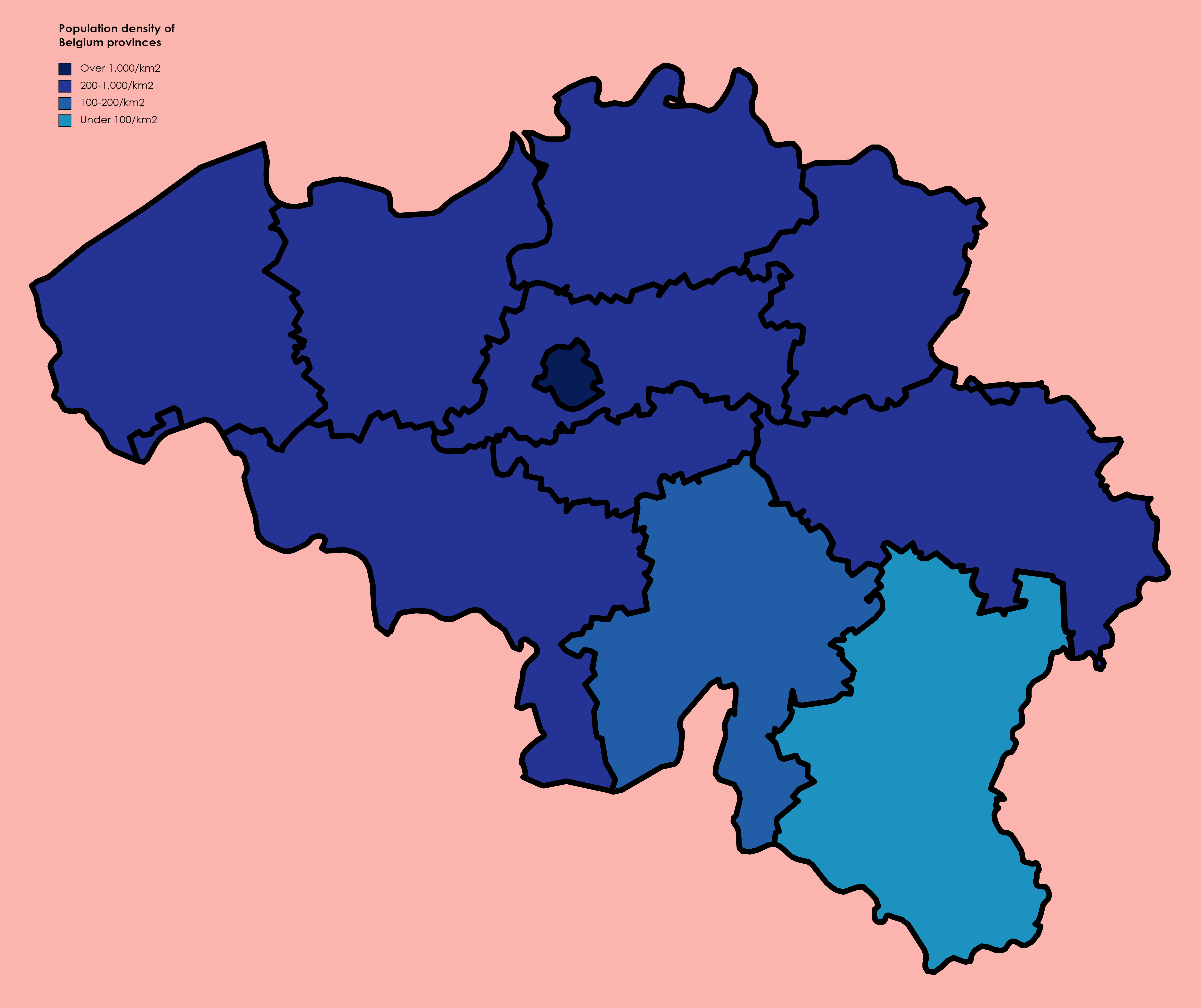
Provinces Of Belgium
The Kingdom of Belgium is divided into three Communities, regions, and language areas of Belgium, regions. Two of these regions, Flanders and Wallonia, are each subdivided into five provinces. The third region, Brussels, does not belong to any province, nor is it subdivided into provinces. Instead, it has amalgamated both regional and provincial functions into a single "Capital Region" administration. Most of the provinces take their name from earlier duchy, duchies and county, counties of similar location, while their territory is mostly based on the 130 departments of the First French Empire, departments installed during French annexation. At the time of the Independence of Belgium, creation of Belgium in 1830, only nine provinces existed, including the province of Brabant, which held the City of Brussels. In 1995, Brabant was split into three areas: Flemish Brabant, which became a part of the region of Flanders; Walloon Brabant, which became part of the region of Wallonia; an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liège Province
Liège ( ; ; ; ; ) is the easternmost province of the Wallonia region of Belgium. Liège Province is the only Belgian province that has borders with three countries. It borders (clockwise from the north) the Dutch province of Limburg, the German states of North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate, the Luxembourgish canton of Clervaux, the Belgian Walloon (French-speaking) provinces of Luxembourg, Namur and Walloon Brabant and the Belgian Flemish (Dutch-speaking) provinces of Flemish Brabant and Limburg. Part of the eastern-most area of the province, bordering Germany, is the German-speaking region of Eupen-Malmedy, which became part of Belgium in the aftermath of World War I. The capital and the largest city of the province is the city of the same name, Liège. The province has an area of , and a population of 1.12 million as of January 2024. History The modern borders of the province of Liège date from 1795, which saw the unification of the Principali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Belgium
Communities, regions, and language areas of Belgium, Belgium comprises 565 municipalities (; ; ), 285 of them grouped into five provinces of Belgium, provinces in Flanders and 261 others in five provinces in Wallonia, while the remaining 19 are in the Brussels, Brussels Capital Region, which is not divided in provinces. In most cases, the municipalities are the smallest administrative subdivisions of Belgium, but in municipalities with more than 100,000 inhabitants, on the initiative of the local council, sub-municipal administrative entities with elected councils may be created. As such, only Antwerp, having over 500,000 inhabitants, became subdivided into Districts of Antwerp, nine districts (). The Belgian Arrondissements of Belgium, arrondissements (; ; ), an administrative level between province (or the capital region) and municipality, or the lowest judicial level, are in English language, English sometimes called districts as well. Lists of municipalities Here are three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Telephone Numbers In Belgium
A telephone number in Belgium is a sequence of nine or ten digits dialed on a telephone to make a call on the Belgian telephone network. Belgium is under a full number dialing plan, meaning that the full national number must be dialed for all calls, while it retains the trunk code, '0', for all national dialling. Exception: Some "special services" use 3 or 4 digits with no area or trunk codes, e.g.: ''112'' and ''100'' (fire brigade and ambulance); ''101'' (police); ''1307'' (info in French) or ''1207'' (info in Dutch), etc. " 112" is an emergency number for contacting the fire brigade, ambulance and police in all 27 countries of the European Union. Operators will help the caller in the country's native language, in English, or the language of any neighbouring country. Calls to this number for contacting the police are forwarded to "101", losing response time. The telephone numbering plan allows for numbers have varying lengths (9 digits for landline numbers, and 10 digits for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallonia
Wallonia ( ; ; or ), officially the Walloon Region ( ; ), is one of the three communities, regions and language areas of Belgium, regions of Belgium—along with Flemish Region, Flanders and Brussels. Covering the southern portion of the country, Wallonia is primarily Geographical distribution of French speakers, French-speaking. It accounts for 55% of Belgium's territory, but only a third of its population. The Walloon Region and the French Community of Belgium, which is the political entity responsible for matters related mainly to culture and education, are independent concepts, because the French Community of Belgium encompasses both Wallonia and the bilingual Brussels-Capital Region but not the German-speaking Community of Belgium, which administers nine municipalities in Eastern Wallonia. During the Industrial Revolution, Wallonia was second only to the United Kingdom in industrialization, capitalizing on its extensive deposits of coal and iron. This brought the regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fief
A fief (; ) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form of feudal allegiance, services or payments. The fees were often lands, land revenue or revenue-producing real property like a watermill, held in feudal land tenure: these are typically known as fiefs or fiefdoms. However, not only land but anything of value could be held in fee, including governmental office, rights of exploitation such as hunting, fishing or felling trees, monopolies in trade, money rents and tax farms. There never existed a standard feudal system, nor did there exist only one type of fief. Over the ages, depending on the region, there was a broad variety of customs using the same basic legal principles in many variations. Terminology In ancient Rome, a " benefice" (from the Latin noun , meaning "benefit") was a gift of land () f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Of Namur
The County of Namur () was a county of the Holy Roman Empire with its military and administrative capital at the town of Namur (city), Namur, at the merging of the Sambre and Meuse rivers in what is now Wallonia, French-speaking Belgium. Under this name it existed from about 990 until about 1790. Like most of what is now Belgium, during the 15th century the County of Namur became part of the Burgundian Netherlands, which subsequently became a possession of the Kings of Spain, and later of Austria. Like its neighbours, the county ceased to exist during the French Revolution, when the entire region was conquered by the revolutionary French Republic. The modern Belgian provinces, Belgian province of Namur (province), Namur is larger than the old county. The boundaries of the province are based upon those of the French Departments of France, départment of Sambre-et-Meuse, and stretch further eastwards and southwards. Prehistory to the Roman period The city of Namur most likely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince-Bishopric Of Liège
The Prince-Bishopric of Liège or Principality of Liège was a Roman Catholic ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire that was situated for the most part in present-day Belgium. It was an Imperial Estate, so the bishop of Liège, as its prince, had a seat and a vote in the Imperial Diet. The Prince-Bishopric of Liège should not be confused with the Diocese of Liège, which was larger and over which the prince-bishop exercised only the usual responsibilities of a bishop. The bishops of Liège acquired their status as prince-bishops between 980 and 985 when Bishop Notker of Liège, who had been the bishop since 972, received secular control of the County of Huy from Emperor Otto II. From 1500, the prince-bishopric belonged to the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle. Its territory included most of the present Belgian provinces of Liège and Limburg, and some exclaves in other parts of Belgium and the Netherlands. The ecclesiastical state briefly became a republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Of Tours
Martin of Tours (; 316/3368 November 397) was the third bishop of Tours. He is the patron saint of many communities and organizations across Europe, including France's Third French Republic, Third Republic. A native of Pannonia (present-day Hungary), he converted to Christianity at a young age. He served in the Roman cavalry in Roman Gaul, Gaul, but left military service prior to 361, when he became a disciple of Hilary of Poitiers, establishing the Ligugé Abbey, monastery at Ligugé. He was consecrated as Bishop of Caesarodunum (Tours) in 371. As bishop, he was active in the suppression of the remnants of Gallo-Roman religion. The contemporary hagiographer Sulpicius Severus wrote a ''Life of St. Martin''. He is best known for the account of his using his sword to cut his cloak in two, to give half to a beggar clad only in rags in winter. His Basilica of Saint Martin, Tours, shrine in Tours became an often-frequented stop for Camino de Santiago, pilgrims on the road to Santiago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |