|
French Battleship Liberté
''Liberté'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the French Navy in the mid-1900s. She was the lead ship of the , which included three other vessels and was a derivative of the preceding , with the primary difference being the inclusion of a heavier secondary armament, secondary battery. ''Liberté'' carried a main battery of four guns, like the ''République'', but mounted ten guns for her secondary armament in place of the guns of the earlier vessels. Like many late pre-dreadnought designs, ''Liberté'' was completed after the revolutionary British battleship had entered service, rendering her obsolescent. On entering service, ''Liberté'' was assigned to the 2nd Division of the Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean (France), Mediterranean Squadron, based in Toulon. She immediately began the normal peacetime training routine of squadron and fleet maneuvers and cruises to various ports in the Mediterranean. She also participated in several naval reviews for a number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York Harbor
New York Harbor is a bay that covers all of the Upper Bay. It is at the mouth of the Hudson River near the East River tidal estuary on the East Coast of the United States. New York Harbor is generally synonymous with Upper New York Bay, which is enclosed by the New York City boroughs of Manhattan, Brooklyn, and Staten Island and the Hudson County, New Jersey, municipalities of Jersey City and Bayonne, although in colloquial usage it can sometimes expand to cover Upper and Lower New York Bay New York Harbor is one of the largest natural harbors in the world. Overview The harbor is fed by the waters of the Hudson River (historically called the North River as it passes Manhattan), as well as the Gowanus Canal. It is connected to Lower New York Bay by the Narrows, to Newark Bay by the Kill Van Kull, and to Long Island Sound by the East River, which, despite its name, is actually a tidal strait. It provides the main passage for the waters of the Hudson River as it em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
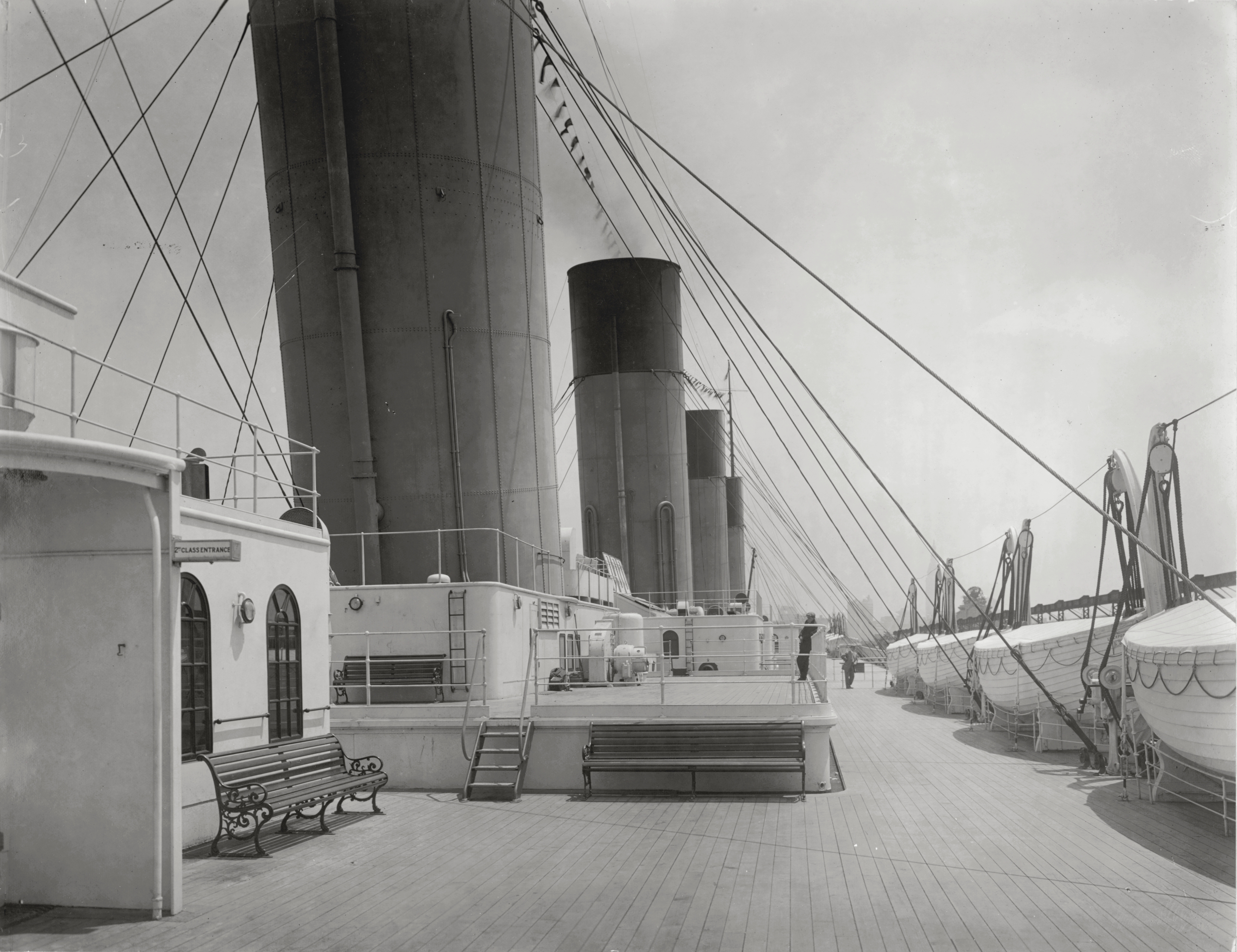
Deck (ship)
A deck is a permanent covering over a Compartment (ship), compartment or a hull (watercraft), hull of a ship. On a boat or ship, the primary or upper deck is the horizontal structure that forms the "roof" of the hull, strengthening it and serving as the primary working surface. Vessels often have more than one level both within the hull and in the superstructure above the primary deck, similar to the floors of a multi-storey building, that are also referred to as decks, as are certain compartments and decks built over specific areas of the superstructure. Decks for some purposes have specific names. Structure The main purpose of the upper or primary deck is structural, and only secondarily to provide weather-tightness and support people and equipment. The deck serves as the lid to the complex box girder which can be identified as the hull. It resists Tension (physics), tension, Compression (physics), compression, and racking forces. The deck's scantling is usually the same as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
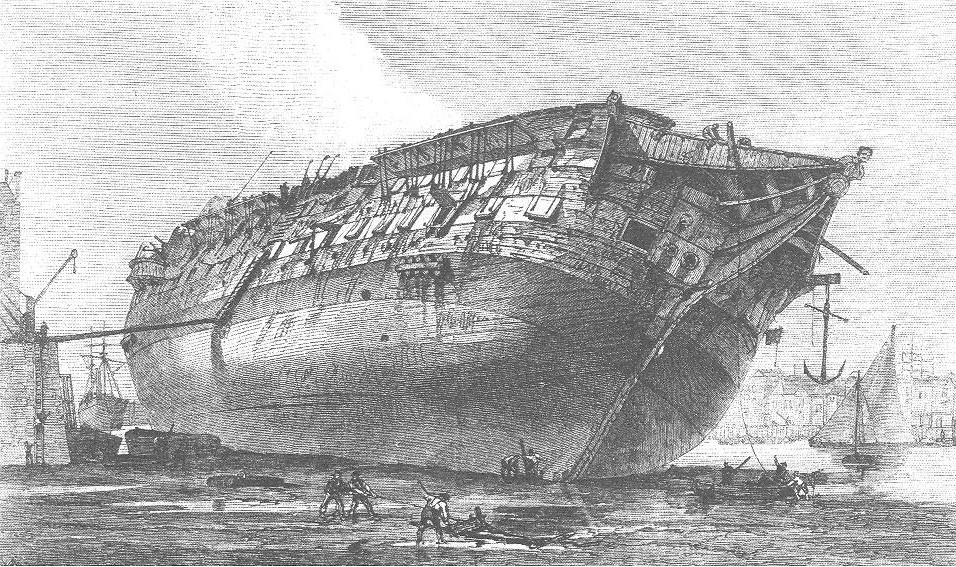
Ship Breaking
Ship breaking (also known as ship recycling, ship demolition, ship scrapping, ship dismantling, or ship cracking) is a type of ship disposal involving the breaking up of ships either as a source of Interchangeable parts, parts, which can be sold for re-use, or for the extraction of raw materials, chiefly scrap. Modern ships have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years before corrosion, Fatigue (material), metal fatigue and a lack of parts render them uneconomical to operate. Ship-breaking allows the materials from the ship, especially steel, to be recycled and made into new products. This lowers the demand for mined iron ore and reduces energy use in the steelmaking process. Fixtures and other equipment on board the vessels can also be reused. While ship-breaking is sustainable, there are concerns about its use by poorer countries without stringent environmental legislation. It is also labour-intensive, and considered one of the world's most dangerous industries. In 2012, roughly 1,250 oce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poudre B
Poudre B was the first practical smokeless gunpowder created in 1884. It was perfected between 1882 and 1884 at "Laboratoire Central des Poudres et Salpêtres" in Paris, France. Originally called "Poudre V" from the name of the inventor, Paul Vieille, it was arbitrarily renamed "Poudre B" (short for ''poudre blanche''—white powder, as distinguished from black powder) to distract German espionage.Davis, Tenney L. ''The Chemistry of Powder & Explosives'' (1943) pages 289–292 "Poudre B" is made from 68.2% insoluble nitrocellulose, 29.8% soluble nitrocellulose gelatinized with ether and 2% paraffin. "Poudre B" is made up of very small paper-thin flakes that are not white but dark greenish grey in colour. "Poudre B" was first used to load the 8mm Lebel cartridges issued in 1886 for the Lebel rifle. History German-Swiss chemist Christian Friedrich Schönbein created the explosive substance nitrocellulose, or "guncotton", in 1846 by treating cotton fibers with a nitric acid and su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magazine (artillery)
A magazine is an item or place within which ammunition or other explosive material is stored. The word is taken originally from the Arabic word ''makhāzin'' (مخازن), meaning "storehouses", via Italian and Middle French. The term is also used for an ammunition dump, a place where large quantities of ammunition are stored for later distribution. This usage is less common. Field magazines In the early history of tube artillery drawn by horses (and later by mechanized vehicles), ammunition was carried in separate unarmored wagons or vehicles. These soft-skinned vehicles were extremely vulnerable to enemy fire and to explosions caused by a weapons malfunction. Therefore, as part of setting up an artillery battery, a designated place would be used to shelter the ready ammunition. In the case of batteries of towed artillery the temporary magazine would be placed, if possible, in a pit, or natural declivity, or surrounded by sandbags or earthworks. Circumstances might requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson–Fulton Celebration
The Hudson–Fulton Celebration from September 25 to October 9, 1909 in New York and New Jersey was an elaborate commemoration of the 300th anniversary of Henry Hudson’s discovery of the Hudson River and the 100th anniversary of Robert Fulton's first successful commercial application of the paddle steamer." 1909 Hudson–Fulton Celebration of the Discovery of the Hudson River and the First Successful Application of Steam to Navigation" Hudson River Maritime Museum. The image above of the Celebration program shows the event closing on Saturday, October 9, 1909. A report to the New York state legislature in 1910 by the official celebration Commission, as shown on the website of this reference, lists the celebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Review
A Naval Review is an event where select vessels and assets of the United States Navy are paraded to be reviewed by the President of the United States or the Secretary of the Navy. Due to the geographic distance separating the modern U.S. Navy and the deployment rotations of a various ships within a fleet, it would be exceedingly difficult to imagine a situation where even an entire numbered fleet could be presented at one event, to say nothing of the physical cost and logistical requirements to support over 460 ships exceeding 3.4 million tons displacement. A naval review can also include warships and delegates from other national navies. The largest modern maritime exercise regularly being conducted by the US Navy is the Rim of the Pacific Exercise (RIMPAC), held biennially during the summer on even-numbered years off the coast of Hawaii. It typically sees the participation of around 50 ships and 200 aircraft, from 2 dozen nations with some 25,000 personnel, culminating in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toulon
Toulon (, , ; , , ) is a city in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region of southeastern France. Located on the French Riviera and the historical Provence, it is the prefecture of the Var (department), Var department. The Commune of Toulon has a population of 176,198 people (2018), making it France's 13th-largest city. It is the centre of an urban unit with 580,281 inhabitants (2018), the ninth largest in France by population. Toulon is the second largest French city by urban area on the Mediterranean coast after Marseille. Toulon is an important centre for naval construction, fishing, wine making, and the manufacture of aeronautical equipment, armaments, maps, paper, tobacco, printing, shoes, and electronic equipment. The military port of Toulon is the major navy, naval centre on France's Mediterranean coast, home of the French aircraft carrier ''French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle, Charles de Gaulle'' and her battle group. The French Mediterranean Fleet is based in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean (France)
The French Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean, also known as CECMED (French for ''Commandant en chef pour la Méditerranée'') is a French Armed Forces regional commander. He commands the zone, the region and the Mediterranean maritime ''arrondissements''. He is usually an admiral of the French Navy, and is under the direct authority of the French Chief of the Defence Staff. the position was held by Admiral Yann Tainguy. CECMED today is simultaneously: * Commander of the région and the Mediterranean maritime ''arrondissement'', * Maritime Zone commander, * Maritime Prefect for the Méditerranean. Today the main French naval combat force in the Mediterranean is the Force d'action navale (FAN) headquartered at Toulon. The Admiral commanding the Naval Action Force (ALFAN) is responsible to the Chief of Staff of the French Navy at the rue Royale in Paris. History Mediterranean Squadron Vice-amiral François Fournier was Commander-in-Chief, Mediterranean Squadron (''Commandant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Main Battery
A main battery is the primary weapon or group of weapons around which a warship is designed. As such, a main battery was historically a naval gun or group of guns used in volleys, as in the broadsides of cannon on a ship of the line. Later, this came to be turreted groups of similar large-caliber naval rifles. With the evolution of technology the term has come to encompass guided missiles and torpedoes as a warship's principal offensive weaponry, deployed both on surface ships and submarines. A main battery features common parts, munition and fire control system across the weapons which it comprises. Description In the age of cannon at sea, the main battery was the principal group of weapons around which a ship was designed, usually its heavies. With the coming of naval rifles and subsequent revolving gun turrets, the main battery became the principal group of heaviest guns, regardless of how many turrets they were placed in. As missiles displaced guns both above and belo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secondary Armament
Secondary armaments are smaller, faster-firing weapons that are typically effective at a shorter range than the main battery, main (heavy) weapons on military systems, including battleship- and cruiser-type warships, tanks/armored personnel carriers, and rarely other systems. The nature, disposition, size and purpose of Naval secondary weapon systems changed dramatically as the threat changed from torpedo boats, to torpedo-carrying destroyers, to aircraft, to anti-ship missiles. Naval Pre-dreadnought era Pre-dreadnoughts, from the period 1890 to 1905, were typically fitted with 3 or 4 different calibres of weapon. The main guns were usually approximately 12-inch caliber, secondary weapons usually 6-inch but typically in the range 5-inch to 7.5-inch. Guns smaller than 4.7-inch are usually considered "tertiary". (Many pre-dreadnoughts also carried 9.2 to 10-inch "secondary" guns, but they are usually treated instead as a mixed-caliber main armament.) Secondary guns were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead Ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships that are all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels. Large ships are very complex and may take five to ten years to build. Improvements based on experience with building and operating the lead ship are likely to be incorporated into the design or construction of later ships in the class, so it is rare to have vessels that are identical. The second and later ships are often started before the first one is completed, launched and tested. Nevertheless, building copies is still more efficient and cost effective than building prototypes, and the lead ship will usually be followed by copies with some improvements rather than radically different versions. The improvements will sometimes be retrofitted to the lead ship. Occasionally, the lead ship will be launched and commissioned for shakedown testing before following ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |