|
French West Indies
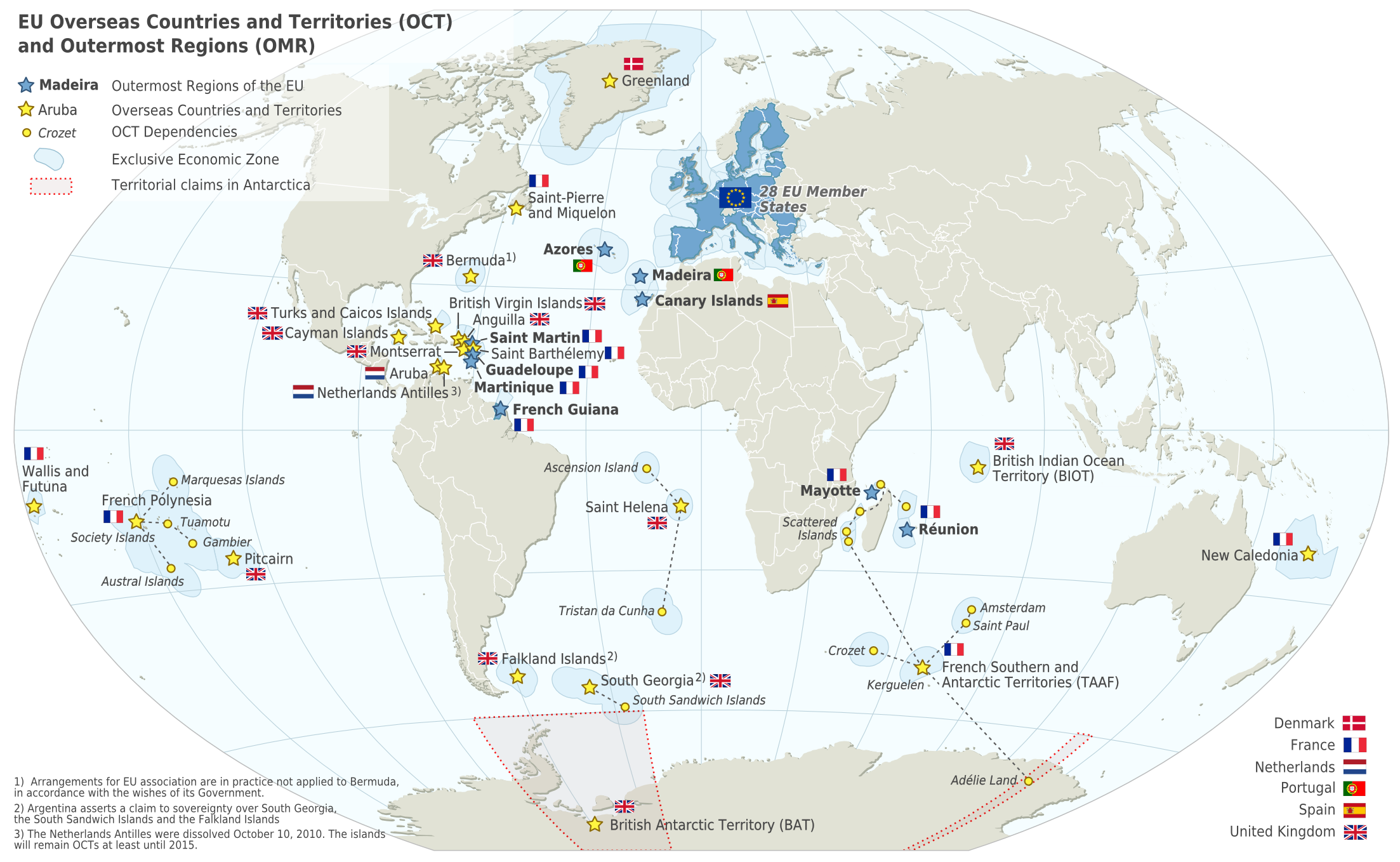
The French West Indies or French Antilles (, ; ) are the parts of France located in the Antilles islands of the Caribbean: * The two overseas departments of: ** Guadeloupe, including the islands of Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Les Saintes, Marie-Galante, and La Désirade. ** Martinique * The two overseas collectivities of: ** Saint Martin, the northern half of the island with the same name, the southern half is Sint Maarten, a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands. ** Saint Barthélemy History Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc was a French trader and adventurer in the Caribbean, who established the first permanent French colony, Saint-Pierre, on the island of Martinique in 1635. Belain sailed to the Caribbean in 1625, hoping to establish a French settlement on the island of St. Christopher (St. Kitts). In 1626 he returned to France, where he won the support of Cardinal Richelieu to establish French colonies in the region. Richelieu became a shareholder in the C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of French Possessions And Colonies
From the 16th to the 17th centuries, the First French colonial empire existed mainly in the Americas and Asia. During the 19th and 20th centuries, the second French colonial empire existed mainly in Africa and Asia. France had about 80 colonies throughout its History of France, history, the second most colonies in the world behind only the United Kingdom, British Empire. Around 40 countries gained independence from French colonial empire, France throughout its history, the second most in the world behind only the British Empire. Over 50% of the world’s borders today, were drawn as a result of British and French imperialism.Lovejoy, Paul E. (2012). Transformations of Slavery: A History of Slavery in Africa. London: Cambridge University Press. France began to establish colonies in North America, the Caribbean and India, following Spanish and Portuguese successes during the Age of Discovery, in rivalry with Britain. A series of wars with Britain during the 18th century and earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort-Royal
Fort-de-France (, , ; ) is a Communes of France, commune and the capital city of Martinique, an overseas department and region of France located in the Caribbean. History Before it was ceded to France by Spain in 1635, the area of Fort-de-France was known as Iguanacaera, which translates to "Iguana Island" in the indigenous Carib language, Kariʼnja language. In 1638, Jacques Dyel du Parquet (1606–1658), nephew of Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc and first governor of Martinique, decided to have Fort Saint Louis built to protect the city against enemy attacks. The fort was soon destroyed, and rebuilt in 1669, when Louis XIV of France, Louis XIV appointed the Marquis of Baas as governor general. Under his orders and those of his successors, particularly the Charles de Courbon de Blénac, Count of Blénac, the fort was built with a Vauban design. In the 1680s, the area was settled and became the French colonial capital in the French West Indies, Caribbean and the French colonization of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Saintes
LES or Les may refer to: People * Les (given name) * Les (surname) * L.E.S. (producer), hip hop producer Space flight * Launch Entry Suit, worn by Space Shuttle crews * Launch escape system, for spacecraft emergencies * Lincoln Experimental Satellite series, 1960s and 1970s Biology and medicine * Lazy eye syndrome, or amblyopia, a disorder in the human optic nerve * The Liverpool epidemic strain of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' * Lower esophageal sphincter * Lupus erythematosus systemicus Places * The Lower East Side neighborhood of Manhattan, New York City * Les, Catalonia, a municipality in Spain * Leş, a village in Nojorid Commune, Bihor County, Romania * ''Les'', the Hungarian name for Leșu Commune, Bistriţa-Năsăud County, Romania * Les, a village in Tejakula district, Buleleng regency, Bali, Indonesia * Lesotho, IOC and UNDP country code * Lès, a word featuring in many French placenames Transport * Leigh-on-Sea railway station, National Rail station code * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
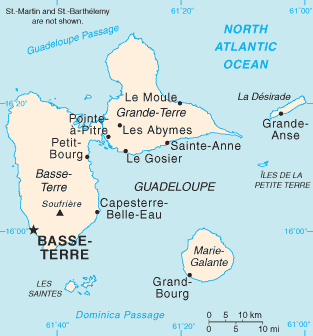
Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe
Grande-Terre Island ( ; or ) is the name of the eastern-half of Guadeloupe proper, in the Lesser Antilles. It is separated from the other half of Guadeloupe island, Basse-Terre, by a narrow sea channel called Rivière Salée (in English, Salt River). Pointe de la Grande Vigie, in Grande-Terre, is the northernmost point of Guadeloupe island. To the east lies La Désirade, and to the south lies Marie Galante. Despite its name, Grande-Terre (literally "Large Land" in French) is smaller than Basse-Terre Island. It was called like that, in contrast with the much smaller Petite Terre Islands ("Small Land" Islands), two very small islands located about 10 km south-east of the Grande-Terre (see map to the left). Grande-Terre's indented coastline is surrounded by coral reefs and the island itself is a limestone plateau. Its surface is a series of rolling hills, white sand beaches and cliffs. The island's beaches consist of both white and black sands, as well as beaches of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basse-Terre Island
Guadeloupe is an Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre Island, Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Guadeloupe, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and two Îles des Saintes—as well as many uninhabited islands and outcroppings. It is south of Antigua and Barbuda and Montserrat and north of Dominica. The capital city is Basse-Terre, on the southern west coast of Basse-Terre Island; the most populous city is Les Abymes and the main centre of business is neighbouring Pointe-à-Pitre, both on Grande-Terre Island. It had a population of 395,726 in 2024. Like the other overseas departments, it is an integral part of France. As a constituent territory of the European Union and the eurozone, the euro is its official currency and any European Union citizen is free to settle and work there indefinitely, but is not part of the Schengen Area. It included Saint Barthélemy and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas Department And Region Of France
The overseas departments and regions of France (, ; DROM) are the five departments and regions of the French Republic which are located outside European France (also known as "metropolitan France"). These overseas entities have exactly the same status as European France's departments and regions. The French Constitution provides that, in general, French laws and regulations (France's civil code, penal code, administrative law, social laws, and tax laws etc.) apply to French overseas departments and regions the same way as in metropolitan France, but can be adapted as needed to suit the region's particular needs. Hence, the local administrations of French overseas departments and regions cannot themselves pass new laws. On occasion, referendums are undertaken to re-assess the sentiment in local status. Since March 2011, the five overseas departments and regions of France are: * French Guiana in South America, a part of The Guianas; * Guadeloupe in the Caribbean Sea, a part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caribbean
The Caribbean ( , ; ; ; ) is a region in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, mostly overlapping with the West Indies. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous List of Caribbean islands, islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo Municipalities of Quintana Roo#Municipalities, islands and Districts of Belize#List, Belizean List of islands of Belize, islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands Department#Islands, Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, Corn Islands, and San Blas Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the Mainland, continental mainland of the Americas bordering the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antilles
The Antilles is an archipelago bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the south and west, the Gulf of Mexico to the northwest, and the Atlantic Ocean to the north and east. The Antillean islands are divided into two smaller groupings: the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. The Greater Antilles includes the Cayman Islands and larger islands of Cuba, Hispaniola (subdivided into the nations of the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and Navassa Island, Jamaica, and Puerto Rico. The Lesser Antilles contains the northerly Leeward Islands and the southeasterly Windward Islands as well as the Leeward Antilles just north of Venezuela. The Lucayan Archipelago (consisting of The Bahamas and the Turks and Caicos Islands), though a part of the West Indies, is generally not included among the Antillean islands. Geography, Geographically, the Antillean islands are generally considered a subregion of North America. Culturally speaking, Cuba, the Dominican Republic, and Puerto Rico – and sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antillean Creole
Antillean French Creole (also known as Lesser Antillean Creole, Kreyol, or Patois) is a French-based creole languages, French-based creole language that is primarily spoken in the Lesser Antilles caribbean. Its grammar and vocabulary include elements of Indigenous languages of the Americas, indigenous languages, Languages of Africa, African languages, French language, French, and English language, English. Geographical situation There are two main geographical and linguistic groups in the Antilles or List of Caribbean islands, Caribbean Islands: the Greater Antilles and the Lesser Antilles. Intercomprehension between these two groups is possible, but despite a large proportion of shared vocabulary and largely similar grammatical functioning, it is limited by varying key vocabulary and different words for basic grammar. Nevertheless, it is easy to begin to understand each other completely, as long as one of the two has a basic knowledge of the other's language. Antillean Creole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Governors General Of The French Antilles
} The governors general of the French Antilles, or lieutenants-general, were the king's representatives in the French West Indies colonies under the Ancien Régime. The colonies were, by date of foundation, Saint-Christophe (1625), Saint-Domingue (1627), Saint Martin (1635), Martinique (1635), Guadeloupe (1635), Dominica (1635), Saint Barthélemy (1648), Grenada (1650), Saint Croix (1650), Saint Lucia (1660), Tobago (1678), the Grenadines and Saint Vincent (1699). History The position was created in 1628, formally named the "Governor-general of the islands and mainland of America" (''Gouverneur général des Isles et Terre Ferme de l'Amérique''). The first office holder was Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc, who had founded the colony of Saint Christophe (Saint Kitts) in 1625, the first French colony in the region. The governor general lived in Basseterre Saint Christophe. Jean-Charles de Baas moved the governor's residence from Saint-Christophe to Martinique, first to Saint-Pier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armand Joseph Bruat
Armand Joseph Bruat ( Colmar, 26 May 1796 – '' Montebello'', off Toulon, 19 November 1855) was a French admiral. Biography Bruat joined the French Navy in 1811, at the height of the Napoleonic Wars. His early career included far-ranging sea duties: in 1815, he served in Brazil and the West Indies. From 1817 to 1820 he was with French forces in the Levant. Then, until 1824, he was stationed first in Senegal and then the Pacific. As a Lieutenant, Bruat took part in the 1827 Battle of Navarino as maneuver officer on ''Breslaw''. In 1830, he received command of the brig ''Silène'' and cruised off Algiers, taking a number of prizes. As ''Silène'' followed the ''Aventure'' commanded by Félix-Ariel d'Assigny (1794–1846), she was wrecked and the crew was captured during the shipwreck of Dellys, 110 men being massacred. While captive, Bruat managed to transmit observations on the state of the defences of Algier to admiral Duperré. After the Invasion of Algiers, Bruat wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Belain D'Esnambuc
Pierre Belain, sieur d'Esnambuc (; 1585–1636) was a French trader and adventurer in the Caribbean, who established the first permanent French colony, Saint-Pierre, on the island of Martinique in 1635. Biography Youth Pierre Belain d'Esnambuc was the fifth child of Nicholas Belain, lord of Quenouville and of Esnambuc. He was baptized in the Saint-Quentin church in Allouville-Bellefosse, in Normandy, on March 9, 1585. The domain of Quenouville suffered under the Wars of Religion which laid waste the Pays de Caux. Nicholas Belain had to borrow 2,400 livres from the Duke of Cossé-Brissac which was swollen by interest. After his death in 1599, his children had to pay the debt. François, the eldest and heir of the domain of Quenouville, decided to sell the domain of Esnambuc. The other land was sold in 1610. Pierre Belain ought not therefore to have borne this title, which he nonetheless did during later years. In 1603, when he was 18 years old, he embarked as "mathelot" on "'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |