|
Free Molecular Flow
Free molecular flow describes the fluid dynamics of gas where the mean free path of the molecules is larger than the size of the chamber or of the object under test. For tubes/objects of the size of several cm, this means pressures well below 10−3 mbar. This is also called the regime of high vacuum, or even ultra-high vacuum. This is opposed to viscous flow encountered at higher pressures. The presence of free molecular flow can be calculated, at least in estimation, with the Knudsen number (Kn). If Kn > 10, the system is in free molecular flow, also known as Knudsen flow. Knudsen flow has been defined as the transitional range between viscous flow and molecular flow, which is significant in the medium vacuum range where λ ≈ d. Gas flow can be grouped in four regimes: For Kn≤0.001, flow is continuous, and the Navier–Stokes equations are applicable, from 0.001 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Dynamics
In physics, physical chemistry and engineering, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that describes the flow of fluids – liquids and gases. It has several subdisciplines, including (the study of air and other gases in motion) and (the study of water and other liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moment (physics), moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipeline transport, pipelines, weather forecasting, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space, understanding large scale Geophysical fluid dynamics, geophysical flows involving oceans/atmosphere and Nuclear weapon design, modelling fission weapon detonation. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecular Distillation
Molecular distillation is a type of short-path vacuum distillation, characterized by an extremely low vacuum pressure, 0.01 torr or below, which is performed using a molecular still. It is a process of separation, purification and concentration of natural products, complex and thermally sensitive molecules for example vitamins and polyunsaturated fatty acids. This process is characterized by short term exposure of the distillate liquid to high temperatures in high vacuum (around mmHg) in the distillation column and a small distance between the evaporator and the condenser around 2 cm. In molecular distillation, fluids are in the free molecular flow regime, i.e. the mean free path of molecules is comparable to the size of the equipment. The gaseous phase no longer exerts significant pressure on the substance to be evaporated, and consequently, rate of evaporation no longer depends on pressure. The motion of molecules is in the line of sight, because they do not form a continuou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
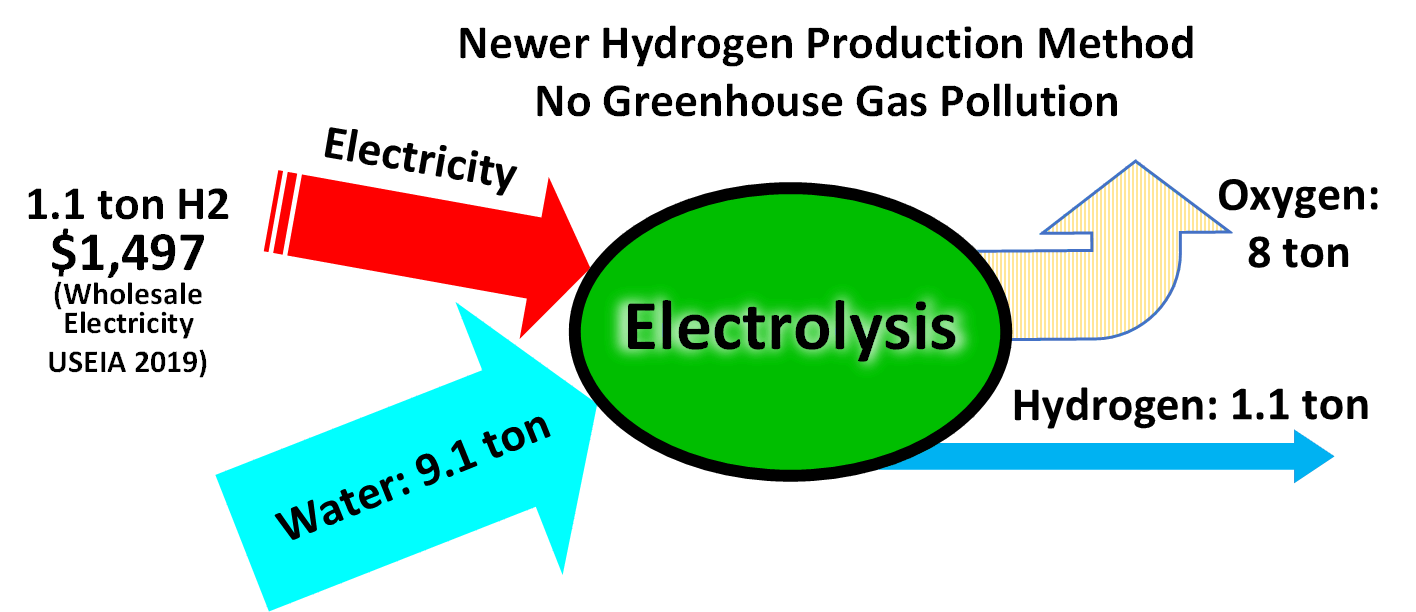
Hydrogen Production
Hydrogen gas is produced by several industrial methods. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. Article in press. Most hydrogen is ''gray hydrogen'' made through steam methane reforming. In this process, hydrogen is produced from a chemical reaction between steam and methane, the main component of natural gas. Producing one tonne of hydrogen through this process emits 6.6–9.3 tonnes of carbon dioxide. When carbon capture and storage is used to remove a large fraction of these emissions, the product is known as ''blue hydrogen''. ''Green hydrogen'' is usually understood to be produced from Renewable energy, renewable electricity via electrolysis of water. Less frequently, definitions of ''green hydrogen'' include hydrogen produced from other low-emission sources such as Biomass (energy), biomass. Producing green hydrogen is currently more expensive than producing gray hydrogen, and the efficiency of energy conversion is inherently low. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaseous Diffusion
Gaseous diffusion is a technology that was used to produce enriched uranium by forcing gaseous uranium hexafluoride (UF6) through microporous membranes. This produces a slight separation (enrichment factor 1.0043) between the molecules containing uranium-235 (235U) and uranium-238 (238U). By use of a large cascade of many stages, high separations can be achieved. It was the first process to be developed that was capable of producing enriched uranium in industrially useful quantities, but is nowadays considered obsolete, having been superseded by the more-efficient gas centrifuge process (enrichment factor 1.05 to 1.2). Gaseous diffusion was devised by Francis Simon and Nicholas Kurti at the Clarendon Laboratory in 1940, tasked by the MAUD Committee with finding a method for separating uranium-235 from uranium-238 in order to produce a bomb for the British Tube Alloys project. The prototype gaseous diffusion equipment itself was manufactured by Metropolitan-Vickers (MetroVick ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium radioactive decay, radioactively decays, usually by emitting an alpha particle. The half-life of this decay varies between 159,200 and 4.5 billion years for different isotopes of uranium, isotopes, making them useful for dating the age of the Earth. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordial nuclide, primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few Parts-per notation#Parts-per expressions, parts per million in soil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Separation
Isotope separation is the process of concentrating specific isotopes of a chemical element by removing other isotopes. The use of the nuclides produced is varied. The largest variety is used in research (e.g. in chemistry where atoms of "marker" nuclide are used to figure out reaction mechanisms). By tonnage, separating natural uranium into enriched uranium and depleted uranium is the largest application. In the following text, mainly uranium enrichment is considered. This process is crucial in the manufacture of uranium fuel for nuclear power plants and is also required for the creation of uranium-based nuclear weapons (unless uranium-233 is used). Plutonium-based weapons use plutonium produced in a nuclear reactor, which must be operated in such a way as to produce plutonium already of suitable isotopic mix or ''grade''. While chemical elements can be purified through chemical processes, isotopes of the same element have nearly identical chemical properties which makes this type ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Characteristic Length
In physics, a characteristic length is an important dimension that defines the scale of a physical system. Often, such a length is used as an input to a formula in order to predict some characteristics of the system, and it is usually required by the construction of a dimensionless quantity, in the general framework of dimensional analysis and in particular applications such as fluid mechanics. In computational mechanics, a characteristic length is defined to force localization of a stress softening constitutive equation. The length is associated with an integration point. For 2D analysis, it is calculated by taking the square root of the area. For 3D analysis, it is calculated by taking the cubic root of the volume associated to the integration point. Examples A characteristic length is usually the volume of a system divided by its surface: L_c = \frac For example, it is used to calculate flow through circular and non-circular tubes in order to examine flow conditions (i.e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Unit
The astronomical unit (symbol: au or AU) is a unit of length defined to be exactly equal to . Historically, the astronomical unit was conceived as the average Earth-Sun distance (the average of Earth's aphelion and perihelion), before its modern redefinition in 2012. The astronomical unit is used primarily for measuring distances within the Solar System or around other stars. It is also a fundamental component in the definition of another unit of astronomical length, the parsec. One au is approximately equivalent to 499 light-seconds. History of symbol usage A variety of unit symbols and abbreviations have been in use for the astronomical unit. In a 1976 resolution, the International Astronomical Union (IAU) had used the symbol ''A'' to denote a length equal to the astronomical unit. In the astronomical literature, the symbol AU is common. In 2006, the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) had recommended ua as the symbol for the unit, from the French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplanetary Medium
The interplanetary medium (IPM) or interplanetary space consists of the mass and energy which fills the Solar System, and through which all the larger Solar System bodies, such as planets, dwarf planet A dwarf planet is a small planetary-mass object that is in direct orbit around the Sun, massive enough to be hydrostatic equilibrium, gravitationally rounded, but insufficient to achieve clearing the neighbourhood, orbital dominance like the ...s, asteroids, and comets, move. The IPM stops at the Heliopause (astronomy), heliopause, outside of which the interstellar medium begins. Before 1950, interplanetary space was widely considered to either be an empty vacuum, or consisting of "Aether theories, aether". Composition and physical characteristics The interplanetary medium includes Interplanetary dust cloud, interplanetary dust, cosmic rays, and hot Plasma (physics), plasma from the solar wind. The density of the interplanetary medium is very low, decreasing in inverse pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Small accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, including particle therapy for oncology, oncological purposes, Isotopes in medicine, radioisotope production for medical diagnostics, Ion implantation, ion implanters for the manufacturing of Semiconductor, semiconductors, and Accelerator mass spectrometry, accelerator mass spectrometers for measurements of rare isotopes such as radiocarbon. Large accelerators include the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York, and the largest accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider near Geneva, Switzerland, operated b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
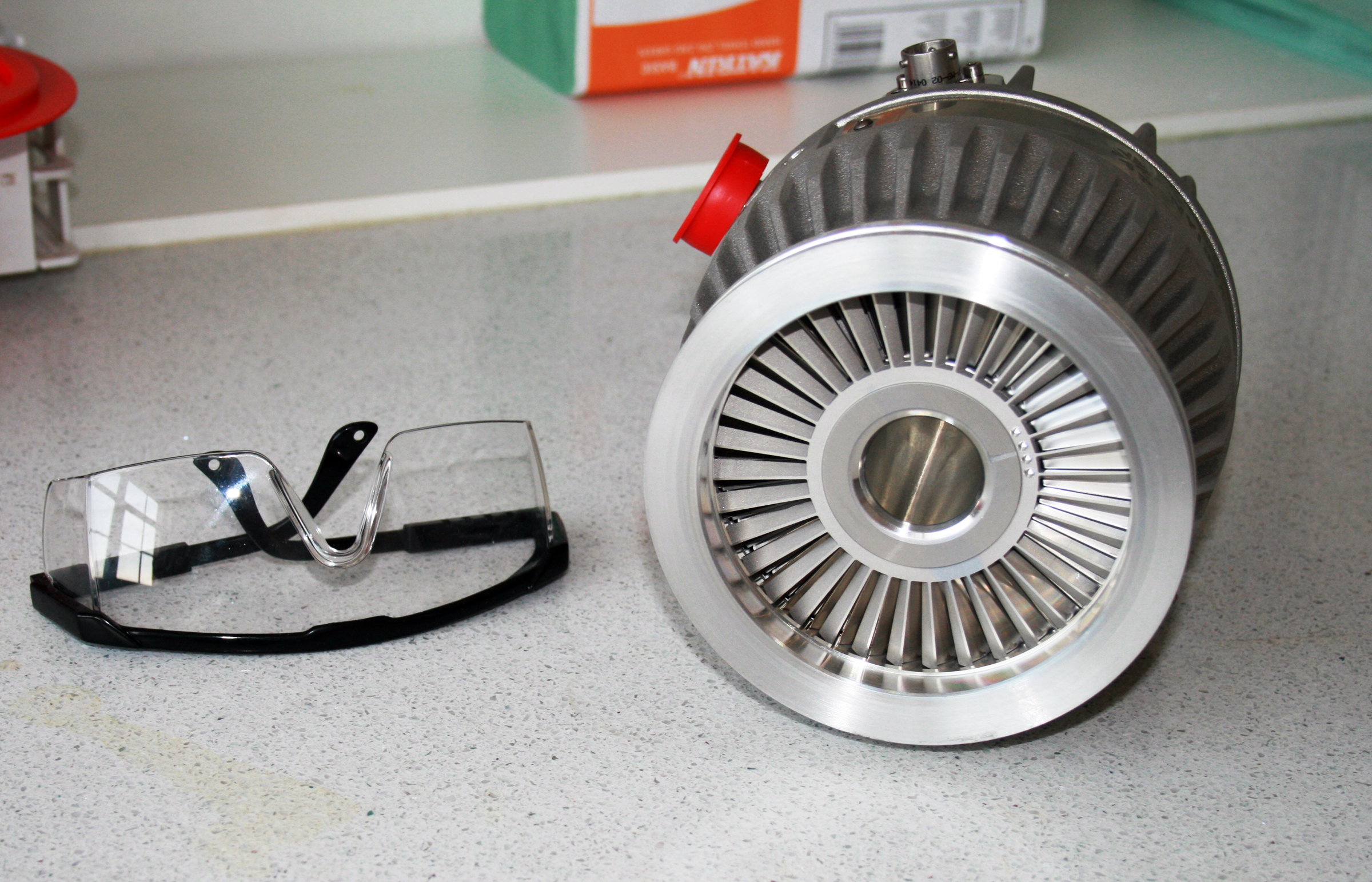
Turbomolecular Pump
A turbomolecular pump is a type of vacuum pump, superficially similar to a turbopump, used to obtain and maintain high vacuum. These pumps work on the principle that gas molecules can be given momentum in a desired direction by repeated collision with a moving solid surface. In a turbomolecular pump, a rapidly spinning fan rotor 'hits' gas molecules from the inlet of the pump towards the exhaust in order to create or maintain a vacuum. Operating principles Most turbomolecular pumps employ multiple stages, each consisting of a quickly rotating rotor blade and stationary stator blade pair. The system is an axial compressor that puts energy into the gas, rather than a turbine, which takes energy out of a moving fluid to create rotary power, thus "turbomolecular pump" is a misnomer. Gas captured by the upper stages is pushed into the lower stages and successively compressed to the level of the fore-vacuum (backing pump) pressure. As the gas molecules enter through the inlet, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |