|
François De La Rochefoucauld, 9th Duke Of La Rochefoucauld
François XIV Marie Auguste Armand Emilien de La Rochefoucauld, 9th Duke of La Rochefoucauld (17 December 1794 – 11 December 1874) was a French aristocrat. Early life De La Rochefoucauld was born on 1794 in The Hague, Netherlands. He was the eldest son and heir of François de La Rochefoucauld, 8th Duke of La Rochefoucauld and the former Marie Françoise de Tott (1770–1854). Among his siblings were Count Olivier de La Rochefoucauld (who married Rosine Cuillier-Perron, a daughter of Gen. Pierre Cuillier-Perron) Countess Sophie Francoise de La Rochefoucauld (who married Armand, Marquis de Castelbajac), Count Charles Frédéric de La Rochefoucauld (who married Anne Charlotte Cuillier-Perron, also a daughter of Gen. Pierre Cuillier-Perron), Count Hippolyte de La Rochefoucauld (who married Marie du Roux, a daughter of Anatole du Roux), and Countess Frances "Fanny" de La Rochefoucauld (who married Count Armand Alexis de Montault, but was one of the mistresses of Anatoly Nikolaievich ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duke Of La Rochefoucauld
The House of La Rochefoucauld is one of France's ancient noble families, with origins dating back to the 10th century. The family's lineage begins with (973–1047), the first Lord of La Roche, later known as La Rochefoucauld (''Roche'' + ''Foucauld''), and possibly the son of (also known as Amaury or Esmerin; ''circa'' 952 – before 1037), Lord of La Roche. Over the centuries, the family rose in prominence, earning numerous titles and distinctions. Overview of titles and roles In April 1622, Louis XIII elevated the County (comté) of La Rochefoucauld to a Duchy and Peerage by ' issued at Niort (registered September 4, 1631). This act formally raised François V of La Rochefoucauld (1588–1650) from Count to the inaugural Duke of La Rochefoucauld, as well as to the status of Peer of France. ::Upon its elevation in 1622, the Duchy of La Rochefoucauld became united with the lordships of Verteuil, Daunart, Joussaume, Vivier, Montignac, Touriers, Celfroin, Saint Clos, La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The is a general knowledge, general-knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It has been published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. since 1768, although the company has changed ownership seven times. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopedia, online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest-running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in Edinburgh, Scotland, in three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size; the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810), it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent contributors, and the 9th (1875–1889) and Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 11th editions (1911) are landmark encyclopaedias for scholarship and literary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadet Branch
A cadet branch consists of the male-line descendants of a monarch's or patriarch's younger sons ( cadets). In the ruling dynasties and noble families of much of Europe and Asia, the family's major assets (realm, titles, fiefs, property and income) have historically been passed from a father to his firstborn son in what is known as primogeniture; younger sons, the cadets, inherited less wealth and authority (such as a small appanage) to pass on to future generations of descendants. In families and cultures in which that was not the custom or law, such as the feudal Holy Roman Empire, the equal distribution of the family's holdings among male members was eventually apt to so fragment the inheritance as to render it too small to sustain the descendants at the socio-economic level of their forefather. Moreover, brothers and their descendants sometimes quarreled over their allocations, or even became estranged. While agnatic primogeniture became a common way of keeping the family's w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Roche-Guyon
La Roche-Guyon () is a commune in the Val-d'Oise department in Île-de-France in northern France. It is located in the , and is a member of Les Plus Beaux Villages de France (The Most Beautiful Villages of France) Association. The commune grew around the Château de La Roche-Guyon, upon which historically it depended for its existence. The commune's population in 2019 was 479. Geography It is located approximately 58 km from Paris and 9 km from Giverny Château de La Roche-Guyon The present Château de La Roche-Guyon was built in the 12th century, controlling a river crossing of the Seine, itself one of the routes to and from Normandy; The Abbé Suger described its grim aspect: "At the summit of a steep promontory, dominating the bank of the great river Seine, rises a frightful castle without title to nobility, called La Roche. Invisible on the surface, it is hollowed out of a high cliff. The able hand of the builder has established in the mountainside, digging i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambroise-Polycarpe De La Rochefoucauld
Ambroise-Polycarpe de La Rochefoucauld Grandee, GE (2 April 1765 – 2 June 1841), 1st Duke of Doudeauville, was a French soldier and politician. He was Minister of the Royal Household from 1821 to 1827. Early life Ambroise-Polycarpe de La Rochefoucauld was born in Paris on 2 April 1765 into the House of La Rochefoucauld. He was a son of Anne-Sabine-Rosalie de Chauvelin and Brigadier Jean-François de La Rochefoucauld (1735-1789), 5th Marquis of Surgères, who was Governor of Chartres. His only surviving sibling, Anne Alexandrine Rosalie de La Rochefoucauld, had married Armand Alexandre Roger de La Rochefoucauld, Count of Durtal (younger brother of François Alexandre Frédéric de La Rochefoucauld, 7th Duke of La Rochefoucauld, François de La Rochefoucauld, 7th Duke of La Rochefoucauld). His sister, the Countess of Durtal, was guillotined in Paris in 1794 during the Reign of Terror alongside their uncle, Louis Desacres de l'Aigle. His paternal grandfather was Alexandre-Nicolas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château De Rastignac
The Château de Rastignac is a neoclassical style country house located in La Bachellerie, near Bordeaux in the Dordogne in France. It was built between 1789 and 1817 to designs by the architect Mathurin Salat (1755–1822), sometimes called "Blanchard". The house was built of limestone by the Marquis de Rastignac. History Construction of the château was delayed by disruptions from the French Revolution and Napoleonic wars. When completed, the house was decorated in the French Empire style. In 1944, fleeing Nazi Schutzstaffel (SS) forces attempted to destroy the Château de Rastignac in retribution against the French Resistance.Lynn H. Nicholas. ''The Rape of Europa: The Fate of Europe's Treasures in the Third Reich and the Second World War'' (New York: Vintage, 1995), pp. 285-86. Using phosphorus as an accelerant, the fire burned for five days. Only the exterior limestone shell survived. After eight years the structure was stabilized and a roof placed overhead for protec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
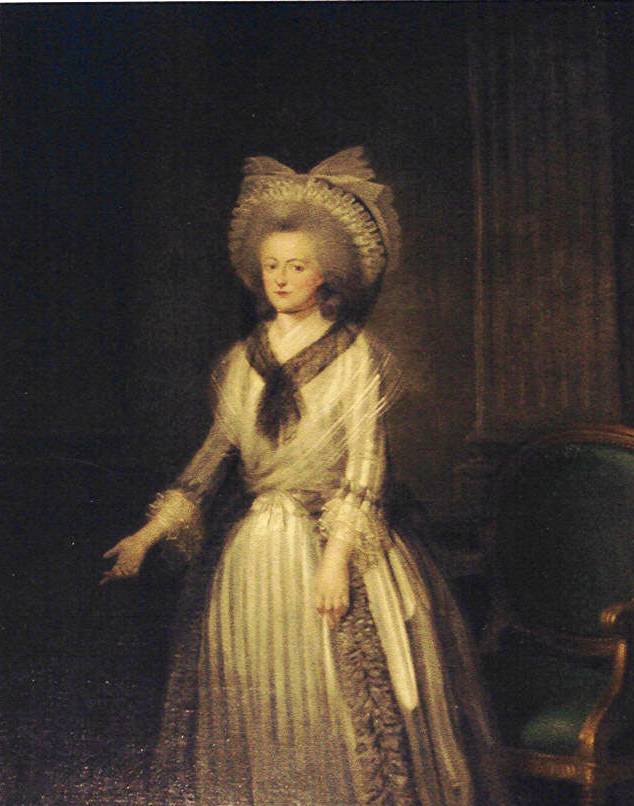
Zenaide Chapt De Rastignac, Duchesse De La Rochefoucauld, 1817, By Edmee Brucy
__NOTOC__ Zenaida, Zenaide (Italian), Zénaïde (French), or Zinaida (), from meaning "dedicated to Zeus". /ref> It is a used in many cultures for women. It can also refer (as ''Zenaida'') to the , named after Princess Zéna� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Officer Of The Legion Of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and civil. Currently consisting of five classes, it was originally established in 1802 by Napoleon Bonaparte, and it has been retained (with occasional slight alterations) by all later French governments and regimes. The order's motto is ' ("Honour and Fatherland"); its seat is the Palais de la Légion d'Honneur next to the Musée d'Orsay, on the left bank of the Seine in Paris. Since 1 February 2023, the Order's grand chancellor has been retired General François Lecointre, who succeeded fellow retired General Benoît Puga in office. The order is divided into five degrees of increasing distinction: ' (Knight), ' (Officer), ' (Commander), ' (Grand Officer) and ' (Grand Cross). History Consulate During the French Revolution, all of the French orders of chivalry were abolished and replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of Saint Louis
The Royal and Military Order of Saint Louis () is a dynastic order of chivalry founded 5 April 1693 by King Louis XIV, named after Saint Louis (King Louis IX of France). It was intended as a reward for exceptional officers, notable as the first decoration that could be granted to non-nobles. By the authorities of the French Republic, it is considered a predecessor of the Legion of Honour, with which it shares the red ribbon (though the Legion of Honour is awarded to military personnel and civilians alike). Although officially abolished by the government authorities of the July Revolution in 1830 following the French Revolution, its activities carried on as a dynastic order of the formerly sovereign royal family. As such, it is still recognised by the International Commission on Orders of Chivalry. (PDF) Members |
Sophie De Tott
Sophie-Ernestine de Tott (1758 – 1848) was a French painter. Born in Constantinople, Tott was the daughter of François Baron de Tott, who served as a consul in that city, and was of Hungarian descent. A ''chanoinesse'' of Sainte-Anne de Munich, she was entitled by rank to be called "Madame" and is usually so described, although she never married. Madame de Tessé took an interest in her and served as a maternal influence, and her sister married François, duc de La Rochefoucauld in 1793. Tott was the subject of a portrait by Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun and corresponded with Thomas Jefferson. She is the subject of a portrait miniature in which she is painting a portrait of Madame de Tessé; sometimes attributed to her father, it may instead be a self-portrait. Tott fled the French Revolution, and between 1801 and 1804 exhibited a handful of portraits at the Royal Academy. In 1807 she was a member of the household of Elizabeth Craven. She had returned to France by 1825, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Baron De Tott
François Baron de Tott (, ) (August 17, 1733, Chamigny, France – September 24, 1793, Hungary) was an aristocrat and a French military officer of Hungarian origin. Born on August 17, 1733, in Chamigny, a village in northern France, the descendant of a Hungarian nobleman, who had emigrated to the Ottoman Empire and then moved on to France with the cavalry of Count Miklós Bercsényi, and was later raised to the rank of baron. Career As a youngster, François joined the regiment his father was serving in, and in 1754 was promoted to the rank of Lieutenant. In 1755 he travelled to Constantinople, the capital city of the Ottoman Empire, as the secretary of his uncle Charles Gravier, comte de Vergennes, who had been appointed ambassador. His main duty was to learn the Turkish language, to investigate the situation in the Ottoman Empire and to gather information about the Crimean Khanate. He returned to Paris in 1763, and was sent to Switzerland in 1766 by the French governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |