|
Flag Of Chicago
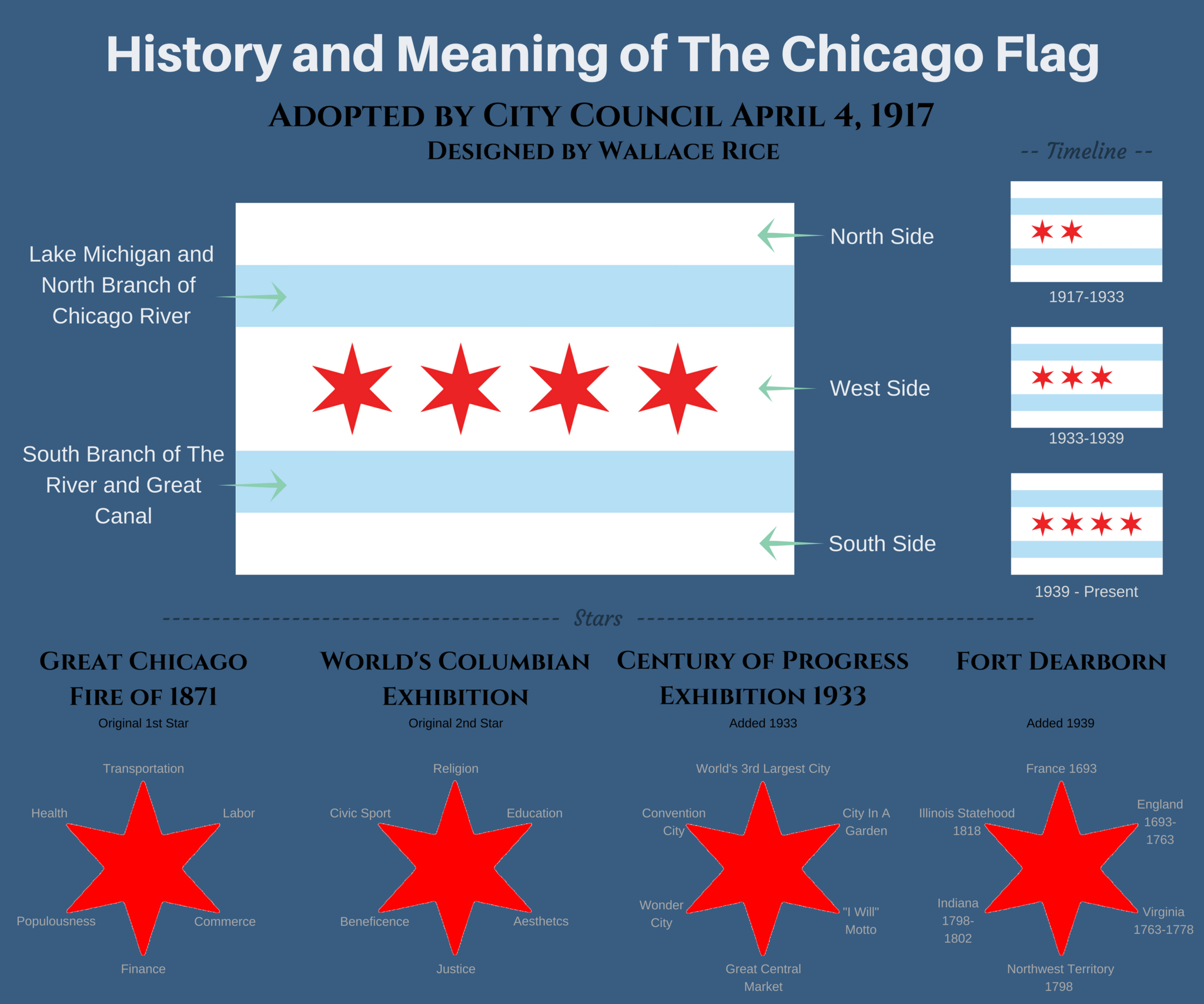
The flag of Chicago consists of two light blue horizontal bars, or stripes, on a field of white, each bar one-sixth the height of the full flag, and placed slightly less than one-sixth of the way from the top and bottom. Four bright red stars, with six sharp points each, are set side by side, close together, in the middle third of the flag's surface. Symbolism Bars The three white background areas of the flag represent, from top to bottom, the North, West, and South sides of the city. The top blue bar represents Lake Michigan and the North Branch of the Chicago River. The bottom blue bar represents the South Branch of the river and the " Great Canal", over the Chicago Portage. The light blue of the flag's two bars is variously called sky blue or pale blue; in a 1917 article of a speech by designer Wallace Rice, it was called "the color of water". Stars There are four red six-pointed stars on the center white bar. Six-pointed stars are used because five-pointed sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argent
In heraldry, argent () is the tincture of silver, and belongs to the class of light tinctures called "metals". It is very frequently depicted as white and usually considered interchangeable with it. In engravings and line drawings, regions to be tinctured ''argent'' are either left blank, or indicated with the abbreviation ''ar''. The name derives from Latin ''argentum'', translated as "silver" or "white metal". The word ''argent'' had the same meaning in Old French ''blazon'', whence it passed into the English language. In some historical depictions of coats of arms, a kind of silver leaf was applied to those parts of the device that were argent. Over time, the silver content of these depictions has tarnished and darkened. As a result, it can sometimes be difficult to distinguish regions that were intended as "argent" from those that were " sable". This leaves a false impression that the rule of tincture has been violated in cases where, when applied next to a dark colour, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History And Meaning Of The Chicago Flag
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the Human history, human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on Primary source, primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Territory
The Territory of Illinois was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from March 1, 1809, until December 3, 1818, when the southern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Illinois. Its capital was the former French village of Kaskaskia on the Mississippi River (which is still a part of the State of Illinois). The northern half of the territory, modern Wisconsin and parts of modern Minnesota and Michigan became part of the Territory of Michigan in 1818. History of the area The area was earlier known as " Illinois Country" (''Pays des Illinois'') while under French control, first as part of French Canada and then in its southern region as part of French Louisiana. The British gained authority over the region east of the Mississippi River from the French, with the 1763 Treaty of Paris marking the end of the French and Indian War and of the French North American colony of New France. During the American Revolutionary W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indiana Territory
The Indiana Territory, officially the Territory of Indiana, was created by an organic act that President of the United States, President John Adams signed into law on May 7, 1800, to form an Historic regions of the United States, organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from July 4, 1800, to December 11, 1816, when the remaining southeastern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the U.S. state, state of Indiana. The territory originally contained approximately of land, but its size was decreased when it was subdivided to create the Michigan Territory (1805) and the Illinois Territory (1809). The Indiana Territory was the first new territory created from lands of the Northwest Territory, which had been organized under the terms of the Northwest Ordinance of 1787. The territorial capital was the settlement around the old French fort of Vincennes, Indiana, Vincennes on the Wabash River, until transferred to Corydon, Indiana, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territory
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from part of the unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolution. Established in 1787 by the Congress of the Confederation through the Northwest Ordinance, it was the nation's first post-colonial Organized incorporated territories of the United States, organized incorporated territory. At the time of its creation, the territory included all the land west of Pennsylvania, northwest of the Ohio River and east of the Mississippi River below the Great Lakes, and what later became known as the Boundary Waters. The region was ceded to the United States in the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris of 1783. Throughout the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, the region was part of the British Province of Quebec (1763–1791), Province of Quebec and the Western theater of the American Revolutionary War, western ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois County, Virginia
Illinois County, Virginia, was a political and geographic region, part of the British Province of Quebec, claimed during the American Revolutionary War on July 4, 1778, by George Rogers Clark of the Virginia Militia as a result of the Illinois Campaign. Though part or all of the area was also claimed by Connecticut and Massachusetts, it was formally organized by the Commonwealth of Virginia later that year. The County was accorded official governmental existence, including legally defined boundaries and a formal governmental structure under the laws of the Commonwealth. The county seat was the old Illinois Country French village of Kaskaskia. John Todd was appointed by Governor Patrick Henry to head the county's government. The county was abolished in January 1782, and Virginia ceded the land to the new United States Confederation government in 1784. The area later became the Northwest Territory by an Act of Congress in 1787. Geographically, the county was bordered to the so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Quebec (1763–1791)
The Province of Quebec () was a colony in British North America which comprised the former French colony of Canada. It was established by the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1763, following the conquest of New France by British forces during the Seven Years' War. As part of the 1763 Treaty of Paris, France gave up its claim to the colony; it instead negotiated to keep the small profitable island of Guadeloupe. Following the Royal Proclamation of 1763, Canada was renamed the Province of Quebec, and from 1774 extended from the coast of Labrador on the Atlantic Ocean, southwest through the Saint Lawrence River Valley to the Great Lakes and beyond to the confluence of the Ohio and Mississippi Rivers in the Illinois Country. Portions of its southwest, those areas south of the Great Lakes, were later ceded to the newly established United States in the 1783 Treaty of Paris at the conclusion of the American Revolution; although the British maintained a military presence there unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois Country
The Illinois Country ( ; ; ), also referred to as Upper Louisiana ( ; ), was a vast region of New France claimed in the 1600s that later fell under Spanish and British control before becoming what is now part of the Midwestern United States. While the area claimed included the entire Upper Mississippi River watershed, French colonial settlement was concentrated along the Mississippi and Illinois Rivers in what is now the U.S. states of Illinois and Missouri, with outposts on the Wabash River in Indiana. Explored in 1673 from Green Bay to the Arkansas River by the '' Canadien'' expedition of Louis Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, the area was claimed by France. It was settled primarily from the '' Pays d'en Haut'' in the context of the fur trade, and in the establishment of missions from Canada by French Catholic religious orders. Over time, the fur trade took some French to the far reaches of the Rocky Mountains, especially along the branches of the broad Missouri River vall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Dearborn
Fort Dearborn was a United States fort, first built in 1803 beside the Chicago River, in what is now Chicago, Illinois. It was constructed by U.S. troops under Captain John Whistler and named in honor of Henry Dearborn, then United States Secretary of War. The original fort was destroyed following the Battle of Fort Dearborn during the War of 1812, and a replacement Fort Dearborn was constructed on the same site in 1816 and decommissioned by 1837. Parts of the fort were lost to the widening of the Chicago River in 1855, and a fire in 1857. The last vestiges of Fort Dearborn were destroyed in the Great Chicago Fire of 1871. The site of the fort is now a Chicago Landmark, located in the Michigan–Wacker Historic District, at the southern end of the DuSable Michigan Avenue Bridge. Background Historic events Human activity in the Chicago area prior to the arrival of European explorers is mostly unknown, although it evidently served as a crossing point among many different peop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Los Angeles
Los Angeles, often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, most populous city in the U.S. state of California, and the commercial, Financial District, Los Angeles, financial, and Culture of Los Angeles, cultural center of Southern California. With an estimated 3,878,704 residents within the city limits , it is the List of United States cities by population, second-most populous in the United States, behind only New York City. Los Angeles has an Ethnic groups in Los Angeles, ethnically and culturally diverse population, and is the principal city of a Metropolitan statistical areas, metropolitan area of 12.9 million people (2024). Greater Los Angeles, a combined statistical area that includes the Los Angeles and Riverside–San Bernardino metropolitan areas, is a sprawling metropolis of over 18.5 million residents. The majority of the city proper lies in Los Angeles Basin, a basin in Southern California adjacent to the Pacific Ocean in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Century Of Progress
A Century of Progress International Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in the city of Chicago, Illinois, United States, from 1933 to 1934. The fair, registered under the Bureau International des Expositions (BIE), celebrated the city's centennial. Designed largely in Art Deco style, the theme of the fair was technological innovation, and its motto was "Science Finds, Industry Applies, Man Conforms", trumpeting the message that science and American life were wedded. Its architectural symbol was the Sky Ride, a transporter bridge perpendicular to the shore on which one could ride from one side of the fair to the other. One description of the fair noted that the world, "then still mired in the malaise of the Great Depression, could glimpse a happier not-too-distant future, all driven by innovation in science and technology". Fair visitors saw the latest wonders in rail travel, automobiles, architecture and even cigarette-smoking robots. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World's Columbian Exposition
The World's Columbian Exposition, also known as the Chicago World's Fair, was a world's fair held in Chicago from May 5 to October 31, 1893, to celebrate the 400th anniversary of Christopher Columbus's arrival in the New World in 1492. The centerpiece of the Fair, held in Jackson Park, was a large water pool representing the voyage that Columbus took to the New World. Chicago won the right to host the fair over several competing cities, including New York City, Washington, D.C., and St. Louis. The exposition was an influential social and cultural event and had a profound effect on American architecture, the arts, American industrial optimism, and Chicago's image. The layout of the Chicago Columbian Exposition was predominantly designed by John Wellborn Root, Daniel Burnham, Frederick Law Olmsted, and Charles B. Atwood. It was the prototype of what Burnham and his colleagues thought a city should be. It was designed to follow Beaux-Arts principles of design, namely ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |