|
Fire (classical Element)
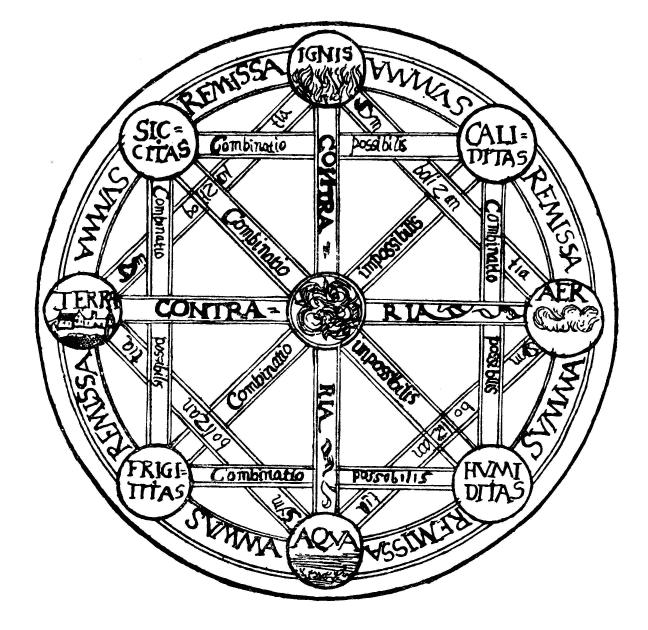
Fire is one of the four classical elements along with earth, water and air in ancient Greek philosophy and science. Fire is considered to be both hot and dry and, according to Plato, is associated with the tetrahedron. Greek and Roman tradition Fire is one of the four classical elements in ancient Greek philosophy and science. It was commonly associated with the qualities of energy, assertiveness, and passion. In one Greek myth, Prometheus stole ''fire'' from the gods to protect the otherwise helpless humans, but was punished for this charity. Fire was one of many '' archai'' proposed by the pre-Socratics, most of whom sought to reduce the cosmos, or its creation, to a single substance. Heraclitus considered ''fire'' to be the most fundamental of all elements. He believed fire gave rise to the other three elements: "All things are an interchange for fire, and fire for all things, just like goods for gold and gold for goods." Diels-Kranz B90 (Freeman 9481970p. 45. He had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Element
The classical elements typically refer to Earth (classical element), earth, Water (classical element), water, Air (classical element), air, Fire (classical element), fire, and (later) Aether (classical element), aether which were proposed to explain the nature and complexity of all matter in terms of simpler Substance theory, substances. Ancient cultures in Ancient Greece, Greece, Angola, Ancient Tibet, Tibet, Ancient India, India, and Mali had similar lists which sometimes referred, in local languages, to "air" as "wind", and to "aether" as "space". These different cultures and even individual philosophers had widely varying explanations concerning their attributes and how they related to observable phenomena as well as cosmology. Sometimes these theories overlapped with mythology and were personification, personified in deities. Some of these interpretations included atomism (the idea of very small, indivisible portions of matter), but other interpretations considered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally appointed by and ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically hereditary and patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, but nobility also existed in such regimes as the Dutch Republic (1581–1795), the Republic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire Symbol (alchemical)
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction products. Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion reaction when the fuel reaches its ignition point temperature. Flames from hydrocarbon fuels consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce plasma. The color and intensity of the flame depend on the type of fuel and composition of the surrounding gases. Fire, in its most common form, has the potential to result in conflagration, which can lead to permanent physical damage. It directly impacts land-based ecological systems worldwide. The positive effects of fire include stimulating plant growth and maintaining ecological balance. Its negative effects include hazards to life and property, atmospheric pollution, and water contamination. When fire removes protective vegetation, heav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masculinity
Masculinity (also called manhood or manliness) is a set of attributes, behaviors, and roles generally associated with men and boys. Masculinity can be theoretically understood as Social construction of gender, socially constructed, and there is also evidence that some behaviors considered masculine are influenced by both cultural factors and biological factors. To what extent masculinity is biologically or socially influenced is subject to debate. It is Sex and gender distinction, distinct from the definition of the Male, biological male sex, as anyone can exhibit masculine traits. Standards of masculinity vary across different cultures and historical periods. In Western cultures, its meaning is traditionally drawn from being contrasted with femininity. Overview Standards of manliness or masculinity vary across different cultures, subcultures, ethnic groups and historical periods. Traits traditionally viewed as masculine in Western world, Western society include physical stren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Medicine Of Western Europe
In the Middle Ages, the medicine of Western Europe was composed of a mixture of existing ideas from antiquity. In the Early Middle Ages, following the fall of the Western Roman Empire, standard medical knowledge was based chiefly upon surviving Ancient Greece, Greek and Ancient Rome, Roman texts, preserved in monasteries and elsewhere. Medieval medicine is widely misunderstood, thought of as a uniform attitude composed of placing hopes in the church and God to heal all sicknesses, while sickness itself exists as a product of destiny, sin, and Astrology, astral influences as physical causes. But, especially in the second half of the medieval period (c. 1100–1500 AD), medieval medicine became a formal body of theoretical knowledge and was institutionalized in universities. Medieval medicine attributed illnesses, and disease, not to sinful behavior, but to natural causes, and sin was connected to illness only in a more general sense of the view that disease manifested in humanity as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bile
Bile (from Latin ''bilis''), also known as gall, is a yellow-green/misty green fluid produced by the liver of most vertebrates that aids the digestion of lipids in the small intestine. In humans, bile is primarily composed of water, is produced continuously by the liver, and is stored and concentrated in the gallbladder. After a human eats, this stored bile is discharged into the first section of the small intestine, known as the duodenum. Composition In the human liver, bile is composed of 97–98% water, 0.7% bile salts, 0.2% bilirubin, 0.51% fats ( cholesterol, fatty acids, and lecithin), and 200 meq/L inorganic salts. The two main pigments of bile are bilirubin, which is orange-yellow, and its oxidised form biliverdin, which is green. When mixed, they are responsible for the brown color of feces. About of bile is produced per day in adult human beings. Function Bile or gall acts to some extent as a surfactant, helping to emulsify the lipids in food. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Humours
Humorism, the humoral theory, or humoralism, was a system of medicine detailing a supposed makeup and workings of the human body, adopted by Ancient Greek and Roman physicians and philosophers. Humorism began to fall out of favor in the 17th century and it was definitively disproved with the discovery of microbes. Origin The concept of "humors" may have origins in Ancient Egyptian medicine, or Mesopotamia, though it was not systemized until ancient Greek thinkers. The word ''humor'' is a translation of Greek , (literally 'juice' or ' sap', metaphorically 'flavor'). Early texts on Indian Ayurveda medicine presented a theory of three or four humors (doṣas), which they sometimes linked with the five elements (): earth, water, fire, air, and space. The concept of "humors" (chemical systems regulating human behaviour) became more prominent from the writing of medical theorist Alcmaeon of Croton (c. 540–500 BC). His list of humors was longer and included fundamental elements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine In Ancient Greece
Ancient Greek medicine was a compilation of theories and practices that were constantly expanding through new ideologies and trials. The Greek term for medicine was ''iatrikē'' (). Many components were considered in ancient Greek medicine, intertwining the spiritual with the physical. Specifically, the ancient Greeks believed health was affected by the humors, geographic location, social class, diet, trauma, beliefs, and mindset. Early on the ancient Greeks believed that illnesses were "divine punishments" and that healing was a "gift from the Gods". As trials continued wherein theories were tested against symptoms and results, the pure spiritual beliefs regarding "punishments" and "gifts" were replaced with a foundation based in the physical, i.e., cause and effect. Asclepieia Asclepius was espoused as the first physician, and myth placed him as the son of Apollo. Temples dedicated to the healer-god Asclepius, known as '' Asclepieia'' (; sing. Ἀσκληπιεῖον ''Ascl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublunary Sphere
In Aristotelian physics and Greek astronomy, the sublunary sphere is the region of the geocentric cosmos below the Moon, consisting of the four classical elements: earth, water, air, and fire. The sublunary sphere was the realm of changing nature. Beginning with the Moon, up to the limits of the universe, everything (to classical astronomy) was permanent, regular and unchanging—the region of aether where the planets and stars are located. Only in the sublunary sphere did the powers of physics hold sway. Evolution of concept Plato and Aristotle helped to formulate the original theory of a sublunary sphere in antiquity, the idea usually going hand in hand with geocentrism and the concept of a spherical Earth. Avicenna carried forward into the Middle Ages the Aristotelian idea of generation and corruption being limited to the sublunary sphere. Medieval scholastics like Thomas Aquinas, who charted the division between celestial and sublunary spheres in his work ''Summa Theolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platonic Solid
In geometry, a Platonic solid is a Convex polytope, convex, regular polyhedron in three-dimensional space, three-dimensional Euclidean space. Being a regular polyhedron means that the face (geometry), faces are congruence (geometry), congruent (identical in shape and size) regular polygons (all angles congruent and all edge (geometry), edges congruent), and the same number of faces meet at each Vertex (geometry), vertex. There are only five such polyhedra: Geometers have studied the Platonic solids for thousands of years. They are named for the ancient Greek philosopher Plato, who hypothesized in one of his dialogues, the ''Timaeus (dialogue), Timaeus'', that the classical elements were made of these regular solids. History The Platonic solids have been known since antiquity. It has been suggested that certain carved stone balls created by the late Neolithic people of Scotland represent these shapes; however, these balls have rounded knobs rather than being polyhedral, the num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timaeus (dialogue)
''Timaeus'' (; , ) is one of Plato's dialogues, mostly in the form of long monologues given by Critias and Timaeus, written 360 BC. The work puts forward reasoning on the possible nature of the physical world and human beings and is followed by the dialogue '' Critias''. Participants in the dialogue include Socrates, Timaeus, Hermocrates, and Critias. Some scholars believe that it is not the Critias of the Thirty Tyrants who appears in this dialogue, but his grandfather, also named Critias. At the beginning of the dialogue, the absence of another, unknown dialogue participant, present on the day before, is bemoaned. It has been suggested from some traditions— Diogenes Laertius (VIII 85) from Hermippus of Smyrna (3rd century BC) and Timon of Phlius ( 320 – 235 BC)—that ''Timaeus'' was influenced by a book about Pythagoras, written by Philolaus, although this assertion is generally considered false. Introduction The dialogue takes place the day after Socrates de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agrigento
Agrigento (; or ) is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. Founded around 582 BC by Greek colonists from Gela, Agrigento, then known as Akragas, was one of the leading cities during the golden age of Ancient Greece. The city flourished under Theron's leadership in the 5th century BC, marked by ambitious public works and the construction of renowned temples. Despite periods of dormancy during the Punic Wars, Agrigento emerged as one of Sicily's largest cities in the Republican era. During the Principate, Agrigento's strategic port and diverse economic ventures, including sulfur mining, trade and agriculture, sustained its importance throughout the high and late Empire. Economic prosperity persisted in the 3rd to 4th centuries AD, but excavations show decline in activity after the 7th century. Agrigento is also the place of birth to several notable personalities, among which it is worth to mention Empedocles (5th century BC), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |