|
Felty's Syndrome
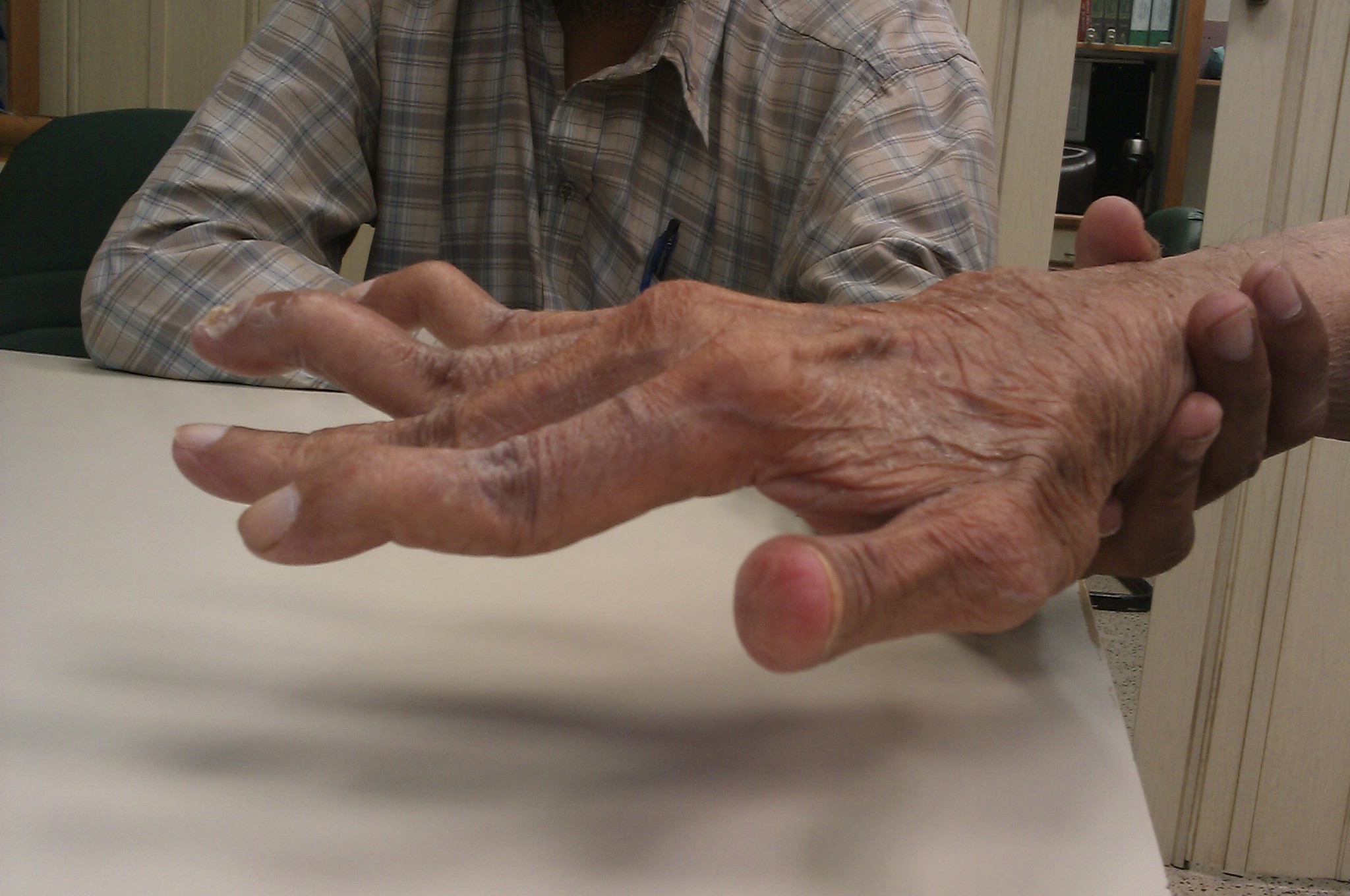
Felty's syndrome (FS), also called Felty syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disease characterized by the triad of rheumatoid arthritis, enlargement of the spleen and low neutrophil count. The condition is more common in those aged 50–70 years, specifically more prevalent in females than males, and more so in Caucasians than those of African descent. It is a deforming disease that causes many complications for the individual. Signs and symptoms The symptoms of Felty's syndrome are similar to those of rheumatoid arthritis. Affected individuals have painful, stiff, and swollen joints, most commonly in the joints of the hands, feet, and arms. In some affected individuals, Felty's syndrome may develop during a period when the symptoms and physical findings associated with rheumatoid arthritis have subsided or are not present; in this case, Felty's syndrome may remain undiagnosed. In more rare instances, the development of Felty's syndrome may precede the development of the symptoms and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects synovial joint, joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are involved, with the same joints typically involved on both sides of the body. The disease may also affect other parts of the body, including skin, eyes, lungs, heart, nerves, and blood. This may result in a anemia, low red blood cell count, pleurisy, inflammation around the lungs, and pericarditis, inflammation around the heart. Fever and low energy may also be present. Often, symptoms come on gradually over weeks to months. While the cause of rheumatoid arthritis is not clear, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. The underlying mechanism involves the body's immune system attacking the joints. This results in inflammation and thickening of the synovium, joint capsule. It also affects the und ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synovial Joint
A synovial joint, also known as diarthrosis, joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones, constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity, and surrounds the bones' articulating surfaces. This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. The synovial cavity/joint is filled with synovial fluid. The joint capsule is made up of an outer layer of fibrous membrane, which keeps the bones together structurally, and an inner layer, the synovial membrane, which seals in the synovial fluid. They are the most common and most movable type of joint in the body. As with most other joints, synovial joints achieve movement at the point of contact of the articulating bones. They originated 400 million years ago in the first jawed vertebrates. Structure Synovial joints contain the following structures: * Synovial cavity: all diarthroses have the characteristic space between the bones that is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Lupus, formally called systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), is an autoimmune disease in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue in many parts of the body. Symptoms vary among people and may be mild to severe. Common symptoms include painful and swollen joints, fever, chest pain, hair loss, mouth ulcers, swollen lymph nodes, feeling tired, and a red rash which is most commonly on the face. Often there are periods of illness, called flares, and periods of remission during which there are few symptoms. Children up to 18 years old develop a more severe form of SLE termed childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. The cause of SLE is not clear. It is thought to involve a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Among identical twins, if one is affected there is a 24% chance the other one will also develop the disease. Female sex hormones, sunlight, smoking, vitamin D deficiency, and certain infections are also believed to increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia; pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and produce high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or '' leukemia cells''. Symptoms may include bleeding and bruising, bone pain, fatigue, fever, and an increased risk of infections. These symptoms occur due to a lack of normal blood cells. Diagnosis is typically made by blood tests or bone marrow biopsy. The exact cause of leukemia is unknown. A combination of genetic factors and environmental (non-inherited) factors are believed to play a role. Risk factors include smoking, ionizing radiation, petrochemicals (such as benzene), prior chemotherapy, and Down syndrome. People with a family history of leukemia are also at higher risk. There are four main types of leukemia—acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), acute myeloid leukemia (AML), chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and chronic myelo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Upper Quadrant
The human abdomen is divided into quadrants and regions by anatomists and physicians for the purposes of study, diagnosis, and treatment. The division into four quadrants allows the localisation of pain and tenderness, scars, lumps, and other items of interest, narrowing in on which organs and tissues may be involved. The quadrants are referred to as the left lower quadrant, left upper quadrant, right upper quadrant and right lower quadrant. These terms are not used in comparative anatomy, since most other animals do not stand erect. The left lower quadrant includes the left iliac fossa and half of the flank. The equivalent in other animals is ''left posterior quadrant''. The left upper quadrant extends from the umbilical plane to the left ribcage. This is the ''left anterior quadrant'' in other animals. The right upper quadrant extends from umbilical plane to the right ribcage. The equivalent in other animals is ''right anterior quadrant''. The right lower quadrant extends f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypertrophy
Hypertrophy is the increase in the volume of an organ or tissue due to the enlargement of its component cells. It is distinguished from hyperplasia, in which the cells remain approximately the same size but increase in number. Although hypertrophy and hyperplasia are two distinct processes, they frequently occur together, such as in the case of the hormonally induced proliferation and enlargement of the cells of the uterus during pregnancy. Eccentric hypertrophy is a type of hypertrophy where the walls and chamber of a hollow organ undergo growth in which the overall size and volume are enlarged. It is applied especially to the left ventricle of heart. Sarcomeres are added in series, as for example in dilated cardiomyopathy (in contrast to hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a type of concentric hypertrophy, where sarcomeres are added in parallel). Gallery Gould Pyle 234.jpg, Breasts Hypertrophied clitoris.jpg, Clitoris Head of a boy with hypertrophy of the ear Wellcome L0062496.j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation#Coagulation factors, coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a thrombus, blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or Lung, lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact agranulocyte, mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion (medicine), adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic
Lymph () is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillary, lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood. Because it is derived from interstitial fluid, with which blood and surrounding cells continually exchange substances, lymph undergoes continual change in composition. It is generally similar to blood plasma, which is the fluid component of blood. Lymph returns proteins and exce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a Multicellular organism, multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. The two main cells that do this are the Macrophages and the Neutrophils of the immune system. Where phagocytosis is used as a means of feeding and provides the organism part or all of its nourishment, it is called phagotrophy and is distinguished from osmotrophy, which is nutrition taking place by absorption. History The history of phag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutrophil
Neutrophils are a type of phagocytic white blood cell and part of innate immunity. More specifically, they form the most abundant type of granulocytes and make up 40% to 70% of all white blood cells in humans. Their functions vary in different animals. They are also known as neutrocytes, heterophils or polymorphonuclear leukocytes. They are formed from stem cells in the bone marrow and differentiated into subpopulations of neutrophil-killers and neutrophil-cagers. They are short-lived (between 5 and 135 hours, see ) and highly mobile, as they can enter parts of tissue where other cells/molecules cannot. Neutrophils may be subdivided into segmented neutrophils and banded neutrophils (or bands). They form part of the polymorphonuclear cells family (PMNs) together with basophils and eosinophils. The name ''neutrophil'' derives from staining characteristics on hematoxylin and eosin ( H&E) histological or cytological preparations. Whereas basophilic white blood cells ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutropenia
Neutropenia is an abnormally low concentration of neutrophils (a type of white blood cell) in the blood. Neutrophils make up the majority of circulating white blood cells and serve as the primary defense against infections by destroying bacteria, bacterial fragments and immunoglobulin-bound viruses in the blood. People with neutropenia are more susceptible to bacterial infections and, without prompt medical attention, the condition may become life-threatening (neutropenic sepsis). Neutropenia can be divided into congenital and acquired, with severe congenital neutropenia (SCN) and cyclic neutropenia (CyN) being autosomal dominant and mostly caused by heterozygous mutations in the ELANE gene ( neutrophil elastase). Neutropenia can be acute (temporary) or chronic (long lasting). The term is sometimes used interchangeably with "leukopenia" ("deficit in the number of white blood cells"). Decreased production of neutrophils is associated with deficiencies of vitamin B12 and fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosis
Ankylosis () is a stiffness of a joint due to abnormal adhesion and rigidity of the bones of the joint, which may be the result of injury or disease. The rigidity may be complete or partial and may be due to inflammation of the Tendon, tendinous or muscular structures outside the joint or of the tissues of the joint itself. When the structures outside the joint are affected, the term "false ankylosis" has been used in contradistinction to "true ankylosis", in which the disease is within the joint. When inflammation has caused the joint-ends of the bones to be fused together, the ankylosis is termed ''osseous'' or complete and is an instance of synostosis. Excision of a completely ankylotic shoulder or elbow may restore free mobility and usefulness to the limb. "Ankylosis" is also used as an anatomical term, bones being said to ankylose (or anchylose) when, from being originally distinct, they coalesce, or become so joined that no motion can take place between them. Causes *A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |