|
Felicific Calculus
The felicific calculus is an algorithm formulated by utilitarianism, utilitarian philosopher Jeremy Bentham (1748–1832) for calculating the degree or amount of pleasure that a specific action is likely to induce. Bentham, an ethics, ethical hedonist, believed the moral rightness or wrongness of an action to be a function of the amount of pleasure or pain that it produced. The felicific calculus could in principle, at least, determine the moral status of any considered act. The algorithm is also known as the utility calculus, the hedonistic calculus and the hedonic calculus. To be included in this calculation are several Variable (math), variables (or vector space, vectors), which Bentham called "circumstances". These are: # Intensity: How strong is the pleasure? # Time, Duration: How long will the pleasure last? # Certainty or uncertainty: How likely or unlikely is it that the pleasure will occur? # Propinquity or remoteness: How soon will the pleasure occur? # Fecundity: The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of Rigour#Mathematics, mathematically rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific Computational problem, problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can use Conditional (computer programming), conditionals to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making) and deduce valid inferences (referred to as automated reasoning). In contrast, a Heuristic (computer science), heuristic is an approach to solving problems without well-defined correct or optimal results.David A. Grossman, Ophir Frieder, ''Information Retrieval: Algorithms and Heuristics'', 2nd edition, 2004, For example, although social media recommender systems are commonly called "algorithms", they actually rely on heuristics as there is no truly "correct" recommendation. As an e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doggerel
Doggerel, or doggrel, is poetry that is irregular in rhythm and in rhyme, often deliberately for burlesque or comic effect. Alternatively, it can mean verse which has a monotonous rhythm, easy rhyme, and cheap or trivial meaning. The word is derived from the Middle English ''dogerel'', probably a derivative of ''dog''. In English, it has been used as an adjective since the 14th century and a noun since at least 1630. Appearing since ancient times in the literatures of many cultures, doggerel is characteristic of nursery rhymes and children's song. Examples The Scottish poet William McGonagall (1825–1902) has become famous for his doggerel, which many remember with affection despite its seeming technical flaws, as in his poem " The Tay Bridge Disaster": Hip hop lyrics have also explored the artful possibilities of doggerel. . Chaucer's Tale of Sir Thopas is written in this format. It irritates the Host of The Tabard so much that he interrupts him and makes him tell a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utilitarian Social Choice Rule
In social choice and operations research, the utilitarian rule (also called the max-sum rule) is a rule saying that, among all possible alternatives, society should pick the alternative which maximizes the ''sum of the utilities'' of all individuals in society. It is a formal mathematical representation of the utilitarian philosophy, and is often justified by reference to Harsanyi's utilitarian theorem or the Von Neumann–Morgenstern theorem. Definition Let X be a set of possible "states of the world" or "alternatives". Society wishes to choose a single state from X. For example, in a single-winner election, X may represent the set of candidates; in a resource allocation setting, X may represent all possible allocations of the resource. Let I be a finite set, representing a collection of individuals. For each i \in I, let u_i:X\longrightarrow\mathbb be a ''utility function'', describing the amount of happiness an individual ''i'' derives from each possible state. A '' so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Of Morality
Science of morality (also known as science of ethics or scientific ethics) may refer to various forms of ethical naturalism grounding morality and ethics in rational, empirical consideration of the natural world. It is sometimes framed as using the scientific approach to determine what is right and wrong, in contrast to the widespread belief that "science has nothing to say on the subject of human values". Overview Moral science may refer to the consideration of what is best for, and how to maximize the flourishing of, either particular individuals or all conscious creatures. It has been proposed that "morality" can be appropriately defined on the basis of fundamental premises necessary for ''any'' empirical, secular, or philosophical discussion and that societies can use the methods of science to provide answers to moral questions. The norms advocated by moral scientists (e.g. rights to abortion, euthanasia, and drug liberalization under certain circumstances) would be founde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning (RL) is an interdisciplinary area of machine learning and optimal control concerned with how an intelligent agent should take actions in a dynamic environment in order to maximize a reward signal. Reinforcement learning is one of the three basic machine learning paradigms, alongside supervised learning and unsupervised learning. Reinforcement learning differs from supervised learning in not needing labelled input-output pairs to be presented, and in not needing sub-optimal actions to be explicitly corrected. Instead, the focus is on finding a balance between exploration (of uncharted territory) and exploitation (of current knowledge) with the goal of maximizing the cumulative reward (the feedback of which might be incomplete or delayed). The search for this balance is known as the exploration–exploitation dilemma. The environment is typically stated in the form of a Markov decision process (MDP), as many reinforcement learning algorithms use dyn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethical Calculus
An ethical calculus is the application of mathematics to calculate issues in ethics. Scope Generally, ethical calculus refers to any method of determining a course of action in a circumstance that is not explicitly evaluated in one's ethical code. A formal philosophy of ethical calculus is a development in the study of ethics, combining elements of natural selection, self-organizing systems, emergence, and algorithm theory. According to ethical calculus, the most ethical course of action in a situation is an absolute, but rather than being based on a static ethical code, the ethical code itself is a function of circumstances. The optimal ethic is the best possible course of action taken by an individual with the given limitations. While ethical calculus is, in some ways, similar to moral relativism, the former finds its grounds in the circumstance while the latter depends on social and cultural context for moral judgment. Ethical calculus would most accurately be regarded as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicurus
Epicurus (, ; ; 341–270 BC) was an Greek philosophy, ancient Greek philosopher who founded Epicureanism, a highly influential school of philosophy that asserted that philosophy's purpose is to attain as well as to help others attain tranquil lives, characterized by freedom from fear and the absence of pain. Epicurus advocated that people were best able to pursue philosophy by living a self-sufficient life surrounded by friends; he and his followers were known for eating simple meals and discussing a wide range of philosophical subjects at "the Garden", the school he established in Athens. Epicurus taught that although the gods exist, they have no involvement in human affairs. Like the earlier philosopher Democritus, Epicurus claimed that all occurrences in the natural world are ultimately the result of tiny, invisible particles known as ''Atomism, atoms'' moving and interacting in empty space, though Epicurus also deviated from Democritus by proposing the idea of Clinamen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
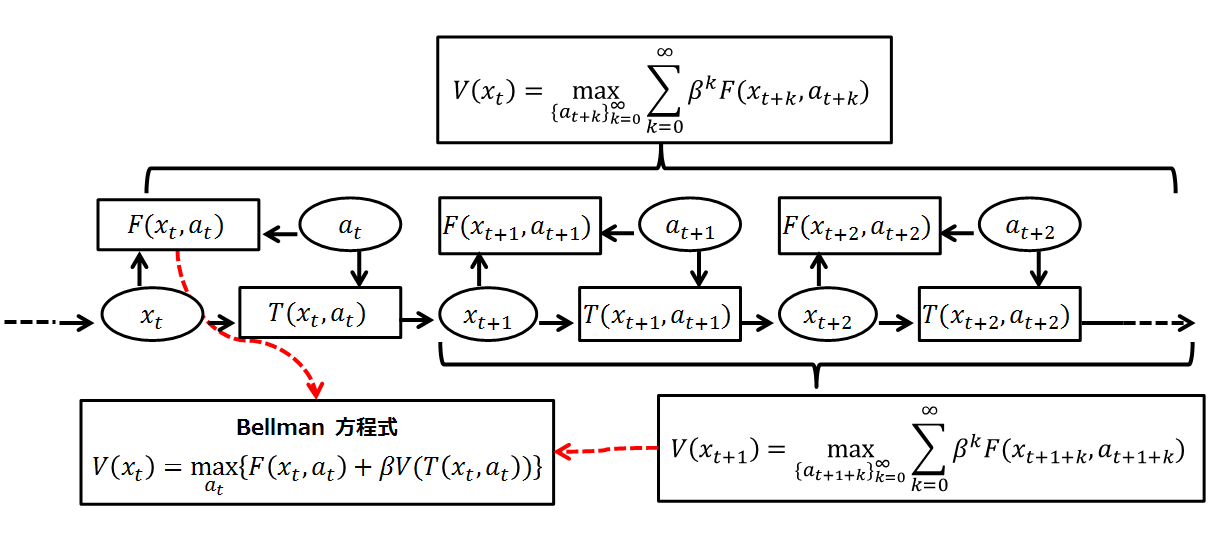
Bellman Equation
A Bellman equation, named after Richard E. Bellman, is a necessary condition for optimality associated with the mathematical Optimization (mathematics), optimization method known as dynamic programming. It writes the "value" of a decision problem at a certain point in time in terms of the payoff from some initial choices and the "value" of the remaining decision problem that results from those initial choices. This breaks a dynamic optimization problem into a sequence of simpler subproblems, as Bellman's “principle of optimality" prescribes. The equation applies to algebraic structures with a total ordering; for algebraic structures with a partial ordering, the generic Bellman's equation can be used. The Bellman equation was first applied to engineering control theory and to other topics in applied mathematics, and subsequently became an important tool in economic theory; though the basic concepts of dynamic programming are prefigured in John von Neumann and Oskar Morgenstern's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Act Utilitarianism
Act utilitarianism is a utilitarian theory of ethics that states that a person's act is morally right if and only if it produces the best possible results in that specific situation. Classical utilitarians, including Jeremy Bentham, John Stuart Mill, and Henry Sidgwick, define happiness as pleasure and the absence of pain. Overview To understand how act utilitarianism works, compare the consequences of watching television all day tomorrow to the consequences of doing charity work tomorrow. One could produce more overall happiness in the world by doing charity work tomorrow than by watching television all day tomorrow. According to act utilitarianism, then, the right thing to do tomorrow is to go out and do charity work; it is wrong to stay home and watch television all day. Act utilitarianism is based on the principle of utility, which is the basis of all utilitarian theories and is best summed up in Bentham's well-known phrase, "the greatest happiness for the greatest number". J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence M
Lawrence may refer to: Education Colleges and universities * Lawrence Technological University, a university in Southfield, Michigan, United States * Lawrence University, a liberal arts university in Appleton, Wisconsin, United States Preparatory & high schools * Lawrence Academy at Groton, a preparatory school in Groton, Massachusetts, United States * Lawrence College, Ghora Gali, a high school in Pakistan * Lawrence School, Lovedale, a high school in India * The Lawrence School, Sanawar, a high school in India Research laboratories * Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, United States * Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory, United States People * Lawrence (given name), including a list of people with the name * Lawrence (surname), including a list of people with the name * Lawrence (band), an American soul-pop group * Lawrence (judge royal) (died after 1180), Hungarian nobleman, Judge royal 1164–1172 * Lawrence (musician), Lawrence Hayward (born 1961), British mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Units Of Measurements
A unit of measurement, or unit of measure, is a definite magnitude of a quantity, defined and adopted by convention or by law, that is used as a standard for measurement of the same kind of quantity. Any other quantity of that kind can be expressed as a multiple of the unit of measurement. For example, a length is a physical quantity. The metre (symbol m) is a unit of length that represents a definite predetermined length. For instance, when referencing "10 metres" (or 10 m), what is actually meant is 10 times the definite predetermined length called "metre". The definition, agreement, and practical use of units of measurement have played a crucial role in human endeavour from early ages up to the present. A multitude of systems of units used to be very common. Now there is a global standard, the International System of Units (SI), the modern form of the metric system. In trade, weights and measures are often a subject of governmental regulation, to ensure fair ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utilitarianism
In ethical philosophy, utilitarianism is a family of normative ethical theories that prescribe actions that maximize happiness and well-being for the affected individuals. In other words, utilitarian ideas encourage actions that lead to the greatest good for the greatest number. Although different varieties of utilitarianism admit different characterizations, the basic idea that underpins them all is, in some sense, to maximize utility, which is often defined in terms of well-being or related concepts. For instance, Jeremy Bentham, the founder of utilitarianism, described ''utility'' as the capacity of actions or objects to produce benefits, such as pleasure, happiness, and good, or to prevent harm, such as pain and unhappiness, to those affected. Utilitarianism is a version of consequentialism, which states that the consequences of any action are the only standard of right and wrong. Unlike other forms of consequentialism, such as egoism and altruism, egalitarian util ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |