|
Federal Reserve Bank
A Federal Reserve Bank is a regional bank of the Federal Reserve System, the central banking system of the United States. There are twelve in total, one for each of the twelve Federal Reserve Districts that were created by the Federal Reserve Act of 1913. The banks are jointly responsible for implementing the monetary policy set forth by the Federal Open Market Committee, and are divided as follows: Some banks also possess List of Federal Reserve branches, branches, with the whole system being headquartered at the Eccles Building in Washington, D.C. History The Federal Reserve Banks are the most recent institutions that the United States government has created to provide functions of a central bank. Prior institutions have included the First Bank of the United States, First (1791–1811) and Second Bank of the United States, Second (1818–1824) Banks of the United States, the Independent Treasury (1846–1920) and the National Bank Act, National Banking System (1863–19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve Bank Of Chicago
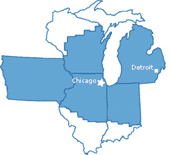
The Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago (informally the Chicago Fed) is one of twelve Federal Reserve Banks that, along with the Federal Reserve Board of Governors, make up the Federal Reserve System, the United States' central bank. The Chicago Fed serves the Seventh District, which encompasses the northern portions of Illinois and Indiana, southern Wisconsin, the Lower Peninsula of Michigan, and the state of Iowa. In addition to participation in the formulation of monetary policy of the United States, monetary policy, each Reserve Bank supervises member banks and Bank holding company, bank holding companies, provides financial services to depository institutions and the U.S. government, and monitors economic conditions in its District. The Chicago Fed was established on May 18, 1914, when representatives from five Seventh District banks formally signed the Chicago Fed's organization certificate. The Bank officially opened for business on Monday, November 16, 1914. Responsibilities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve Bank Of New York
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York is one of the 12 Federal Reserve Banks of the United States. It is responsible for the Second District of the Federal Reserve System, which encompasses the New York (state), State of New York, the 12 northern counties of New Jersey, Fairfield County, Connecticut, Fairfield County in Connecticut, Puerto Rico, and the U.S. Virgin Islands. Located at Federal Reserve Bank of New York Building, 33 Liberty Street in Lower Manhattan, it is the largest (by assets), the most active (by volume), and the most influential of the Reserve Banks. The Federal Reserve Bank of New York is uniquely responsible for implementing monetary policy on behalf of the Federal Open Market Committee and acts as the market agent of the entire Federal Reserve System (as it houses the Open Market Trading Desk and manages System Open Market Account). It is also the sole fiscal agent of the U.S. Department of the Treasury, the bearer of the Treasury's General Account, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve Districts Map - Banks & Branches
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to: Politics General *Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies *Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or regional governments that are partially self-governing; a union of states *Federal republic, a federation which is a republic *Federalism, a political philosophy *Federalist, a political belief or member of a political grouping *Federalization, implementation of federalism Particular governments *Government of Argentina *Government of Australia *Federal government of Brazil *Government of Canada *Cabinet of Germany *Federal government of Iraq *Government of India *Federal government of Mexico *Federal government of Nigeria *Government of Pakistan *Government of the Philippines *Government of Russia *Government of South Africa *Federal government of the United States **United States federal law **United States federal courts *Federal gover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Federal Reserve Branches
There are 24 Federal Reserve branches. There were 25 branches but in October 2008 the Federal Reserve Bank of New York Buffalo Branch was closed. List of Federal Reserve branches * Boston * New York ** '' Federal Reserve Bank of New York Buffalo Branch (closed 2008)'' * Philadelphia * Cleveland ** Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland Cincinnati Branch ** Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland Pittsburgh Branch * Richmond ** Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Baltimore Branch ** Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Charlotte Branch * Atlanta ** Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Birmingham Branch ** Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Jacksonville Branch ** Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Miami Branch ** Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta Nashville Branch ** Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta New Orleans Branch * Chicago ** Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago Detroit Branch * St. Louis ** Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Little Rock Branch ** Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Louisville Branch ** Fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Court Of Appeals For The Ninth Circuit
The United States Court of Appeals for the Ninth Circuit (in case citations, 9th Cir.) is the U.S. federal court of appeals that has appellate jurisdiction over the U.S. district courts for the following federal judicial districts: * District of Alaska * District of Arizona * Central District of California * Eastern District of California * Northern District of California * Southern District of California * District of Hawaii * District of Idaho * District of Montana * District of Nevada * District of Oregon * Eastern District of Washington * Western District of Washington The Ninth Circuit also has appellate jurisdiction over the territorial courts for the District of Guam and the District of the Northern Mariana Islands. Additionally, it sometimes handles appeals that originate from American Samoa, which has no district court and partially relies on the District of Hawaii for its federal cases. Headquartered in San Francisco, California, the Ninth Circuit is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve Board Of Governors
The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, commonly known as the Federal Reserve Board, is the main governing body of the Federal Reserve System. It is charged with overseeing the Federal Reserve Banks and with helping implement the monetary policy of the United States. Governors are appointed by the president of the United States and confirmed by the Senate for staggered 14-year terms.See It is headquartered in the Eccles Building on Constitution Avenue, N.W. in Washington, D.C. Statutory description By law, the appointments must yield a "fair representation of the financial, agricultural, industrial, and commercial interests and geographical divisions of the country". As stipulated in the Banking Act of 1935, the chair and vice chair of the Board are two of seven members of the Board of Governors who are appointed by the president from among the sitting governors of the Federal Reserve Banks. The terms of the seven members of the Board span multiple presidential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corporation
A corporation or body corporate is an individual or a group of people, such as an association or company, that has been authorized by the State (polity), state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law as "born out of statute"; a legal person in a legal context) and recognized as such in Corporate law, law for certain purposes. Early incorporated entities were established by charter (i.e., by an ''ad hoc'' act granted by a monarch or passed by a parliament or legislature). Most jurisdictions now allow the creation of new corporations through List of company registers, registration. Corporations come in many different types but are usually divided by the law of the jurisdiction where they are chartered based on two aspects: whether they can issue share capital, stock, or whether they are formed to make a profit (accounting), profit. Depending on the number of owners, a corporation can be classified as ''aggregate'' (the subject of this articl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Monetary Commission
The National Monetary Commission was a U.S. congressional commission created by the Aldrich–Vreeland Act of 1908. After the Panic of 1907, the Commission studied the banking laws of the United States, and the leading countries of Europe. The chairman of the commission, Senator Nelson Aldrich, a Republican leader in the Senate, personally led a team of experts to major European capitals. They were stunned to discover how much more efficient the European financial system appeared to be and how much more important than the dollar were the pound, the franc and the mark in international trade. The commission's reports and recommendations became one of the principal bases in the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act of 1913 which created the modern Federal Reserve system. Background Following the panics of the late 1890s and early 1900s, the American people were aroused to the need for basic reforms. One of the most painful aspects of the economic crisis before World War I was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic Of 1907
The Panic of 1907, also known as the 1907 Bankers' Panic or Knickerbocker Crisis, was a financial crisis that took place in the United States over a three-week period starting in mid-October, when the New York Stock Exchange suddenly fell almost 50% from its peak the previous year. The panic occurred during a time of economic recession, and there were numerous bank run, runs affecting banks and trust company, trust companies. The 1907 panic eventually spread throughout the nation when many state and local banks and businesses entered bankruptcy. The primary causes of the run included a retraction of market liquidity by a number of New York City banks and a loss of confidence among depositors, exacerbated by unregulated side bets at bucket shop (stock market), bucket shops. The panic was triggered by the failed attempt in October 1907 to cornering the market, corner the market on stock of the United Copper, United Copper Company. When the bid failed, banks that had lent money to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Bank Act
The National Banking Acts of 1863 and 1864 were two United States federal banking acts that established a system of national banks chartered at the federal level, and created the United States National Banking System. They encouraged development of a national currency backed by bank holdings of U.S. Treasury securities and established the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency as part of the United States Department of the Treasury. The Act shaped today's national banking system and its support of a uniform U.S. banking policy. Background Antebellum Period At the end of the Second Bank of the United States in 1836, the control of banking regimes devolved mostly to the states. Different states adopted policies including a total ban on banking (as in Wisconsin), a single state-chartered bank (as in Indiana and Illinois), limited chartering of banks (as in Ohio), and free entry (as in New York). While the relative success of New York's "free banking" laws led several states also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Independent Treasury
The Independent Treasury was the system for managing the money supply of the United States federal government through the U.S. Treasury and its sub-treasuries, independently of the national banking and financial systems. It was created on August 6, 1846, by the 29th Congress, with the enactment of the Independent Treasury Act of 1846 (ch. 90, ). It was expanded with the creation of the national banking system in 1863. It functioned until the early 20th century, when the Federal Reserve System replaced it. During this time, the Treasury took over an ever-larger number of functions of a central bank and the U.S. Treasury Department came to be the major force in the U.S. money market. Background The Panic of 1819 unleashed a wave of popular resentment against the Second Bank of the United States (the "national bank"), which, under profitable private ownership, handled various fiscal duties for the U.S. government after its establishment in 1816; in particular, like the first Bank ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Bank Of The United States
The Second Bank of the United States was the second federally authorized Second Report on Public Credit, Hamiltonian national bank in the United States. Located in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, the bank was chartered from February 1816 to January 1836.. The bank's formal name, according to section 9 of its charter as passed by Congress, was "The President, Directors, and Company, of the Bank of the United States". While other banks in the US were chartered by and only allowed to have branches in a single state, it was authorized to have branches in multiple states and lend money to the US government. A private corporation with Public–private partnership, public duties, the bank handled all fiscal transactions for the U.S. government, and was accountable to United States Congress, Congress and the U.S. Treasury. Twenty percent of its capital was owned by the federal government, the bank's single largest stockholder.. Four thousand private investors held 80 percent of the bank's ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |