|
Farsightedness
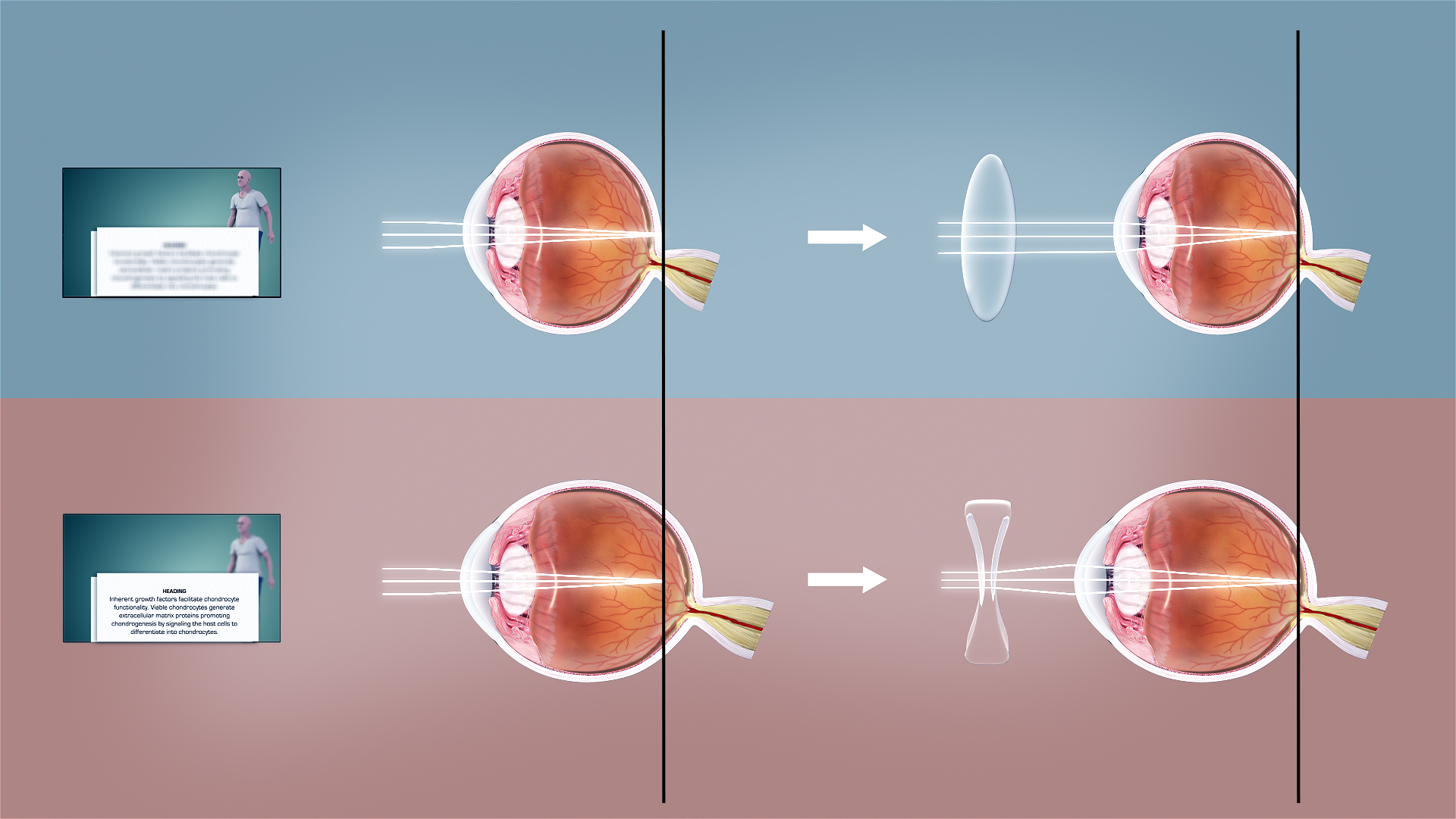
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, and hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blur is due to incoming light being focused behind, instead of on, the retina due to insufficient accommodation by the lens. Minor hypermetropia in young patients is usually corrected by their accommodation, without any defects in vision. But, due to this accommodative effort for distant vision, people may complain of eye strain during prolonged reading. If the hypermetropia is high, there will be defective vision for both distance and near. People may also experience accommodative dysfunction, binocular dysfunction, amblyopia, and strabismus. Newborns are almost invariably hypermetropic, but it gradually decreases as the newborn gets older. There are many causes for this condition. It may occur when the axial length of eyeball is too short or if the lens or cornea is flatter than normal. Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbyopia
Presbyopia is a physiological insufficiency of optical Accommodation (vertebrate eye), accommodation associated with the aging of the human eye, eye; it results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as age-related farsightedness (or as age-related long sight in the UK), it affects many adults over the age of 40. A common sign of presbyopia is difficulty in reading small print, which results in having to hold reading material farther away. Other symptoms associated can be headaches and eyestrain. Different people experience different degrees of problems. Other types of refractive errors may exist at the same time as presbyopia. This condition is similar to hypermetropia or far-sightedness, which starts in childhood and exhibits similar symptoms of blur in the vision for close objects. Presbyopia is a typical part of the aging process. It occurs due to age-related changes in the Lens (anatomy), lens (decreased elasticity and increased h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Error
Refractive error is a problem with focus (optics), focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and/or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are myopia, near-sightedness, hyperopia, far-sightedness, astigmatism, and presbyopia. Near-sightedness results in far away objects being blurred vision, blurry, far-sightedness and presbyopia result in close objects being blurry, and astigmatism causes objects to appear stretched out or blurry. Other symptoms may include double vision, headaches, and eye strain. Near-sightedness is due to the length of the eyeball being too long; far-sightedness the eyeball too short; astigmatism the cornea being the wrong shape, while presbyopia results from aging of the lens of the eye such that it cannot change shape sufficiently. Some refractive errors occur more often among those whose parents are affected. Diagnosis is by eye examination. Refractive errors are corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or surgery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabismus
Strabismus is an eye disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is pointed at an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a large part of childhood, it may result in amblyopia, or lazy eyes, and loss of depth perception. If onset is during adulthood, it is more likely to result in diplopia, double vision. Strabismus can occur out of muscle dysfunction (e.g., myasthenia gravis), farsightedness, problems in the brain, trauma, or infections. Risk factors include premature birth, cerebral palsy, and a family history of the condition. Types include esotropia, where the eyes are crossed ("cross eyed"); exotropia, where the eyes diverge ("lazy eyed" or "wall eyed"); and hypertropia or hypotropia, where they are vertically misaligned. They can also be classified by whether the problem is present in all directions a person looks (comitant) or varies by direction (inco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-sightedness
Myopia, also known as near-sightedness and short-sightedness, is an eye condition where light from distant objects focuses in front of, instead of on, the retina. As a result, distant objects appear blurred vision, blurry, while close objects appear normal. Other symptoms may include headaches and eye strain. Severe myopia is associated with an increased risk of macular degeneration, retinal detachment, cataracts, and glaucoma. Myopia results from the length of the eyeball growing too long or less commonly the Lens (anatomy), lens being too strong. It is a type of refractive error. Diagnosis is by the use of Cycloplegic refraction, cycloplegics during eye examination. Tentative evidence indicates that the risk of myopia can be decreased by having young children spend more time outside. This decrease in risk may be related to Daylighting (architecture), natural light exposure. Myopia can be corrected with eyeglasses, contact lenses, or by refractive surgery. Eyeglasses are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aphakia
Aphakia is the absence of the lens of the eye, due to surgical removal, such as in cataract surgery, a perforating wound or ulcer, or congenital anomaly. It causes a loss of ability to maintain focus ( accommodation), high degree of farsightedness ( hyperopia), and a deep anterior chamber. Complications include detachment of the vitreous or retina, and glaucoma. Babies are rarely born with aphakia. Occurrence most often results from surgery to remove a congenital cataract. Congenital cataracts usually develop as a result of infection of the fetus or genetic reasons. It is often difficult to identify the exact cause of these cataracts, especially if only one eye is affected. People with aphakia have relatively small pupils and their pupils dilate to a lesser degree. Causes Surgical removal of a lens, mainly in cataract surgery, is the most common cause of aphakia. Spontaneous traumatic absorption or congenital absence of lens matter is rare. Traumatic subluxation or disloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eyeglasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses (American English), spectacles (Commonwealth English), or colloquially as specs, are Visual perception, vision eyewear with clear or tinted lens (optics), lenses mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's Human eyes, eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms, known as temples or temple pieces, that rest over the ears for support. Glasses are typically used for Corrective lens, vision correction, such as with reading glasses and glasses used for nearsightedness; however, without the specialized lenses, they are sometimes used for cosmetic purposes. Safety glasses are eye protection, a form of personal protective equipment (Personal protective equipment, PPE) that are worn by workers around their eyes for protection. Safety glasses act as a shield to protect the eyes from any type of foreign debris that may cause irritation or injury; these glasses may have protection on the sides of the eyes as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraocular Lens
An intraocular lens (IOL) is a lens (optics), lens implanted in the human eye, eye usually as part of a treatment for cataracts or for correcting other vision problems such as myopia, near-sightedness (myopia) and farsightedness, far-sightedness (hyperopia); a form of refractive surgery. If the natural lens is left in the eye, the IOL is known as Phakic intraocular lens, ''phakic'', otherwise it is a ''pseudophakic'' lens (or false lens). Both kinds of IOLs are designed to provide the same light-focusing function as the natural crystalline lens. This can be an alternative to LASIK, but LASIK is not an alternative to an IOL for treatment of cataracts. IOLs usually consist of a small plastic lens with plastic side struts, called haptics, to hold the lens in place in the capsular bag inside the eye. IOLs were originally made of a rigid material (Poly(methyl methacrylate), PMMA), although this has largely been superseded by the use of flexible materials, such as silicone. Most IOLs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Surgery
Refractive surgery is an optional eye surgery used to improve the refractive state of the eye and decrease or eliminate dependency on glasses or contact lenses. This can include various methods of surgical remodeling of the cornea ( keratomileusis), lens implantation or lens replacement. The most common methods today use excimer lasers to reshape the curvature of the cornea. Refractive eye surgeries are used to treat common vision disorders such as myopia, hyperopia, presbyopia and astigmatism. History The first theoretical work on the potential of refractive surgery was published in 1885 by Hjalmar August Schiøtz, an ophthalmologist from Norway. In 1930, the Japanese ophthalmologist Tsutomu Sato made the first attempts at performing this kind of surgery, hoping to correct the vision of military pilots. His approach was to make radial cuts in the cornea, correcting effects by up to 6 diopters. The procedure unfortunately produced a high rate of corneal degeneration, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amblyopia
Amblyopia, also called lazy eye, is a disorder of sight in which the brain fails to fully process input from one eye and over time favors the other eye. It results in decreased vision in an eye that typically appears normal in other aspects. Amblyopia is the most common cause of decreased vision in a single eye among children and younger adults. The cause of amblyopia can be any condition that interferes with focusing during early childhood. This can occur from poor alignment of the eyes (strabismic), an eye being irregularly shaped such that focusing is difficult, one eye being more nearsighted or farsighted than the other (refractive), or clouding of the lens of an eye (deprivational). After the underlying cause is addressed, vision is not restored right away, as the mechanism also involves the brain. Amblyopia can be difficult to detect, so vision testing is recommended for all children around the ages of four to five as early detection improves treatment success. Glas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eye Exam
An eye examination, commonly known as an eye test, is a series of tests performed to assess Visual acuity, vision and ability to Focus (optics), focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations of the human eye, eyes. Eye examinations are primarily performed by an optometrist, ophthalmologist, or an orthoptist. Health care professionals often recommend that all people should have periodic and thorough eye examinations as part of routine primary care, especially since many eye diseases are asymptomatic. Typically, a healthy individual who otherwise has no concerns with their eyes receives an eye exam once in their 20s and twice in their 30s. Eye examinations may detect potentially treatable blindness, blinding eye diseases, ocular manifestation of systemic disease, ocular manifestations of systemic disease, or signs of tumour, tumors or other anomalies of the Human brain, brain. A full eye examination consists of a comprehensive evaluation of medical h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |