|
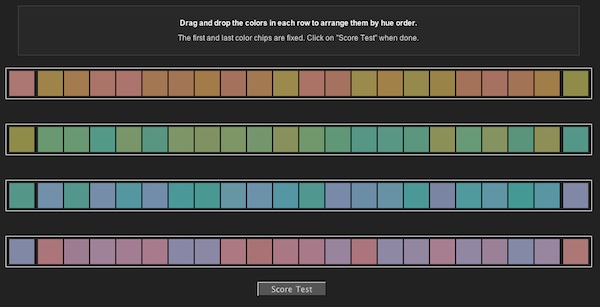
Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Test
The Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision test is a color vision test often used to test for color blindness. The system was developed by Dean Farnsworth in the 1940s and it tests the ability to isolate and arrange minute differences in various color targets with constant lightness, value and colorfulness, chroma that cover all the visual hues described by the Munsell color system. There are several variations of the test, one featuring 100 color hues and one featuring 15 color hues. Originally taken in an analog environment with physical hue tiles, the test is now taken from computer consoles. An accurate quantification of color vision accuracy is particularly important to designers, photographers and colorists, who all rely on accurate color vision to produce quality content. Vision tests 100 hue test The most common form of the Farnsworth–Munsell 100 Hue Color Vision Test contains four distinct rows of similar color hues, each containing 25 distinct variations of each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Blindness
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to color vision, see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a Sex linkage, sex-linked Heredity, inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical dam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protanomaly
Color blindness, color vision deficiency (CVD) or color deficiency is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. The severity of color blindness ranges from mostly unnoticeable to full absence of color perception. Color blindness is usually a sex-linked inherited problem or variation in the functionality of one or more of the three classes of cone cells in the retina, which mediate color vision. The most common form is caused by a genetic condition called congenital red–green color blindness (including protan and deutan types), which affects ''up to'' 1 in 12 males (8%) and 1 in 200 females (0.5%). The condition is more prevalent in males, because the opsin genes responsible are located on the X chromosome. Rarer genetic conditions causing color blindness include congenital blue–yellow color blindness (tritan type), blue cone monochromacy, and achromatopsia. Color blindness can also result from physical or chemical damage to the eye, the optic nerve, pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luminosity Function
A luminous efficiency function or luminosity function represents the average spectral sensitivity of human visual perception of light. It is based on subjective judgements of which of a pair of different-colored lights is brighter, to describe relative sensitivity to light of different wavelengths. It is not an absolute reference to any particular individual, but is a standard observer representation of visual sensitivity of a theoretical human eye. It is valuable as a baseline for experimental purposes, and in colorimetry. Different luminous efficiency functions apply under different lighting conditions, varying from photopic in brightly lit conditions through mesopic to scotopic under low lighting conditions. When not specified, ''the luminous efficiency function'' generally refers to the photopic luminous efficiency function. The CIE photopic luminous efficiency function or is a standard function established by the Commission Internationale de l'Éclairage (CIE) and st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Model
In color science, a color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components. When this model is associated with a precise description of how the components are to be interpreted (viewing conditions, etc.), taking account of visual perception, the resulting set of colors is called "color space." This article describes ways in which human color vision can be modeled, and discusses some of the models in common use. Tristimulus color space One can picture this space as a region in three-dimensional Euclidean space if one identifies the ''x'', ''y'', and ''z'' axes with the stimuli for the long-wavelength (''L''), medium-wavelength (''M''), and short-wavelength (''S'') Cone cell, light receptors. This is called the LMS color space. The origin, (''S'',''M'',''L'') = (0,0,0), corresponds to black. White has no definite position in this diagram; rather it is defined accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiant Intensity
In radiometry, radiant intensity is the radiant flux emitted, reflected, transmitted or received, per unit solid angle, and spectral intensity is the radiant intensity per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. These are ''directional'' quantities. The SI unit of radiant intensity is the watt per steradian (), while that of spectral intensity in frequency is the watt per steradian per hertz () and that of spectral intensity in wavelength is the watt per steradian per metre ()—commonly the watt per steradian per nanometre (). Radiant intensity is distinct from irradiance and radiant exitance, which are often called ''intensity'' in branches of physics other than radiometry. In radio-frequency engineering, radiant intensity is sometimes called radiation intensity. Mathematical definitions Radiant intensity Radiant intensity, denoted ''I''e,Ω ("e" for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wavelength
In physics and mathematics, wavelength or spatial period of a wave or periodic function is the distance over which the wave's shape repeats. In other words, it is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same ''phase (waves), phase'' on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, troughs, or zero crossings. Wavelength is a characteristic of both traveling waves and standing waves, as well as other spatial wave patterns. The multiplicative inverse, inverse of the wavelength is called the ''spatial frequency''. Wavelength is commonly designated by the Greek letter lambda (''λ''). For a modulated wave, ''wavelength'' may refer to the carrier wavelength of the signal. The term ''wavelength'' may also apply to the repeating envelope (mathematics), envelope of modulated waves or waves formed by Interference (wave propagation), interference of several sinusoids. Assuming a sinusoidal wave moving at a fixed phase velocity, wave speed, wavelength is inversely proportion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angle Of Incidence (optics)
The angle of incidence, in geometric optics, is the angle between a ray incident on a surface and the line perpendicular (at 90 degree angle) to the surface at the point of incidence, called the normal. The ray can be formed by any waves, such as optical, acoustic, microwave, and X-ray. In the figure below, the line representing a ray makes an angle θ with the normal (dotted line). The angle of incidence at which light is first totally internally reflected is known as the critical angle. The angle of reflection and angle of refraction are other angles related to beams. In computer graphics and geography, the angle of incidence is also known as the illumination angle of a surface with a light source, such as the Earth's surface and the Sun. It can also be equivalently described as the angle between the tangent plane of the surface and another plane at right angles to the light rays. This means that the illumination angle of a certain point on Earth's surface is 0° if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
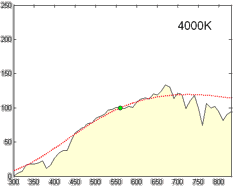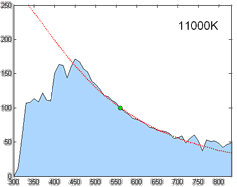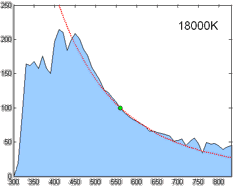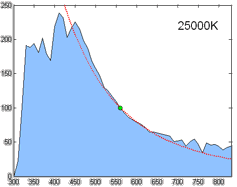
Spectral Power Distribution
In radiometry, photometry (optics), photometry, and color science, a spectral power distribution (SPD) measurement describes the Power (physics), power per unit area per unit wavelength of an illumination (lighting), illumination (radiant exitance). More generally, the term ''spectral power distribution'' can refer to the concentration, as a function of wavelength, of any radiometric or photometric quantity (e.g. radiant energy, radiant flux, radiant intensity, radiance, irradiance, radiant exitance, Radiosity (heat transfer), radiosity, luminance, luminous flux, luminous intensity, illuminance, luminous emittance). Knowledge of the SPD is crucial for optical-sensor system applications. Optical properties such as transmittance, reflectivity, and absorbance as well as the sensor response are typically dependent on the incident wavelength. Physics Mathematically, for the spectral power distribution of a radiant exitance or irradiance one may write: : M(\lambda)=\frac\approx\fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Calibration
The aim of color calibration is to measure and/or adjust the color response of a device (input or output) to a known state. In International Color Consortium (ICC) terms, this is the basis for an additional color characterization of the device and later profiling. In non-ICC workflows, calibration sometimes refers to establishing a known relationship to a standard color space in one go. The device that is to be calibrated is sometimes known as a ''calibration source''; the color space that serves as a standard is sometimes known as a ''calibration target''. Color calibration is a requirement for all devices taking an active part in a color management, color-managed workflow and is used by many industries, such as television production, gaming, photography, engineering, chemistry, medicine, and more. Information flow and output distortion Input data can come from device sources like digital cameras, image scanners, or any other measuring devices. Those inputs can be either mono ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting. CIE illuminants The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name) is the body responsible for publishing all of the well-known standard illuminants. Each of these is known by a letter or by a letter-number combination. Illuminants A, B, and C were introduced in 1931, with the intention of respectively representing average incandescent light, direct sunlight, and average daylight. Illuminants D (1967) represent variations of daylight, illuminant E is the equal-energy illuminant, while illuminants F (2004) represent fluorescent lamps of various composition. There are instructions on how to experimentally produce light sources ("standard sources") corresponding to the older illuminants. For the relatively newer ones (such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Commission On Illumination
The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name Commission internationale de l'éclairage) is the international authority on light, illumination, colour, and colour spaces. It was established in 1913 as a successor to the Commission Internationale de Photométrie, which was founded in 1900, and is today based in Vienna, Austria. Organization The CIE has six active divisions, each of which establishes technical committees to carry out its program: * Division 1: Vision and Colour * Division 2: Physical Measurement of Light and Radiation * Division 3: Interior Environment and Lighting Design * Division 4: Transportation and Exterior Applications * Division 6: Photobiology and Photochemistry * Division 8: Image Technology Two divisions are no longer active. * Division 5: Exterior Lighting and Other Applications * Division 7: General Aspects of Lighting The President of the CIE from 2023 is Jennifer Veitch from Canada. CIE publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |