|
Failing Badly
Failing badly and failing well are concepts in systems security and network security (and engineering in general) describing how a system reacts to failure. The terms have been popularized by Bruce Schneier, a cryptographer and security consultant.Homeland Insecurity , '''', September 2002 Failing badly A system that fails badly is one that has a catastrophic result when failure occurs. A |
Reinforced Concrete
Reinforced concrete, also called ferroconcrete or ferro-concrete, is a composite material in which concrete's relatively low tensile strength and ductility are compensated for by the inclusion of reinforcement having higher tensile strength or ductility. The reinforcement is usually, though not necessarily, steel reinforcing bars (known as rebar) and is usually embedded passively in the concrete before the concrete sets. However, post-tensioning is also employed as a technique to reinforce the concrete. In terms of volume used annually, it is one of the most common engineering materials. In corrosion engineering terms, when designed correctly, the alkalinity of the concrete protects the steel rebar from corrosion. Description Reinforcing schemes are generally designed to resist tensile stresses in particular regions of the concrete that might cause unacceptable cracking and/or structural failure. Modern reinforced concrete can contain varied reinforcing materials made o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engineering Failures
Engineering is the practice of using natural science, mathematics, and the engineering design process to Problem solving#Engineering, solve problems within technology, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve Systems engineering, systems. Modern engineering comprises many subfields which include designing and improving infrastructure, machinery, vehicles, electronics, Materials engineering, materials, and energy systems. The Academic discipline, discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more Academic specialization, specialized fields of engineering, each with a more specific emphasis for applications of applied mathematics, mathematics and applied science, science. See glossary of engineering. The word '':wikt:engineering, engineering'' is derived from the Latin . Definition The American Engineers' Council for Professional Development (the predecessor of the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology aka ABET) has defined "engineering" as: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backup
In information technology, a backup, or data backup is a copy of computer data taken and stored elsewhere so that it may be used to restore the original after a data loss event. The verb form, referring to the process of doing so, is "wikt:back up, back up", whereas the noun and adjective form is "wikt:backup, backup". Backups can be used to data recovery, recover data after its loss from File deletion, data deletion or Data corruption, corruption, or to recover data from an earlier time. Backups provide a simple form of IT disaster recovery; however not all backup systems are able to reconstitute a computer system or other complex configuration such as a computer cluster, active directory server, or database server. A backup system contains at least one copy of all data considered worth saving. The computer data storage, data storage requirements can be large. An information repository model may be used to provide structure to this storage. There are different types of data stor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ductile
Ductility refers to the ability of a material to sustain significant plastic deformation before fracture. Plastic deformation is the permanent distortion of a material under applied stress, as opposed to elastic deformation, which is reversible upon removing the stress. Ductility is a critical mechanical performance indicator, particularly in applications that require materials to bend, stretch, or deform in other ways without breaking. The extent of ductility can be quantitatively assessed using the percent elongation at break, given by the equation: \% \mathrm= \left ( \frac \right )\times100 where l_ is the length of the material after fracture and l_0 is the original length before testing. This formula helps in quantifying how much a material can stretch under tensile stress before failure, providing key insights into its ductile behavior. Ductility is an important consideration in engineering and manufacturing. It defines a material's suitability for certain manufactur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesh Network
A mesh network is a local area network topology in which the infrastructure nodes (i.e. bridges, switches, and other infrastructure devices) connect directly, dynamically and non-hierarchically to as many other nodes as possible and cooperate with one another to efficiently route data to and from clients. This lack of dependency on one node allows for every node to participate in the relay of information. Mesh networks dynamically self-organize and self-configure, which can reduce installation overhead. The ability to self-configure enables dynamic distribution of workloads, particularly in the event a few nodes should fail. This in turn contributes to fault-tolerance and reduced maintenance costs. Mesh topology may be contrasted with conventional star/tree local network topologies in which the bridges/switches are directly linked to only a small subset of other bridges/switches, and the links between these infrastructure neighbours are hierarchical. While star-and-tree topologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
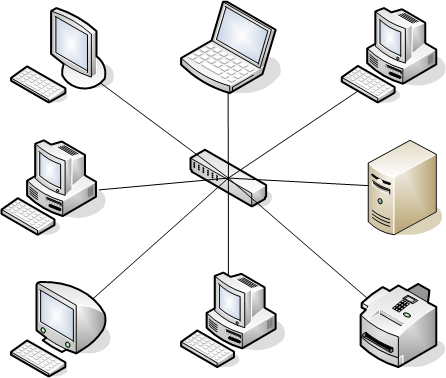
Star Network
A star network is an implementation of a spoke–hub distribution paradigm in computer networks. In a star network, every host is connected to a central hub. In its simplest form, one central hub acts as a conduit to transmit messages. The star network is one of the most common computer network topologies. Network The hub and hosts, and the transmission lines between them, form a graph with the topology of a star. Data on a star network passes through the hub before continuing to its destination. The hub manages and controls all functions of the network. It also acts as a repeater for the data flow. In a typical network the hub can be a network switch, Ethernet hub, wireless access point or a router The star topology reduces the impact of a transmission line failure by independently connecting each host to the hub. Each host may thus communicate with all others by transmitting to, and receiving from, the hub. The failure of a transmission line linking any host to the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multihoming
Multihoming is the practice of connecting a Host (network), host or a computer network to more than one network. This can be done in order to increase reliability or performance. A typical host or end-user network is connected to just one network. Connecting to multiple networks can increase reliability because if one connection fails, packets can still be routed through the remaining connection. Connecting to multiple networks can also improve performance because data can be transmitted and received through the multiple connections simultaneously multiplying throughput and, depending on the destination, it may be more efficient to route through one network or the other. Variants There are several different ways to perform multihoming. Host multihoming A single host may be connected to multiple networks. For example, a mobile phone might be simultaneously connected to a WiFi network and a 4G network, and a desktop computer might be connected to both a home network and a V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cockpit
A cockpit or flight deck is the area, on the front part of an aircraft, spacecraft, or submersible, from which a pilot controls the vehicle. The cockpit of an aircraft contains flight instruments on an instrument panel, and the controls that enable the pilot to fly the aircraft. In most airliners, a door separates the cockpit from the aircraft cabin. After the September 11, 2001 attacks, all major airlines fortified their cockpits against access by hijackers. Etymology The word cockpit seems to have been used as a nautical term in the 17th century, without reference to cock fighting. It referred to an area in the rear of a ship where the cockswain's station was located, the cockswain being the pilot of a smaller "boat" that could be dispatched from the ship to board another ship or to bring people ashore. The word "cockswain" in turn derives from the old English terms for "boat-servant" (''coque'' is the French word for "shell"; and ''swain'' was old English for boy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
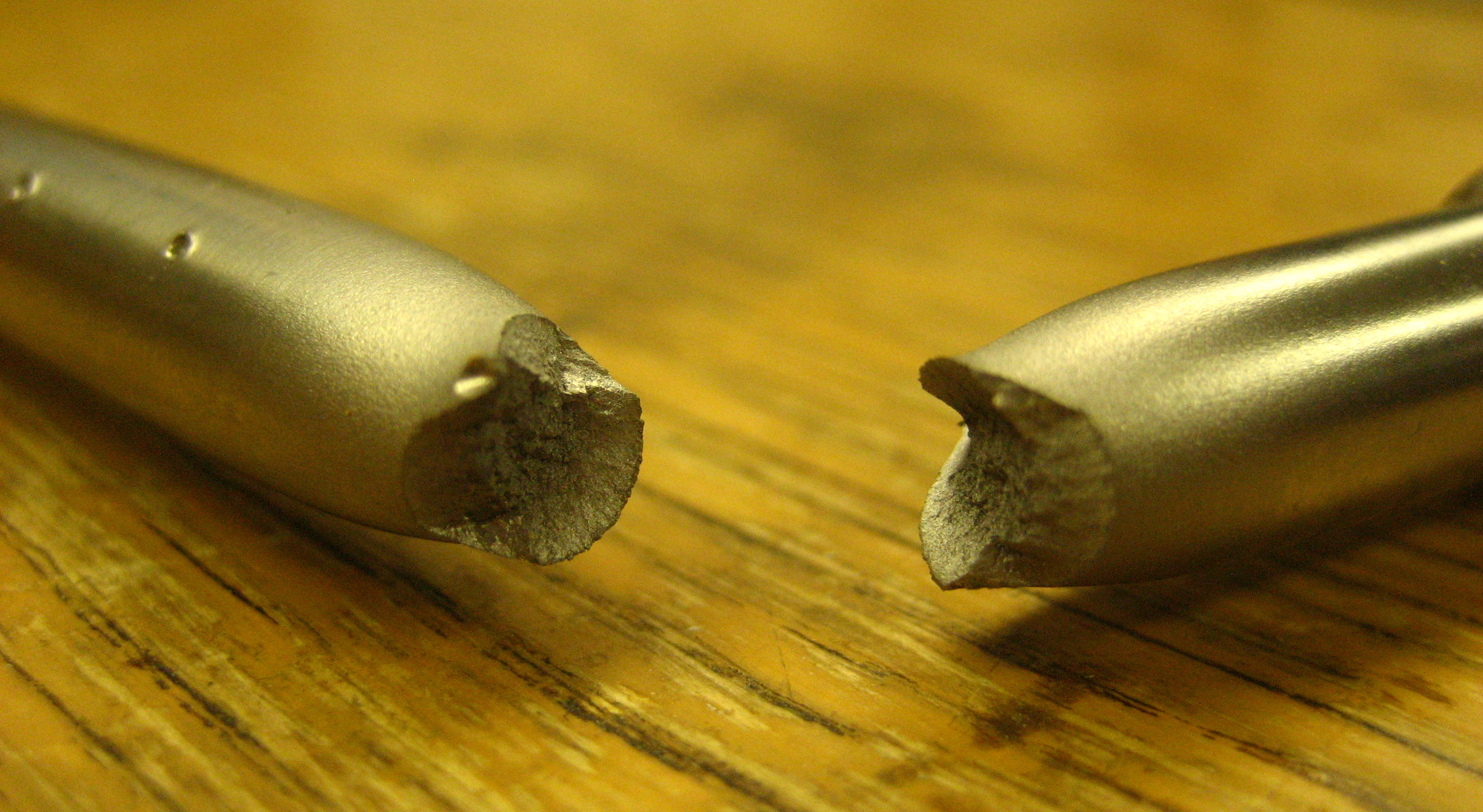
Fracture
Fracture is the appearance of a crack or complete separation of an object or material into two or more pieces under the action of stress (mechanics), stress. The fracture of a solid usually occurs due to the development of certain displacement discontinuity surfaces within the solid. If a displacement develops perpendicular to the surface, it is called a normal tensile crack or simply a crack; if a displacement develops tangentially, it is called a shear crack, slip band, or dislocation. #Brittle, Brittle fractures occur without any apparent deformation before fracture. #Ductile, Ductile fractures occur after visible deformation. Fracture strength, or breaking strength, is the stress when a specimen fails or fractures. The detailed understanding of how a fracture occurs and develops in materials is the object of fracture mechanics. Strength Fracture strength, also known as breaking strength, is the stress at which a specimen structural integrity and failure, fails via fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of aggregate bound together with a fluid cement that cures to a solid over time. It is the second-most-used substance (after water), the most–widely used building material, and the most-manufactured material in the world. When aggregate is mixed with dry Portland cement and water, the mixture forms a fluid slurry that can be poured and molded into shape. The cement reacts with the water through a process called hydration, which hardens it after several hours to form a solid matrix that binds the materials together into a durable stone-like material with various uses. This time allows concrete to not only be cast in forms, but also to have a variety of tooled processes performed. The hydration process is exothermic, which means that ambient temperature plays a significant role in how long it takes concrete to set. Often, additives (such as pozzolans or superplasticizers) are included in the mixture to improve the physical prop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redundancy (engineering)
In engineering and systems theory, redundancy is the intentional duplication of critical components or functions of a system with the goal of increasing reliability of the system, usually in the form of a backup or fail-safe, or to improve actual system performance, such as in the case of GNSS receivers, or multi-threaded computer processing. In many safety-critical systems, such as fly-by-wire and hydraulic systems in aircraft, some parts of the control system may be triplicated, which is formally termed triple modular redundancy (TMR). An error in one component may then be out-voted by the other two. In a triply redundant system, the system has three sub components, all three of which must fail before the system fails. Since each one rarely fails, and the sub components are designed to preclude common failure modes (which can then be modelled as independent failure), the probability of all three failing is calculated to be extraordinarily small; it is often outweighed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |