|
Faculty Of Engineering, University Of Tokyo
The School of Engineering at the University of Tokyo comprises the Faculty of Engineering and the Graduate School of Engineering. The former oversees undergraduate education, while the latter is responsible for postgraduate studies. In practice, they share faculty, facilities, and other research and educational resources, and operate as a single entity. The School of Engineering traces its origins back to the Imperial College of Engineering, which was founded in 1873 to train engineers by recruiting a large number of British scholars and engineers as its faculty. At the time, Japan had just ended its two-century-long self-imposed seclusion, while Western Europe was in the midst of the Industrial Revolution. Thus, there was an urgent need to import advanced engineering knowledge. In March 1886, the college merged with the Department of Industrial Arts of the Graduate School of Science and Faculty of Science, University of Tokyo, School of Science at the University of Tokyo, forming th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial College Of Engineering
The Imperial College of Engineering (工部大学校, ''Kōbudaigakkō'') was a Empire of Japan, Japanese institution of higher education that was founded during the Meiji era. The college was established under the auspices of the Ministry of Public Works (Japan), Ministry of Public Works for the training of young Japanese engineers. Supporting Japan’s rapid industrialization at the end of the 19th century, the college commenced teaching in October 1873 soon after the initial cohort of teaching staff arrived from United Kingdom. The college was an immediate precursor to the establishment of the University of Tokyo’s Faculty of Engineering, University of Tokyo, Faculty of Engineering in 1877. Foundation file:Henry Dyer.gif, 250px, Henry Dyer In the process of founding the Ministry of Public Works (Japan), Public Works, Edmund Morel (railway engineer), Edmund Morel, a chief engineer for Railway Department of the Meiji Japanese government emphasized importance of engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bunkyō
is a Special wards of Tokyo, special ward in the Tokyo, Tokyo Metropolis in Japan. Situated in the middle of the ward area, Bunkyō is a residential and educational center. Beginning in the Meiji period, literati like Natsume Sōseki, as well as scholars and politicians have lived there. Bunkyō is home to the Tokyo Dome, Judo's Kodokan Judo Institute, Kōdōkan, and the University of Tokyo's Hongō campus, Hongo Campus. It was formed in 1947 as a merger of Hongo and Koishikawa wards following Tokyo City's Local Autonomy Act, transformation into Tokyo Metropolis. The modern Bunkyo ward exhibits contrasting Shitamachi and Yamanote geographical and cultural division. The Nezu and Sendagi neighborhoods in the ward's eastern corner is attached to the Shitamachi area in Ueno. On the other hand, the remaining areas of the ward typically represent Yamanote districts. As of 2022, the ward has a population of 240,069 (including about 8,500 foreign residents), and a population density of . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokyo
Tokyo, officially the Tokyo Metropolis, is the capital of Japan, capital and List of cities in Japan, most populous city in Japan. With a population of over 14 million in the city proper in 2023, it is List of largest cities, one of the most populous urban areas in the world. The Greater Tokyo Area, which includes Tokyo and parts of six neighboring Prefectures of Japan, prefectures, is the most populous metropolitan area in the world, with 41 million residents . Lying at the head of Tokyo Bay, Tokyo is part of the Kantō region, on the central coast of Honshu, Japan's largest island. It is Japan's economic center and the seat of the Government of Japan, Japanese government and the Emperor of Japan. The Tokyo Metropolitan Government administers Tokyo's central Special wards of Tokyo, 23 special wards, which formerly made up Tokyo City; various commuter towns and suburbs in Western Tokyo, its western area; and two outlying island chains, the Tokyo Islands. Although most of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo (, abbreviated as in Japanese and UTokyo in English) is a public research university in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Founded in 1877 as the nation's first modern university by the merger of several pre-westernisation era institutions, its direct precursors include the '' Tenmongata'', founded in 1684, and the Shōheizaka Institute. Although established under its current name, the university was renamed in 1886 and was further retitled to distinguish it from other Imperial Universities established later. It served under this name until the official dissolution of the Empire of Japan in 1947, when it reverted to its original name. Today, the university consists of 10 faculties, 15 graduate schools, and 11 affiliated research institutes. As of 2023, it has a total of 13,974 undergraduate students and 14,258 graduate students. The majority of the university's educational and research facilities are concentrated within its three main Tokyo campuses: Hongō, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduate School Of Science And Faculty Of Science, University Of Tokyo
Faculty of Science (東京大学理学部) is one of the 10 constituent faculties, and Graduate School of Science (東京大学大学院理学系研究科) is one of the constituent 15 graduate schools at University of Tokyo. The faculty and the graduate school operate as one with the exception of mathematics and computer science. Founded in 1877, Faculty of Science is one of the oldest 4 faculties (Science, Medicine, Law and Letters) of the University of Tokyo. Faculty of Science and Graduate School of Science have produced 6 Nobel laureates ( Esaki, Koshiba, Nanbu, Kajita, Osumi, Manabe) and one Fields Medallist ( Kodaira). Organization Faculty of Science (Undergraduate Departments) * Departments: ** Mathematics (UG) - affiliated with Graduate School of Mathematical Sciences ** Information Science (UG) - affiliated with Graduate School of Information Science and Technology ** Physics (UG) ** Astronomy (UG) ** Earth and Planetary Physics (UG) ** Earth and Planetary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josiah Conder (architect)
Josiah Conder (28 September 1852 – 21 June 1920) was a British architect who was hired by the Meiji Japanese government as a professor of architecture for the Imperial College of Engineering and became architect of Japan's Public Works. He started his own practice after 1888. Conder designed numerous public buildings in Tokyo, including the ''Rokumeikan'', which became a controversial symbol of Westernisation in the Meiji period. He educated young Japanese architects, notably Tatsuno Kingo and Katayama Tōkuma, earning him the nickname "father of Japanese modern architecture." Early career Conder was born in Hundred of Brixton, Brixton, Surrey, London, to Josiah Conder, a banker, and his wife, Elizabeth (Willsher). Conder was educated at Bedford Modern School, and then became an architect pupil with Thomas Roger Smith. He later studied architecture at the Royal College of Art, South Kensington School of Art and the University of London. His grandfather, Josiah Conder (editor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faculty Of Engineering Building 2, University Of Tokyo
Faculty or faculties may refer to: Academia * Faculty (academic staff), professors, researchers, and teachers of a given university or college (North American usage) * Faculty (division), a large department of a university by field of study (used outside North America) Biology * An ability of an individual ** Cognitive skills, colloquially ''faculties'' ** Senses or ''perceptive faculties''—such as sight, hearing or touch ** Faculty Psychology, suggests the mind is divided into sections, each assigned specific mental tasks. Business * Faculty (company), a British tech firm (formerly ''ASI'') Film and television * ''The Faculty'', a 1998 horror/sci-fi movie by Robert Rodriguez * ''The Faculty'' (TV series), a 1996 American sitcom Religious law * Faculty (canon law) A faculty is a legal instrument or warrant in canon law, usually an authorisation to do something. Catholic Church In the canon law of the Catholic Church, a faculty is "the authority, privilege, or p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
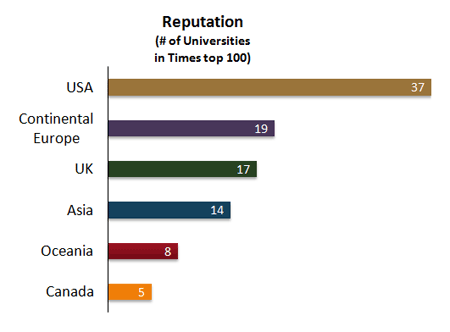
Times Higher Education World University Rankings
The ''Times Higher Education World University Rankings'', often referred to as the THE Rankings, is the annual publication of university rankings by the ''Times Higher Education'' magazine. The publisher had collaborated with Quacquarelli Symonds (QS) to publish the joint ''Times Higher Education–QS World University Rankings, THE-QS World University Rankings'' from 2004 to 2009 before it turned to Thomson Reuters for a new ranking system from 2010 to 2013. In 2014, the magazine signed an agreement with Elsevier to provide it with the data used in compiling its annual rankings. The publication includes global rankings of universities, including by subject and reputation. It also has begun publishing three regional tables for universities in Asia, Latin America, and BRICS and emerging economies, which are ranked with separate criteria and weightings. The THE Rankings is often considered one of the most widely observed university rankings together with the ''Academic Ranking of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
College Of Arts And Sciences, University Of Tokyo
The is one of the ten undergraduate faculties of the University of Tokyo and the only one referred to as a college. The is the postgraduate and research school attached to it. Originally, the college was a university preparatory boarding school called the First Higher School until 1950, and it still operates on the Komaba Campus, which used to belong to the higher school and is separate from the rest of the university. Hence, the word is synonymous with the College of Arts and Sciences within the university. Overview Masato Hirai argues that the College's liberal arts education has been based on two different concepts: 'culture' as understood in Victorian England or 'bildung' in Germany, and the American concept of General Education. The former has traditionally been at the core of the education offered at the First Higher School, while the latter, which aims to equip students with the ability to see beyond their fields of specialisation, was introduced after the Second Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graduate School Of Medicine And Faculty Of Medicine, University Of Tokyo
The Graduate School of Medicine and Faculty of Medicine, University of Tokyo are a single, merged department at the University of Tokyo. The Faculty of Medicine (東京大学医学部) is one of the 10 constituent faculties, and the Graduate School of Medicine (東京大学大学院医学系研究科) is one of the 15 constituent graduate schools at University of Tokyo. The Faculty of Medicine was founded in 1877 and is one of the four oldest faculties (along with the Faculties of Science, Medicine, Law, and Letters) at the University of Tokyo. Degree Programs Faculty of Medicine (Undergraduate Courses) * School of Medicine (6-year medical degree A medical degree is a professional degree admitted to those who have passed coursework in the fields of medicine and/or surgery from an accredited medical school. Obtaining a degree in medicine allows for the recipient to continue on into special ... program) * School of Integrated Health Sciences (4-year bachelor's degree progr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QS World University Rankings
The ''QS World University Rankings'' is a portfolio of comparative college and university rankings compiled by Quacquarelli Symonds, a higher education analytics firm. Its first and earliest edition was published in collaboration with '' Times Higher Education'' (''THE'') magazine as ''Times Higher Education''–QS World University Rankings, inaugurated in 2004 to provide an independent source of comparative data about university performance. In 2009, the two organizations parted ways to produce independent university rankings, the QS World University Rankings and ''THE'' World University Rankings. QS's rankings portfolio has since been expanded to consist of the QS World University Rankings, the QS World University Rankings by Subject, four regional rankings tables (including Asia, Latin America and The Caribbean, Europe, and the Arab Region), several MBA rankings, and the QS Best Student Cities rankings. In 2022, QS launched the QS World University Rankings: Sustainability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |