|
FBI Index
The FBI Indexes, or Index List, was a system used to track American citizens and other people by the Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) before the adoption of computerized databases. The Index List was originally made of paper index cards, first compiled by J. Edgar Hoover at the Bureau of Investigations before he was appointed director of the FBI. The Index List was used to track U.S. citizens and others believed by the FBI to be dangerous to national security, and was subdivided into various divisions which generally were rated based on different classes of danger the subject was thought to represent. General Intelligence Division In 1919, during the First Red Scare, William J. Flynn of the Bureau of Investigation appointed J. Edgar Hoover chief of the General Intelligence Division (GID). Hoover used his experience working as a library clerk at the Library of Congress to create an index tracking system which used extensive cross-referencing. The GID took files from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
FBI Rabble Rouser Index
The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) is the domestic intelligence and security service of the United States and its principal federal law enforcement agency. An agency of the United States Department of Justice, the FBI is a member of the U.S. Intelligence Community and reports to both the attorney general and the director of national intelligence. A leading American counterterrorism, counterintelligence, and criminal investigative organization, the FBI has jurisdiction over violations of more than 200 categories of federal crimes. Although many of the FBI's functions are unique, its activities in support of national security are comparable to those of the British MI5 and NCA, the New Zealand GCSB and the Russian FSB. Unlike the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), which has no law enforcement authority and is focused on intelligence collection abroad, the FBI is primarily a domestic agency, maintaining 56 field offices in major cities throughout the United States, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
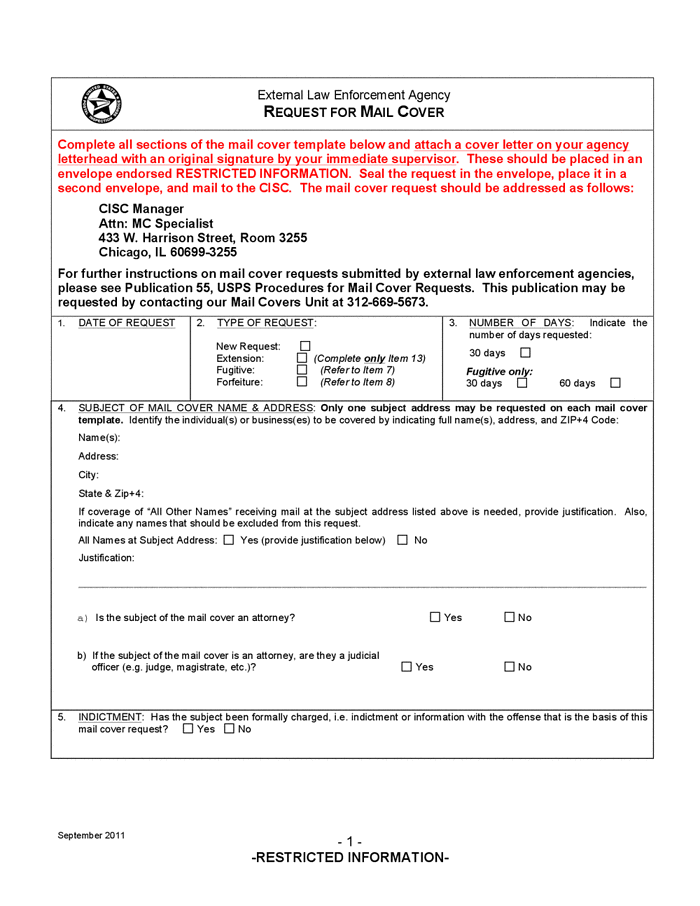
Mail Cover
Mail cover is a law enforcement investigative technique in which the United States Postal Service, acting at the request of a law enforcement agency, records information from the outside of letters and parcels before they are delivered and then sends the information to the agency that requested it. The Postal Service grants mail cover surveillance requests for about 30 days and may extend them for up to 120 days. Mail covers can be requested to investigate criminal activity or to protect national security. On average the Postal Service grants 15,000 to 20,000 criminal activity requests each year. It rarely denies a request. Mail cover is defined by the U.S. Postal Regulations 39 CFR 233.3 and the Internal Revenue Manual as follows: :Mail cover is the process by which a nonconsensual record is made of any data appearing on the outside cover of sealed or unsealed mail; or by which a record is made of the contents of any unsealed mail, as allowed by law, to obtain information to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
American Heritage (magazine)
''American Heritage'' is a magazine dedicated to covering the history of the United States for a mainstream readership. Until 2007, the magazine was published by Forbes.Grosvenor, Edwin S. "Editor's Letter," ''American Heritage'', Winter 2008. Since that time, Edwin S. Grosvenor has been its editor and publisher. Print publication was suspended early in 2013, but the magazine relaunched in digital format with the Summer 2017 issue after a Kickstarter campaign raised $31,203 from 587 backers. The 70th Anniversary issue of the magazine (Winter 2020) on the subject "What Makes America Great?" includes essays by such historians as Fergus Bordewich, Douglas Brinkl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Francis Biddle
Francis Beverley Biddle (May 9, 1886 – October 4, 1968) was an American lawyer and judge who was the United States Attorney General during World War II. He also served as the primary American judge during Nuremberg trials following World War II and a United States circuit judge of the Court of Appeals for the Third Circuit. Early life and education Biddle was born in Paris, France, while his family was living abroad. He was one of four sons of Frances Brown (née Robinson) and Algernon Sydney Biddle, a law professor at the University of Pennsylvania Law School of the Biddle family. He was also a great-great-grandson of Edmund Randolph (1753–1813) the seventh Governor of Virginia, the second United States Secretary of State, and the first United States Attorney General. He graduated from Groton School, where he participated in boxing. He earned a Bachelor of Arts degree in 1909 from Harvard College and a Bachelor of Laws in 1911 from Harvard Law School. Career Biddle f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general (: attorneys general) or attorney-general (AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have executive responsibility for law enforcement and prosecutions, or even responsibility for legal affairs generally. In practice, the extent to which the attorney general personally provides legal advice to the government varies between jurisdictions, and even between individual office-holders within the same jurisdiction, often depending on the level and nature of the office-holder's prior legal experience. Where the attorney general has ministerial responsibility for legal affairs in general (as is the case, for example, with the United States Attorney General or the Attorney-General for Australia, and the respective attorneys general of the states in each country), the ministerial portfolio is largely equivalent to that of a Minister of Justice in some other countries. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Executive Order 9066
Executive Order 9066 was a President of the United States, United States presidential executive order signed and issued during World War II by United States president Franklin D. Roosevelt on February 19, 1942. "This order authorized the forced removal of all persons deemed a threat to national security from the West Coast of the United States, West Coast to 'relocation centers' further inland—resulting in the incarceration of Japanese Americans." Two-thirds of the 125,000 people displaced were U.S. citizens. Notably, far more Americans of Asian descent were forcibly interned than Americans of European descent, both in total and as a share of their relative populations. German and Italian Americans who were sent to internment camps during the war were sent under the provisions of Presidential Proclamation 2526 and the Alien Enemy Act, part of the Alien and Sedition Act of 1798. Transcript of Executive Order 9066 The text of Executive Order 9066 was as follows: Backgrou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Japanese American Internment
During World War II, the United States forcibly relocated and incarcerated about 120,000 people of Japanese descent in ten concentration camps operated by the War Relocation Authority (WRA), mostly in the western interior of the country. About two-thirds were U.S. citizens. These actions were initiated by Executive Order 9066, issued by President Franklin D. Roosevelt on February 19, 1942, following the outbreak of war with the Empire of Japan in December 1941. About 127,000 Japanese Americans then lived in the continental U.S., of which about 112,000 lived on the West Coast. About 80,000 were '' Nisei'' ('second generation'; American-born Japanese with U.S. citizenship) and '' Sansei'' ('third generation', the children of ''Nisei''). The rest were '' Issei'' ('first generation') immigrants born in Japan, who were ineligible for citizenship. In Hawaii, where more than 150,000 Japanese Americans comprised more than one-third of the territory's population, only 1,200 to 1,80 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
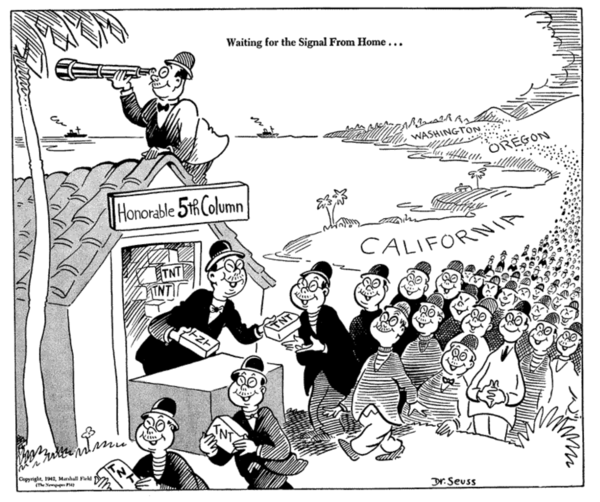
Fifth Column
A fifth column is a group of people who undermine a larger group or nation from within, usually in favor of an enemy group or another nation. The activities of a fifth column can be overt or clandestine. Forces gathered in secret can mobilize openly to assist an external attack. The term is also applied to organized actions by military personnel. Clandestine fifth column activities can involve acts of sabotage, disinformation, espionage or terrorism executed within defense lines by secret sympathizers with an external force. History Internal Enemy in Antiquity The distinction between internal and external enemies to a people or government was a topic of discussion in antiquity, mentioned most notably in Plato's ''Republic''. Origin of Modern Term The term "fifth column" originated in Spain (originally ) during the early phase of the Spanish Civil War. It gained popularity in the Republican faction media in early October 1936 and immediately started to spread abroad. The exac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering, as a subfield of the intelligence field, is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence). A person who commits espionage on a mission-specific contract is called an ''espionage agent'' or ''spy''. A person who commits espionage as a fully employed officer of a government is called an intelligence officer. Any individual or spy ring (a cooperating group of spies), in the service of a government, company, criminal organization, or independent operation, can commit espionage. The practice is clandestine, as it is by definition unwelcome. In some circumstances, it may be a legal tool of law enforcement and in others, it may be illegal and punishable by law. Espionage is often part of an institutional effort by a government or commercial concern. However, the term tends to be associated with state spying on potential or actual enemies for military purposes. Spying involving corporations is known as c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Axis Powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Germany, Fascist Italy, Kingdom of Italy and the Empire of Japan. The Axis were united in their far-right positions and general opposition to the Allies, but otherwise lacked comparable coordination and ideological cohesion. The Axis grew out of successive diplomatic efforts by Germany, Italy, and Japan to secure their own specific expansionist interests in the mid-1930s. The first step was the Italo-German protocol of 23 October 1936, protocol signed by Germany and Italy in October 1936, after which Italian leader Benito Mussolini declared that all other European countries would thereafter rotate on the Rome–Berlin axis, thus creating the term "Axis". The following November saw the ratification of the Anti-Comintern Pact, an anti-communis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
University Of Vermont
The University of Vermont and State Agricultural College, commonly referred to as the University of Vermont (UVM), is a Public university, public Land-grant university, land-grant research university in Burlington, Vermont, United States. Founded in 1791, UVM is the oldest university in Vermont and the fifth-oldest in New England. UVM comprises ten colleges and schools, including the Robert Larner College of Medicine, and offers more than 100 undergraduate majors along with various graduate and professional programs. The University of Vermont Medical Center, has its primary facility on the UVM campus. It is Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities—Very high research activity". In athletics, UVM's teams, known as the Vermont Catamounts, Catamounts, compete in NCAA Division I, primarily in the America East Conference and Hockey East, Hockey East Association. History The University of Vermont was founded as a pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Judicial Oversight
Judicial review is a process under which a government's executive, legislative, or administrative actions are subject to review by the judiciary. In a judicial review, a court may invalidate laws, acts, or governmental actions that are incompatible with a higher authority. For example, an executive decision may be invalidated for being unlawful, or a statute may be invalidated for violating the terms of a constitution. Judicial review is one of the checks and balances in the separation of powers—the power of the judiciary to supervise (judicial supervision) the legislative and executive branches when the latter exceed their authority. The doctrine varies between jurisdictions, so the procedure and scope of judicial review may differ between and within countries. The judiciary in United States has been described as having unusually strong powers of judicial review from a comparative perspective. General principles Judicial review can be understood in the context of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |