|
FAST20XX
FAST20XX (Future High-Altitude High Speed Transport 20XX ) was a European Space Agency (ESA) programme to develop the necessary technologies for a hypersonic suborbital spaceplane. Funding for the programme was established under the European Commission's Seventh Framework Programme. Overview The FAST 20XX programme run from 2009 to 2012 and was intended to provide a technological foundation for the industrial introduction of advanced hypersonic suborbital spaceplanes in the medium to longer term. No detailed vehicle design was planned under the program, with work instead focusing on mastering the technologies required for the development of such designs. Once the needed technologies were identified, researchers developed the dedicated analytical, numerical and experimental tools needed to investigate them. The project also looked at the legal and regulatory issues related to suborbital flight in consultation with government and international authorities. Two concepts have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can flight, fly and gliding flight, glide as an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and function as a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceflight, Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes as of 2024 have been rocket engine, rocket-powered for takeoff and climb, but have then landed as unpowered glider (aircraft), gliders. Four examples of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, Atmospheric entry, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and Landing#Aircraft, landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran (spacecraft), Buran, U.S. Boeing X-37, X-37, and the Chinese Shenlong (spacecraft), Shenlong. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2024 all past and current orbital spaceplanes VTHL, launch vertically; some are carried as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suborbital Spaceplane
A spaceplane is a vehicle that can fly and glide as an aircraft in Earth's atmosphere and function as a spacecraft in outer space. To do so, spaceplanes must incorporate features of both aircraft and spacecraft. Orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to conventional spacecraft, while sub-orbital spaceplanes tend to be more similar to fixed-wing aircraft. All spaceplanes as of 2024 have been rocket-powered for takeoff and climb, but have then landed as unpowered gliders. Four examples of spaceplanes have successfully launched to orbit, reentered Earth's atmosphere, and landed: the U.S. Space Shuttle, Russian Buran, U.S. X-37, and the Chinese Shenlong. Another, Dream Chaser, is under development in the U.S. As of 2024 all past and current orbital spaceplanes launch vertically; some are carried as a payload in a conventional fairing, while the Space Shuttle used its own engines with the assistance of boosters and an external tank. Orbital spaceflight takes place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
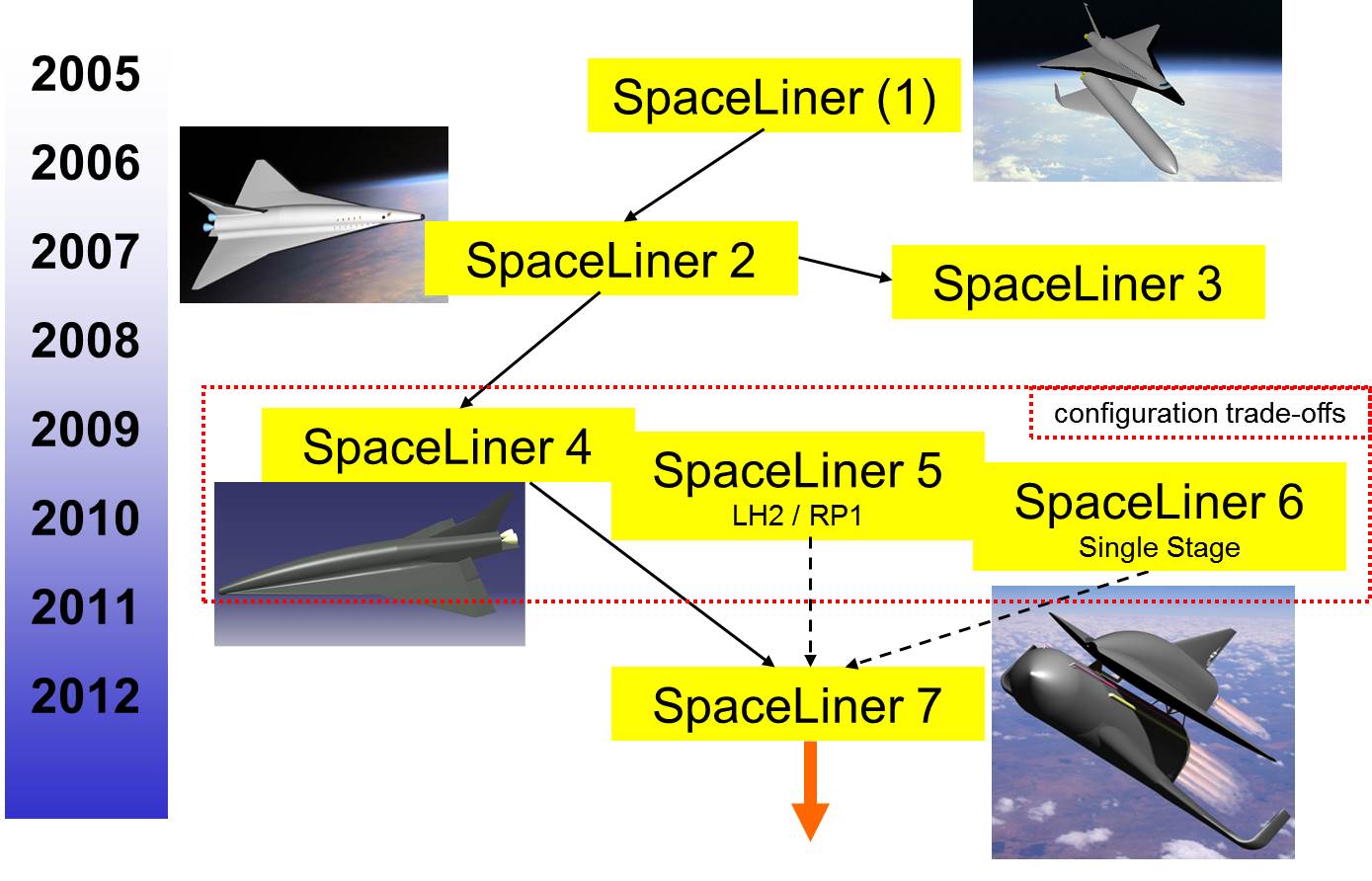
SpaceLiner
SpaceLiner is a concept for a Sub-orbital spaceflight, suborbital, hypersonic, winged passenger supersonic transport, conceived at the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt, or DLR) in 2005. In its second role the SpaceLiner is intended as a reusable launch vehicle (RLV) capable of delivering heavy payloads into orbit. The SpaceLiner is a very long-term project, and does not currently have funding lined up to initiate system New product development, development as of 2017. Projections in 2015 were that if adequate funding was eventually secured, the SpaceLiner concept might become an operational spaceplane in the 2040s. Concept The SpaceLiner concept consists of a two-stage, VTHL, vertical takeoff, horizontal landing configuration with a large uncrewed booster and a crewed stage designed for 50 passengers and 2 crew members. The fully reusable system is accelerated by a total of eleven liquid rocket engines (9 for the booster stage, 2 for the pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SpaceShipOne
SpaceShipOne is an experimental air launch, air-launched rocket-powered aircraft with sub-orbital spaceflight capability at speeds of up to / using a hybrid rocket motor. The design features a unique "Feathering (reentry), feathering" atmospheric reentry system where the rear half of the wing and the twin tail booms folds 70 degrees upward along a hinge running the length of the wing; this increases drag (physics), drag while retaining stability. SpaceShipOne completed the first human spaceflight, crewed private spaceflight in 2004. That same year, it won the US$10 million Ansari X Prize and was immediately retired from active service. Its Mother ship (aviation), mother ship was named "Scaled Composites White Knight, White Knight". Both craft were developed and flown by Mojave Aerospace Ventures, which was a joint venture between Paul Allen and Scaled Composites, Burt Rutan's aviation company. Allen provided the funding of approximately US$25 million. Rutan has indicated that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Space Agency
The European Space Agency (ESA) is a 23-member International organization, international organization devoted to space exploration. With its headquarters in Paris and a staff of around 2,547 people globally as of 2023, ESA was founded in 1975 in the context of European integration. Its 2025 annual budget was €7.7 billion. The ESA Human and Robotic Exploration programme includes human spaceflight (mainly through participation in the International Space Station programme); as well as the launch and operation of missions to Mars and Moon. Further activities include science missions to Jupiter, Mercury, the Sun, Earth observation, Asteroid impact avoidance and Telecommunications missions, designing launch vehicles; and maintaining Europe's Spaceport, the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou (French Guiana). Further programmes include space safety, satellite navigation, applications and commercialisation. The main European launch vehicle Ariane 6 is operated through Arianespace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypersonic
In aerodynamics, a hypersonic speed is one that exceeds five times the speed of sound, often stated as starting at speeds of Mach 5 and above. The precise Mach number at which a craft can be said to be flying at hypersonic speed varies, since individual physical changes in the airflow (like molecular dissociation and ionization) occur at different speeds; these effects collectively become important around Mach 5–10. The hypersonic regime can also be alternatively defined as speeds where specific heat capacity changes with the temperature of the flow as kinetic energy of the moving object is converted into heat. Characteristics of flow While the definition of hypersonic flow can be quite vague and is generally debatable (especially because of the absence of discontinuity between supersonic and hypersonic flows), a hypersonic flow may be characterized by certain physical phenomena that can no longer be analytically discounted as in supersonic flow. The peculiarities in hyperso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suborbital
A sub-orbital spaceflight is a spaceflight in which the spacecraft reaches outer space, but its trajectory intersects the surface of the gravitating body from which it was launched. Hence, it will not complete one orbital revolution, will not become an artificial satellite nor will it reach escape velocity. For example, the path of an object launched from Earth that reaches the Kármán line (about – above sea level), and then falls back to Earth, is considered a sub-orbital spaceflight. Some sub-orbital flights have been undertaken to test spacecraft and launch vehicles later intended for orbital spaceflight. Other vehicles are specifically designed only for sub-orbital flight; examples include crewed vehicles, such as the X-15 and SpaceShipTwo, and uncrewed ones, such as ICBMs and sounding rockets. Flights which attain sufficient velocity to go into low Earth orbit, and then de-orbit before completing their first full orbit, are not considered sub-orbital. Examples o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seventh Framework Programme
The Framework Programmes for Research and Technological Development, also called Framework Programmes or abbreviated FP1 to FP9, are funding programmes created by the European Union/European Commission to support and foster research in the European Research Area (ERA). Starting in 2014, the funding programmes were named Horizon. The funding programmes began in 1984 and continue to the present day. The most recent programme, Horizon Europe, has a budget of 95.5 billion Euros to be distributed over 7 years. The specific objectives and actions vary between funding periods. In FP6 and FP7, focus was on technological research. In Horizon 2020, the focus was on innovation, delivering economic growth faster, and delivering solutions to end users that are often governmental agencies. Background Conducting European research policies and implementing European research programmes is an obligation under the Amsterdam Treaty, which includes a chapter on research and technological development ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ansari X-Prize
The Ansari X Prize was a space competition in which the X Prize Foundation offered a US$10,000,000 () prize for the first non-government organization to launch a reusable crewed spacecraft into space twice within two weeks. It was modeled after early 20th-century aviation prizes, and aimed to spur development of low-cost spaceflight. Created in May 1996 and initially called just the "X Prize", it was renamed the "Ansari X Prize" on May 6, 2004, following a multimillion-dollar donation from entrepreneurs Anousheh Ansari and Amir Ansari. The prize was won on October 4, 2004, the 47th anniversary of the Sputnik 1 launch, by the Tier One project designed by Burt Rutan and financed by Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen, using the experimental spaceplane SpaceShipOne. $10 million was awarded to the winner, and more than $100 million was invested in new technologies in pursuit of the prize. Several other X Prizes have since been announced by the X Prize Foundation, promoting furth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (, abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 35 locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. The DLR acts as the German space agency and is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries. As of 2020, the German Aerospace Center had a national budget of €1.348 billion. Overview DLR has approximately 10.000 employees at 30 locations in Germany. Institutes and facilities are spread over 13 sites, as well as offices in Brussels, Paris and Washington, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |