|
Extrinsic Religious Orientation
An individual's or community's religious orientation involves presumptions about the existence and nature of God or gods, religious prescriptions about morality and communal and personal spirituality. Such presumptions involve the study of psychology, ethics, sociology and anthropology. Psychology According to Whitley and Kite, researchers who were interested in studying the psychological effects of religion on prejudice initially studied the relationship between simple indicators of religiosity such as whether or not a person went to church and the level of prejudice that that person showed. Surprisingly these researchers found that "religious involvement was consistently correlated with a variety of forms of prejudice." (Whitley & Kite, 2010) Whitley, B.E. & Kite, M.E. (2010). The psychology of prejudice and discrimination. Belmont, CA. Wadsworth. Naturally these findings were not well received by religious leaders or the religious community in general. It was at this point that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presumption
In the law of evidence, a presumption of a particular fact can be made without the aid of proof in some situations. The invocation of a presumption shifts the burden of proof from one party to the opposing party in a court trial. There are two types of presumption: ''rebuttable presumption'' and '' conclusive presumption''. A rebuttable presumption is assumed true until a person proves otherwise (for example the presumption of innocence). In contrast, a conclusive (or irrebuttable) presumption cannot be refuted in any case (such as defense of infancy in some legal systems). Presumptions are sometimes categorized into two types: presumptions without basic facts, and presumptions with basic facts. In the United States, mandatory presumptions are impermissible in criminal cases, but permissible presumptions are allowed. An example of presumption without basic facts is presumption of innocence. An example of presumption ''with'' basic facts is Declared death in absentia, e.g., t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gordon Allport
Gordon Willard Allport (November 11, 1897 – October 9, 1967) was an American psychologist. Allport was one of the first psychologists to focus on the study of the personality, and is often referred to as one of the founding figures of personality psychology. He contributed to the formation of values scales and rejected both a psychoanalytic approach to personality, which he thought often was too deeply interpretive, and a behavioral approach, which he thought did not provide deep enough interpretations from their data. Instead of these popular approaches, he developed an eclectic theory based on traits. He emphasized the uniqueness of each individual, and the importance of the present context, as opposed to history, for understanding the personality. Allport had a profound and lasting influence on the field of psychology, even though his work is cited much less often than that of other well-known figures. Part of his influence stemmed from his knack for exploring and broadly c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana, that is, freedom from ignorance, craving, rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind that includes meditation and instruction in Buddhist ethics such as right effort, mindfulness, and '' jhana''. He di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malcolm X
Malcolm X (born Malcolm Little, later Malik el-Shabazz; May 19, 1925 – February 21, 1965) was an American Muslim minister and human rights activist who was a prominent figure during the civil rights movement. A spokesman for the Nation of Islam until 1964, he was a vocal advocate for Black empowerment and the promotion of Islam within the Black community. A posthumous autobiography, on which he collaborated with Alex Haley, was published in 1965. Malcolm spent his adolescence living in a series of foster homes or with relatives after his father's death and his mother's hospitalization. He committed various crimes, being sentenced to 10 years in prison in 1946 for larceny and burglary. In prison he joined the Nation of Islam (adopting the name MalcolmX to symbolize his unknown African ancestral surname while discarding "the White slavemaster name of 'Little'"), and after his parole in 1952 quickly became one of the organization's most influential leaders. He was the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
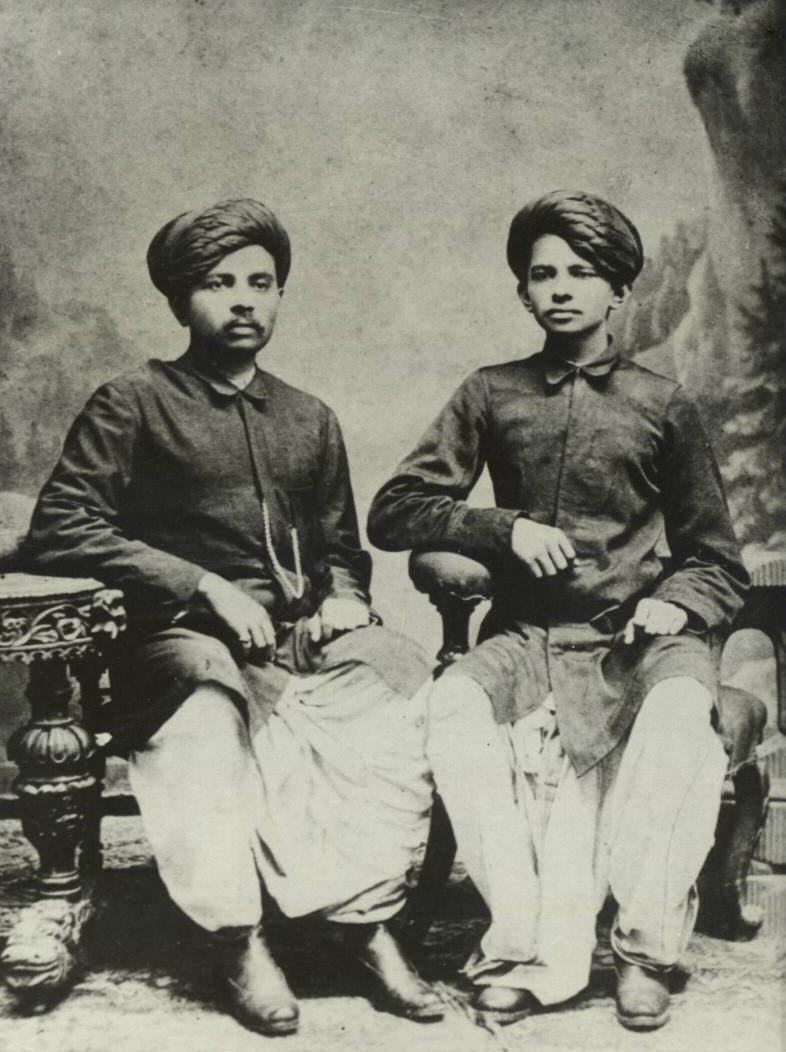
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi
Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi (; ; 2 October 1869 – 30 January 1948), popularly known as Mahatma Gandhi, was an Indian lawyer, anti-colonial nationalist Quote: "... marks Gandhi as a hybrid cosmopolitan figure who transformed ... anti-colonial nationalist politics in the twentieth-century in ways that neither indigenous nor westernized Indian nationalists could." and political ethicist Quote: "Gandhi staked his reputation as an original political thinker on this specific issue. Hitherto, violence had been used in the name of political rights, such as in street riots, regicide, or armed revolutions. Gandhi believes there is a better way of securing political rights, that of nonviolence, and that this new way marks an advance in political ethics." who employed nonviolent resistance to lead the successful campaign for India's independence from British rule, and to later inspire movements for civil rights and freedom across the world. The honorific ''Mahātmā'' (Sanskri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Batson
C. Daniel Batson (born March 15, 1943) is an American social psychologist. He has two doctoral degrees, in theology (from Princeton Theological Seminary) and psychology (from Princeton University's Department of Psychology). Batson obtained his doctorate under John Darley and taught at the University of Kansas. He retired in 2006 and now is an emeritus professor in the psychology department at the University of Tennessee. He is best known for his contributions to three fields: the social psychology of altruism, empathic concern, and psychology of religion. On altruism Batson has become well known for the empathy-altruism hypothesis, which states that "feeling empathy for person in need evokes motivation to help hat personin which these benefits to self are not the ultimate goal of helping; they are unintended consequences" (Batson & Shaw 1991, p. 114). The theory, initially proposed as an explanation of the so-called "empathy-helping relationship", implies that pure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus Of Control
Locus of control is the degree to which people believe that they, as opposed to external forces (beyond their influence), have control over the outcome of events in their lives. The concept was developed by Julian B. Rotter in 1954, and has since become an aspect of personality psychology. A person's "locus" (plural "loci", Latin for "place" or "location") is conceptualized as internal (a belief that one can control one's own life) or external (a belief that life is controlled by outside factors which the person cannot influence, or that chance or fate controls their lives). Individuals with a strong internal locus of control believe events in their life are primarily a result of their own actions: for example, when receiving exam results, people with an internal locus of control tend to praise or blame themselves and their abilities. People with a strong external locus of control tend to praise or blame external factors such as the teacher or the exam.Carlson, N.R., et al. (20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonism directed against other people because they are of a different race or ethnicity. Modern variants of racism are often based in social perceptions of biological differences between peoples. These views can take the form of social actions, practices or beliefs, or political systems in which different races are ranked as inherently superior or inferior to each other, based on presumed shared inheritable traits, abilities, or qualities. There have been attempts to legitimize racist beliefs through scientific means, such as scientific racism, which have been overwhelmingly shown to be unfounded. In terms of political systems (e.g. apartheid) that support the expression of prejudice or aversion in discriminatory practices or laws, racist ideolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stereotype
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example, an expectation about the group's personality, preferences, appearance or ability. Stereotypes are sometimes overgeneralized, inaccurate, and resistant to new information, but can sometimes be accurate. While such generalizations about groups of people may be useful when making quick decisions, they may be erroneous when applied to particular individuals and are among the reasons for prejudicial attitudes. Explicit stereotypes An explicit stereotype refers to stereotypes that one is aware that one holds, and is aware that one is using to judge people. If person ''A ''is making judgments about a ''particular'' person ''B'' from a group ''G'', and person ''A'' has an explicit stereotype for group ''G'', their decision bias can be partia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prejudice
Prejudice can be an affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classification of another person based on that person's perceived political affiliation, sex, gender, gender identity, beliefs, values, social class, age, disability, religion, sexuality, race, ethnicity, language, nationality, culture, complexion, beauty, height, body weight, occupation, wealth, education, criminality, sport-team affiliation, music tastes or other personal characteristics. The word "prejudice" can also refer to unfounded or pigeonholed beliefs and it may apply to "any unreasonable attitude that is unusually resistant to rational influence". Gordon Allport defined prejudice as a "feeling, favorable or unfavorable, toward a person or thing, prior to, or not based on, actual experience". Auestad (2015) defines prejudice as characterized by "symbolic transfer", transfe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychology Of Religion
Psychology of religion consists of the application of psychological methods and interpretive frameworks to the diverse contents of religious traditions as well as to both religious and irreligious individuals. The various methods and frameworks can be summarized regarding the classic distinction between the natural-scientific and human-scientific approaches. The first cluster amounts to objective, quantitative, and preferably experimental procedures for testing hypotheses for causal connections among the objects of one's study. In contrast, the human-scientific approach accesses the human world of experience using qualitative, phenomenological, and interpretive methods. The goal of this approach is to discern meaningful, rather than causal, connections among the phenomena one seeks to understand. Psychologists of religion pursue three major projects: #systematic description, especially of religious contents, attitudes, experiences, and expressions #explanation of the origins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)