|
Eukaryotic Translation Elongation Factor 1 Alpha 1
Elongation factor 1-alpha 1 (eEF1a1) is a translation elongation protein, expressed across eukaryotes. In humans, it is encoded by the ''EEF1A1'' gene. This gene encodes an isoform of the alpha subunit of the elongation factor-1 complex, which is responsible for the enzymatic delivery of aminoacyl tRNAs to the ribosome. This isoform (alpha 1) is expressed in brain, placenta, lung, liver, kidney, and pancreas, and the other isoform (alpha 2) is expressed in brain, heart and skeletal muscle. This isoform is identified as an autoantigen in 66% of patients with Felty's syndrome. This gene has been found to have multiple copies on many chromosomes, some of which, if not all, represent different pseudogenes. Structure Mammalian eEF1A possesses two paralogs, eEF1A1 and eEF1A2, with high amino acid sequence homology (approximately 90% identity). The sequences of their promoter regions are also highly similar, though that of the ''eEF1A2'' gene contains an additional 81 bp SV40 small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat Shock
The heat shock response (HSR) is a cell stress response that increases the number of molecular chaperones to combat the negative effects on proteins caused by stressors such as increased temperatures, oxidative stress, and heavy metals. In a normal cell, proteostasis (protein homeostasis) must be maintained because proteins are the main functional units of the cell. Many proteins take on a defined configuration in a process known as protein folding in order to perform their biological functions. If these structures are altered, critical processes could be affected, leading to cell damage or death. The heat shock response can be employed under stress to induce the expression of heat shock proteins (HSP), many of which are molecular chaperones, that help prevent or reverse protein misfolding and provide an environment for proper folding. Protein folding is already challenging due to the crowded intracellular space where aberrant interactions can arise; it becomes more difficult when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Proliferation
Cell proliferation is the process by which ''a cell grows and divides to produce two daughter cells''. Cell proliferation leads to an exponential increase in cell number and is therefore a rapid mechanism of tissue growth. Cell proliferation requires both cell growth and cell division to occur at the same time, such that the average size of cells remains constant in the population. Cell division can occur without cell growth, producing many progressively smaller cells (as in cleavage of the zygote), while cell growth can occur without cell division to produce a single larger cell (as in growth of neurons). Thus, cell proliferation is not synonymous with either cell growth or cell division, despite the fact that these terms are sometimes used interchangeably. Stem cells undergo cell proliferation to produce proliferating "transit amplifying" daughter cells that later differentiate to construct tissues during normal development and tissue growth, during tissue regeneration aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Growth
Cell growth refers to an increase in the total mass of a cell, including both cytoplasmic, nuclear and organelle volume. Cell growth occurs when the overall rate of cellular biosynthesis (production of biomolecules or anabolism) is greater than the overall rate of cellular degradation (the destruction of biomolecules via the proteasome, lysosome or autophagy, or catabolism). Cell growth is not to be confused with cell division or the cell cycle, which are distinct processes that can occur alongside cell growth during the process of cell proliferation, where a cell, known as the mother cell, grows and divides to produce two daughter cells. Importantly, cell growth and cell division can also occur independently of one another. During early embryonic development ( cleavage of the zygote to form a morula and blastoderm), cell divisions occur repeatedly without cell growth. Conversely, some cells can grow without cell division or without any progression of the cell cycle, such as g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins are said to produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are copied into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs). mRNA comprises only 1–3% of total RNA samples. Less than 2% of the human genome can be transcribed into mRNA ( Human genome#Coding vs. noncoding DNA), while at least 80% of mammalian genomic DNA can be actively transcribed (in one or more types of cells), with the majority of this 80% considered to be ncRNA. Both DNA and RNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language. During transcription, a DNA sequence is read by an RNA polymerase, which produces a complementary, antiparallel RNA strand called a primary transcript. Transcription proceeds in the following general steps: # RNA polymerase, together with one or more general transcription factors, binds to promoter DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase II
RNA polymerase II (RNAP II and Pol II) is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription. Discovery Early studies suggested a minimum of two RNAPs: one which synthesized rRNA in the nucleolus, and one which synthesized other RNA in the nucleoplasm, part of the nucleus but outside the nucleolus. In 1969, science experimentalists Robert Roeder and William Rutter definitively discovered an additional RNAP that was responsible for transcription of some kind of RNA in the nucleoplasm. The finding was obtained by the use of ion-exchange chromatography via DEAE coated Sephadex beads. The technique separated the enzymes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PABPC1
Polyadenylate-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PABPC1'' gene. The protein PABP1 binds mRNA and facilitates a variety of functions such as transport into and out of the nucleus, degradation, translation, and stability. There are two separate PABP1 proteins, one which is located in the nucleus (PABPN1) and the other which is found in the cytoplasm (PABPC1). The location of PABP1 affects the role of that protein and its function with RNA. Function The poly(A)-binding protein (PAB or PABP), which is found complexed to the 3' poly(A) tail of eukaryotic mRNA, is required for poly(A) lengthening and the termination of translation. In humans, the PABPs comprise a small nuclear isoform and a conserved gene family of other poly(A)-binding proteins. upplied by OMIMref name="entrez"> PABPC1 is usually diffused within the cytoplasm and concentrated at sites of high mRNA concentration such as stress granules, processing bodies, and locations of high translat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
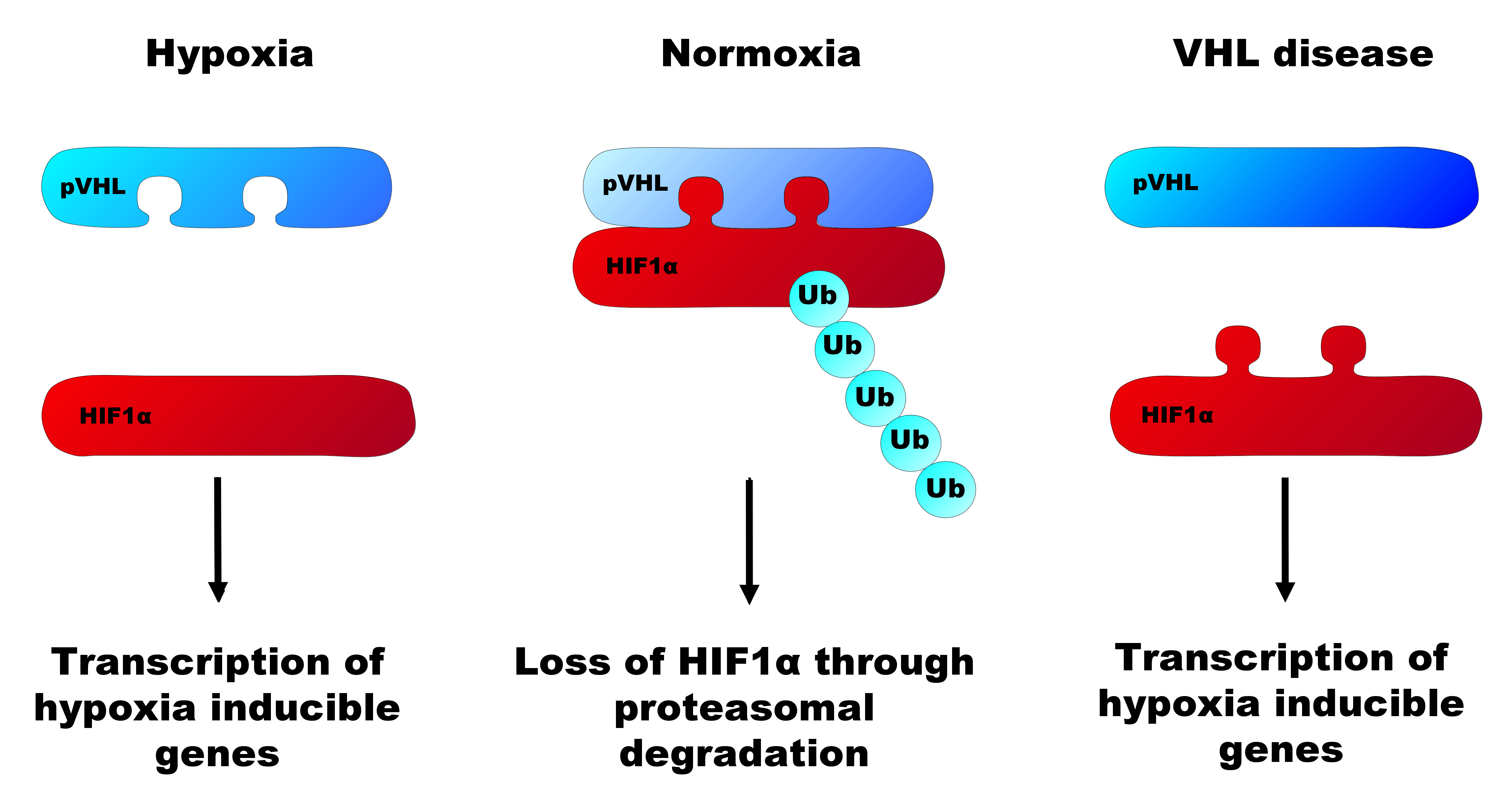
Von Hippel–Lindau Tumor Suppressor
) hockey league, Supreme Hockey League The Von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor also known as pVHL is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''VHL'' gene. Mutations of the VHL gene are associated with Von Hippel–Lindau disease. Function The protein encoded by the VHL gene is the substrate recognition component of a protein complex that includes elongin B, elongin C, and cullin-2, and possesses E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. This complex is involved in the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which are transcription factors that play a central role regulating gene expression in response to changing oxygen levels. RNA polymerase II subunit POLR2G/RPB7 is also reported to be a target of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been observed. The resultant protein is produced in two forms, an 18 kDa and a 30 kDa protein that functions as a tumor suppressor. The main action of the VH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Nucleus
The cell nucleus (pl. nuclei; from Latin or , meaning ''kernel'' or ''seed'') is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells usually have a single nucleus, but a few cell types, such as mammalian red blood cells, have no nuclei, and a few others including osteoclasts have many. The main structures making up the nucleus are the nuclear envelope, a double membrane that encloses the entire organelle and isolates its contents from the cellular cytoplasm; and the nuclear matrix, a network within the nucleus that adds mechanical support. The cell nucleus contains nearly all of the cell's genome. Nuclear DNA is often organized into multiple chromosomes – long stands of DNA dotted with various proteins, such as histones, that protect and organize the DNA. The genes within these chromosomes are structured in such a way to promote cell function. The nucleus maintains the integrity of genes and controls the activities of the cell by regulating gene expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
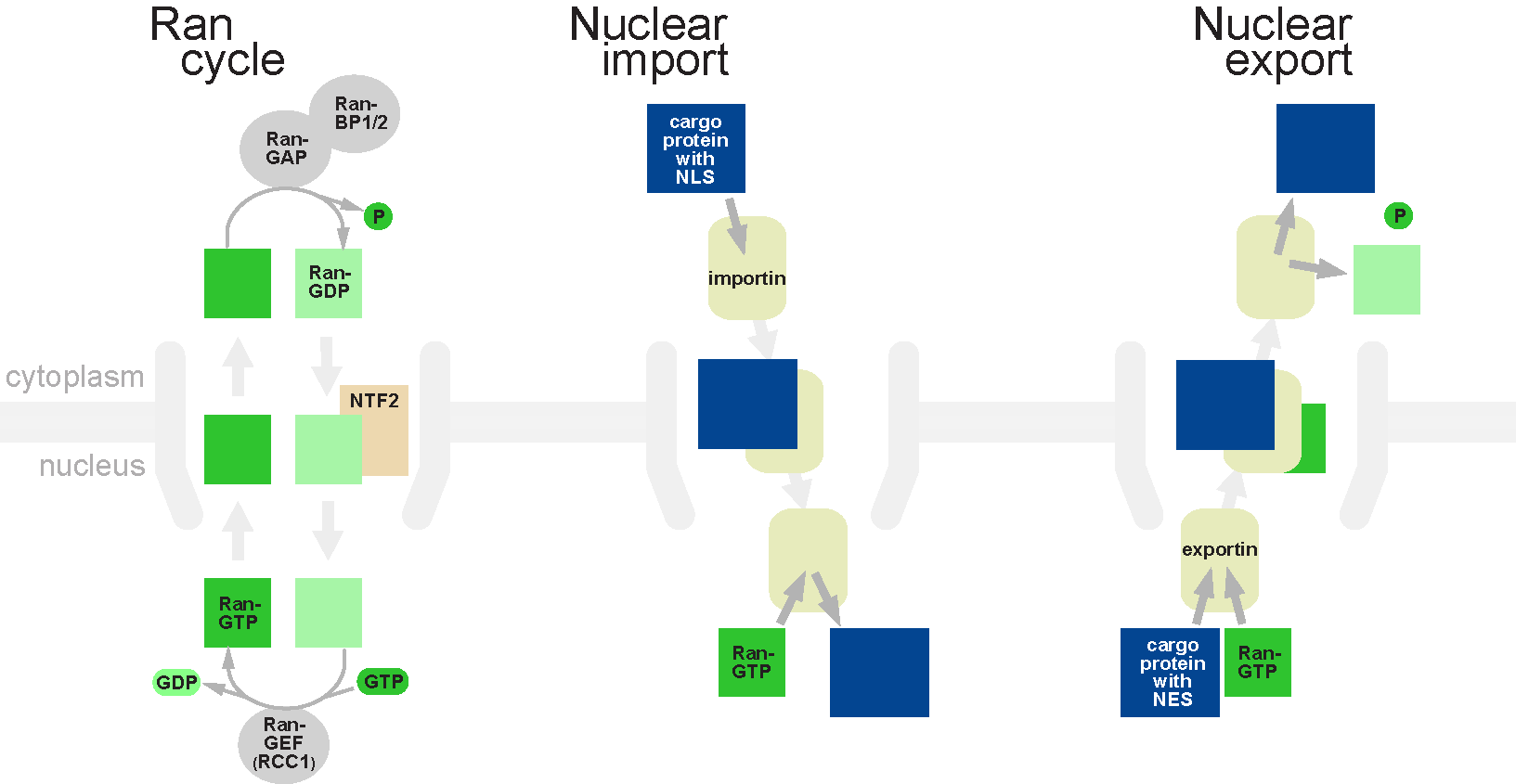
Nuclear Transport
Nuclear transport refers to the mechanisms by which molecules move across the nuclear membrane of a cell. The entry and exit of large molecules from the cell nucleus is tightly controlled by the nuclear pore complexes (NPCs). Although small molecules can enter the nucleus without regulation, macromolecules such as RNA and proteins require association with transport factors known as nuclear transport receptors, like karyopherins called importins to enter the nucleus and exportins to exit. Nuclear import Protein that must be imported to the nucleus from the cytoplasm carry nuclear localization signals (NLS) that are bound by importins. An NLS is a sequence of amino acids that acts as a tag. They are most commonly hydrophilic proteins containing lysine and arginine residues, although diverse NLS sequences have been documented. Proteins, transfer RNA, and assembled ribosomal subunits are exported from the nucleus due to association with exportins, which bind signaling sequences called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Translation (biology)
In molecular biology and genetics, translation is the process in which ribosomes in the cytoplasm or endoplasmic reticulum synthesize proteins after the process of transcription (biology), transcription of DNA to RNA in the cell's nucleus (cell), nucleus. The entire process is called gene expression. In translation, mRNA, messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded in a ribosome, outside the nucleus, to produce a specific amino acid chain, or polypeptide. The polypeptide later protein folding, folds into an Activation energy, active protein and performs its functions in the Cell (biology), cell. The ribosome facilitates decoding by inducing the binding of Base pair, complementary tRNA anticodon sequences to mRNA codons. The tRNAs carry specific amino acids that are chained together into a polypeptide as the mRNA passes through and is "read" by the ribosome. Translation proceeds in three phases: # Initiation: The ribosome assembles around the target mRNA. The first tRNA is attached a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)