|
Engineers Line Reference
{{Use British English, date=April 2020 An Engineer's Line Reference (ELR) is a three alpha, or four alpha-numeric, code used to uniquely identify a railway line on the main-line railway of Britain owned, or maintained, by Network Rail but official railway records retain the ELR codes for lifted branch lines and any structures such as bridge abutments, tunnels, viaducts, retaining walls etc., still maintained by the former British Railways Properties Board. Highways England's Historical Railways Estate group succeeded that organisation and further changes recently came about with the National Highways Organisation. Such structures are identified on records by the locational branch mileage and chainage and is repeated on the actual structure and therefore essential for reporting to site for works projects and maintenance, and most important, for any mishaps. In particular, bridge strikes are still prevalent by high-sided vehicles and Network Rail fix a metal plate to bridge abutments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Rail
Network Rail Limited is the owner (via its subsidiary Network Rail Infrastructure Limited, which was known as Railtrack plc before 2002) and infrastructure manager of most of the railway network in Great Britain. Network Rail is an "arm's length" public body of the Department for Transport with no shareholders, which reinvests its income in the railways. Network Rail's main customers are the private train operating companies (TOCs), responsible for passenger transport, and freight operating companies (FOCs), who provide train services on the infrastructure that the company owns and maintains. Since 1 September 2014, Network Rail has been classified as a "public sector body". To cope with fast-increasing passenger numbers, () Network Rail has been undertaking a £38 billion programme of upgrades to the network, including Crossrail, electrification of lines and upgrading Thameslink. In May 2021, the Government announced its intent to replace Network Rail in 2023 with a ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Railways Estate
The Historical Railways Estate (HRE) is a group of over 3,200 structures—predominantly bridges, but also including tunnels, embankments, and other works—associated with former railways in the United Kingdom. The structures are owned by the Department for Transport (DfT) and managed by National Highways (NH). Controversially, NH has proposed to demolish or infill dozens of bridges. Background The railways came into public ownership as a result of the Transport Act 1947. When they were privatised in 1997, operational infrastructure became the responsibility of Railtrack and then Network Rail. The Historical Railways Estate is the land and infrastructure associated with closed lines. This transferred to BRB (Residuary) Limited, which was dissolved in 2013, and the HRE was transferred to the Highways Agency, which later became Highways England (HE) and then National Highways (NH). NH states that the HRE comprises 2,055 bridges, 152 tunnels, 93 viaducts and aqueducts, 643 partiall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Eastern Main Line
The South Eastern Main Line is a major long-distance railway route in South East England, UK, one of the three main routes crossing the county of Kent, going via Sevenoaks, Tonbridge, Ashford and Folkestone to Dover. The other routes are the Chatham Main Line which runs along the north Kent coast to Ramsgate or Dover via Chatham and High Speed 1 which runs through the centre of Kent to the coast at Folkestone where it joins the Channel Tunnel. History Construction The line was built by the South Eastern Railway (SER), which was in competition with the London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LCDR), hence the duplication of routes in Kent. The original main line was given sanction by Act of Parliament in 1836. The route first authorised was from via Oxted, Tunbridge, Maidstone, Ashford and Folkestone. The route was to make use of the existing London and Croydon Railway and London and Greenwich Railway companies' tracks. The SER did not have much spare capital. As a cost-cutt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charing Cross Railway Station
Charing Cross railway station (also known as London Charing Cross) is a central London railway terminus between the Strand and Hungerford Bridge in the City of Westminster. It is the terminus of the South Eastern Main Line to Dover via Ashford. All trains are operated by Southeastern, which provides the majority of commuter and regional services to south-east London and Kent. It is connected to Charing Cross Underground station and is near to Embankment Underground station and Embankment Pier. The station was originally opened by the South Eastern Railway in 1864. It takes its name from its proximity to the road junction Charing Cross, the notional "centre of London" from which distances from the city are measured. During the 19th century the station became the main London terminus for continental traffic via boat trains, and served several prestigious international services. It was badly damaged by an engineering accident in 1905 and extensively rebuilt, subsequently beco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonbridge Railway Station
Tonbridge railway station is on the South Eastern Main Line in England, serving the town of Tonbridge, Kent. It is from London Charing Cross via . Trains calling at the station are operated by Southeastern and Southern. Tonbridge forms a junction between the South Eastern Main Line, the Hastings Line and the Redhill–Tonbridge line. There are four platforms. Platform 4 is a terminating platform. History The South Eastern Railway (SER) first reached Tonbridge (then known as ''Tunbridge'') in May 1842. The site of the original station was on the east side of the road bridge over the railway, opposite its current location to the west of the bridge. The building of the station obliterated the last remains of Tonbridge Priory. At the time, the line ran to London Bridge via Redhill and Croydon, using the Brighton Main Line. It served as a temporary terminus until December 1842, when the line reached Ashford. A couple of years later the through line to Dover opened. A smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
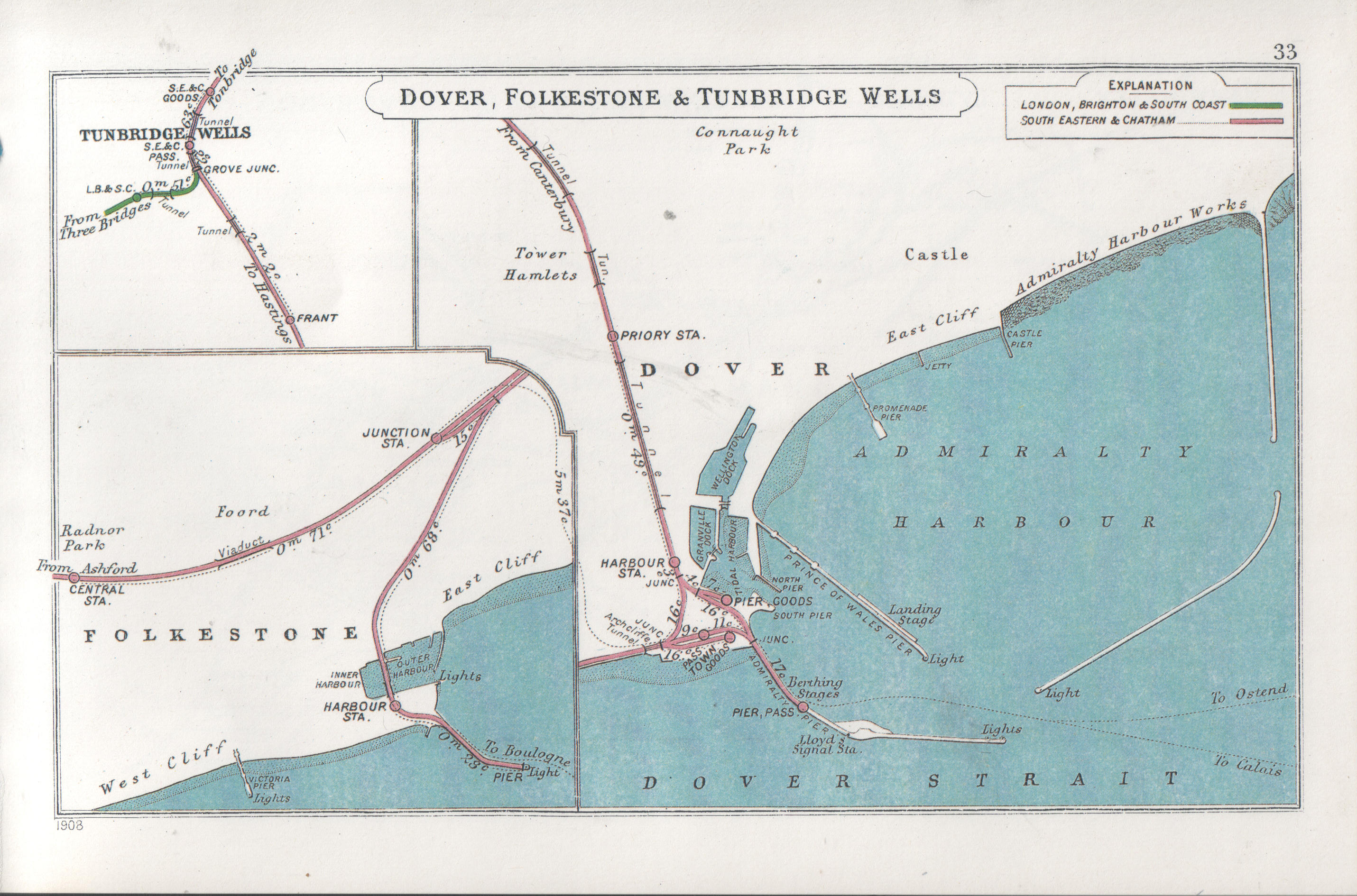
Dover Priory Railway Station
Dover Priory railway station is the southern terminus of the South Eastern Main Line in England, and is the main station serving the town of Dover, Kent, the other open station being , on the outskirts. It is down the line from London Victoria. The station and all trains that serve the station are operated by Southeastern. This station is a 25 min walk away from the Ferry Port. History Dover Priory opened on 22 July 1861 as the temporary terminus of the London, Chatham & Dover Railway (LCDR). It became a through station on 1 November 1861, with the completion of a tunnel through the Western Heights to gain access to the Western Docks area, where LCDR created Dover Harbour station The station was known as Dover Town but was renamed in July 1863 (leading to rival SER to adopt the name for one of its Dover stations). In 1868 stationmaster Edward Walsh(e) was murdered by 18-year-old Thomas Wells, a porter for the LCDR, after having rebuked him for poor work. Wells was convicte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton Main Line
The Brighton Main Line (also known as the South Central Main Line) is a major railway line in the United Kingdom that links Brighton, on the south coast of England, with central London. In London the line has two branches, out of and stations respectively, which join up in Croydon and continue towards Brighton as one line. The line is electrified throughout using the third rail system. Aside from London and Brighton themselves, the line serves multiple large urban areas along its route, including Redhill, eastern Crawley, Haywards Heath and Burgess Hill. It also serves the major London suburbs of south-west Battersea, Balham, Streatham, Croydon and Purley, as well as London Gatwick Airport the second-busiest passenger airport in the country. In addition, the line operates as a "trunk" route for both mainline and suburban services all across Sussex, east Surrey and the southern boroughs of London. Towns such as Sutton, Epsom, Caterham, Reigate, East Grinstead, Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Victoria Railway Station
Victoria station, also known as London Victoria, is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station in Victoria, in the City of Westminster, managed by Network Rail. Named after the nearby Victoria Street (not the Queen), the main line station is a terminus of the Brighton Main Line to and and the Chatham Main Line to and Dover via . From the main lines, trains can connect to the Catford Loop Line, the Dartford Loop Line, and the Oxted line to and . Southern operates most commuter and regional services to south London, Sussex and parts of east Surrey, while Southeastern operates trains to south-east London and Kent, alongside limited services operated by Thameslink. Gatwick Express trains run direct to Gatwick. The Underground station is on the Circle and District lines between and , and the Victoria line between and . The area around the station is an important interchange for other forms of transport: a local bus station is in the forecourt an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brighton Railway Station
Brighton railway station is the southern terminus of the Brighton Main Line in England, and the principal station serving the city of Brighton, East Sussex. It is from via . The station is managed by Govia Thameslink Railway, which operates all of the services. It was built by the London & Brighton Railway in 1840–41, initially only connecting Brighton to Shoreham-by-Sea, westwards along the coast, in May 1840. It finally connected a year later inland to Haywards Heath and London Bridge in September 1841 via the just-completed Clayton Tunnel; and then in 1846 to the county town of Lewes to the east via the London Road Viaduct. The railway became the London, Brighton & South Coast Railway in 1846 following mergers with other railways with lines between Portsmouth and Hastings. With over 17 million passenger entries and exits in 2018/19, Brighton is the seventh-busiest station in the country outside London. History and development The London & Brighton Railway (L&BR) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Kent Line
The North Kent Line is a railway line which branches off the South East Main Line at St Johns junction west of Lewisham station in Greater London and runs to Rochester Bridge Junction near Strood, Medway where it links to the Chatham Main Line. The section from Charlton to Dartford is also referred to as the "Woolwich Line" in the context of Southeastern Metro services. History Construction The North Kent Line was the means by which the South Eastern Railway (SER) was able to connect its system to London at London Bridge. In 1846 the SER purchased the Thames and Medway Canal tunnel near Higham and laid railway tracks through it; in 1847 trains were working through from the Strood terminus, on the River Medway to Gravesend. From 30 July 1849 the line was extended, via Blackheath, to a junction with the London and Greenwich Railway at North Kent East Junction, near Deptford, and through trains were now able to operate. Electrification The line is electrified (750 V DC third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge Miles And Chains
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, and the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge (dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese) is one of the oldest arch bridges still in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_p142_-_Victoria_Station_(plan).jpg)

