|
Emoia Kuekenthali
Kuekenthal's emo skink (''Emoia kuekenthali'') is a species of skink. It is found in Indonesia and the Admiralty Islands The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-co .... References Emoia Reptiles of Indonesia Reptiles of Papua New Guinea Reptiles described in 1895 Taxa named by Oskar Boettger Skinks of New Guinea {{Skink-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oskar Boettger
Oskar Boettger (german: Böttger; 31 March 1844 – 25 September 1910) was a German zoologist who was a native of Frankfurt am Main. He was an uncle of the noted malacologist Caesar Rudolf Boettger (1888–1976). From 1863 to 1866 he studied at the Bergakademie Freiberg, then worked for a year in a chemical factory in Frankfurt am Main."Boettger, Oskar" p. 410. In: (1955). '' Neue Deutsche Biographie (NDB). Band 2''. Berlin: Duncker & Humblot. . (in German). In 1869 he received his doctorate from the . The following year (1870), he became a |
Species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction. Other ways of defining species include their karyotype, DNA sequence, morphology, behaviour or ecological niche. In addition, paleontologists use the concept of the chronospecies since fossil reproduction cannot be examined. The most recent rigorous estimate for the total number of species of eukaryotes is between 8 and 8.7 million. However, only about 14% of these had been described by 2011. All species (except viruses) are given a two-part name, a "binomial". The first part of a binomial is the genus to which the species belongs. The second part is called the specific name or the specific epithet (in botanical nomenclature, also sometimes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skink
Skinks are lizards belonging to the family Scincidae, a family in the infraorder Scincomorpha. With more than 1,500 described species across 100 different taxonomic genera, the family Scincidae is one of the most diverse families of lizards. Skinks are characterized by their smaller legs in comparison to typical lizards and are found in different habitats except arctic and subarctic regions. Description Skinks look like lizards of the family Lacertidae (sometimes called ''true lizards''), but most species of skinks have no pronounced neck and relatively small legs. Several genera (e.g., ''Typhlosaurus'') have no limbs at all. This is not true for all skinks, however, as some species such as the red-eyed crocodile skink have a head that is very distinguished from the body. These lizards also have legs that are relatively small proportional to their body size. Skinks' skulls are covered by substantial bony scales, usually matching up in shape and size, while overlapping. Other gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
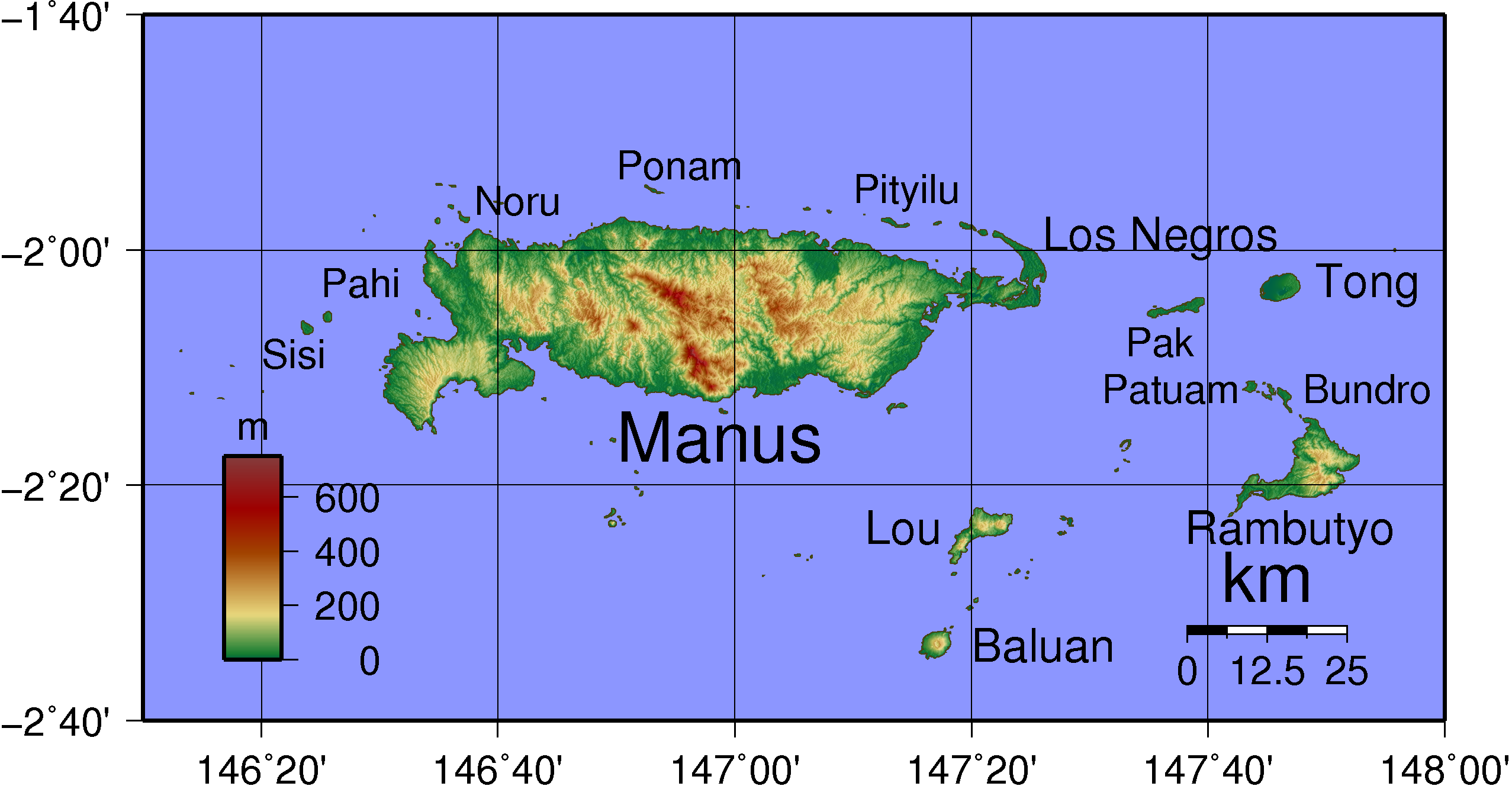
Admiralty Islands
The Admiralty Islands are an archipelago group of 18 islands in the Bismarck Archipelago, to the north of New Guinea in the South Pacific Ocean. These are also sometimes called the Manus Islands, after the largest island. These rainforest-covered islands form part of Manus Province, the smallest and least-populous province of Papua New Guinea, in its Islands Region. The total area is . Many of the Admiralty Islands are atolls and uninhabited. Islands The larger islands in the center of the group are Manus Island and Los Negros Island. The other larger islands are Tong Island, Pak Island, Rambutyo Island, Lou Island, and Baluan Island to the east, Mbuke Island to the south and Bipi Island to the west of Manus Island. Other islands that have been noted as significant places in the history of Manus include Ndrova Island, Pitylu Island and Ponam Island. Geography The temperature of the Admiralty Islands varies little throughout the year, reaching daily highs of and at night. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emoia
''Emoia'' is a genus of skinks, lizards in the subfamily Eugongylinae. The genus ''Emoia'' belongs to a group of genera mainly from the southwestern Pacific-Australian region. These small skinks are commonly known as emoias or skinks. Species List of 78 valid ''Emoia'' species and their respective authors, geographical ranges, and common names from the Reptile Database: ''Nota bene'': A binomial authority In taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called nomenclature ("two-name naming system") or binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, bot ... in parentheses indicates that the species was originally described in a genus other than ''Emoia''. References {{Taxonbar, from=Q898029 Lizard genera Taxa named by John Edward Gray ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Indonesia
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Of Papua New Guinea
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated around 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles Described In 1895
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates ( lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile orders, historically combined with that of modern amphibians, is called herpetology. The earliest known proto-reptiles originated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taxa Named By Oskar Boettger
In biology, a taxon (back-formation from ''taxonomy''; plural taxa) is a group of one or more populations of an organism or organisms seen by taxonomists to form a unit. Although neither is required, a taxon is usually known by a particular name and given a particular ranking, especially if and when it is accepted or becomes established. It is very common, however, for taxonomists to remain at odds over what belongs to a taxon and the criteria used for inclusion. If a taxon is given a formal scientific name, its use is then governed by one of the nomenclature codes specifying which scientific name is correct for a particular grouping. Initial attempts at classifying and ordering organisms (plants and animals) were set forth in Carl Linnaeus's system in ''Systema Naturae'', 10th edition (1758), as well as an unpublished work by Bernard and Antoine Laurent de Jussieu. The idea of a unit-based system of biological classification was first made widely available in 1805 in the intro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |