|
Eight-segment Display
An eight-segment display is a type of display based on eight segments that can be turned on or off according to the font pattern to be produced. It is similar to a nine-segment display whose middle vertical bars are vertical, except that on an eight-segment display, the bars ''F'' and ''G'' are merged. Applications It was used, for instance, in the calculator Sharp EL-8, producing more rounded digits than a seven-segment display, but fewer possible digits it can display because the bars ''F'' and ''G'' are merged (see table below). Displaying An eight segment display can sometimes display characters with less readability because the segments ''F'' and ''G'' are combined and the corners are rounded. It is unable to display the following characters for this reason: Examples File:Sharp EL-8 The First Portable Electronic Calculator.jpg, Sharp EL-8 with eight-segment displays File:Sharp EL-8 Itron vacuum-fluorescent Display Tube.jpg, Eight-segment display of the Sharp EL-8 Fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine-segment Display
A nine-segment display is a type of display based on nine segments that can be turned on or off according to the graphic pattern to be produced. It is an extension of the more common seven-segment display, having an additional two diagonal or vertical segments (one between the top and the middle, and the other between the bottom and the horizontal segments). It provides an efficient method of displaying alphanumeric characters. The letters displayed by a nine-segment display are not consistently uppercase or lowercase in shape. A common compromise is to use a lower-case "n" instead of "N". Depending on the design of the display segments, the use of the extra two segments may be avoided whenever possible, as in the Nixxo X-Page "tall" lowercase "r" and "y". Perhaps to avoid this awkward inconsistency, the Scope Geo N8T does not allow the use of uppercase or lowercase versions of the letters "J" (even though it could easily be displayed on a 7-segment display). Some other letters li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharp EL-8
The Sharp EL-8, also known as the ELSI-8, was one of the earliest mass-produced hand-held electronic calculators and the first hand-held calculator to be made by Sharp. Introduced around the start of 1971, it was based on Sharp's preceding QT-8D and QT-8B compact desktop calculators and used the same logic circuits, but it was redesigned to fit in a much smaller case. Most electronic calculators before the EL-8 were intended for desktop use. Sharp's predecessor to the EL-8, the battery-powered QT-8B, was just a portable version of a compact desk calculator. The EL-8 was much smaller, small enough to be used in one's hand: long, wide, and thick, and weighing with batteries. Although it was still too bulky to easily fit in a pocket, it was an important step toward the development of the pocket calculator. The EL-8's original price in Japan was 84,800 Japanese yen. The retail price in 1971 was . The operation and performance of the EL-8 are identical to its predecessor calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
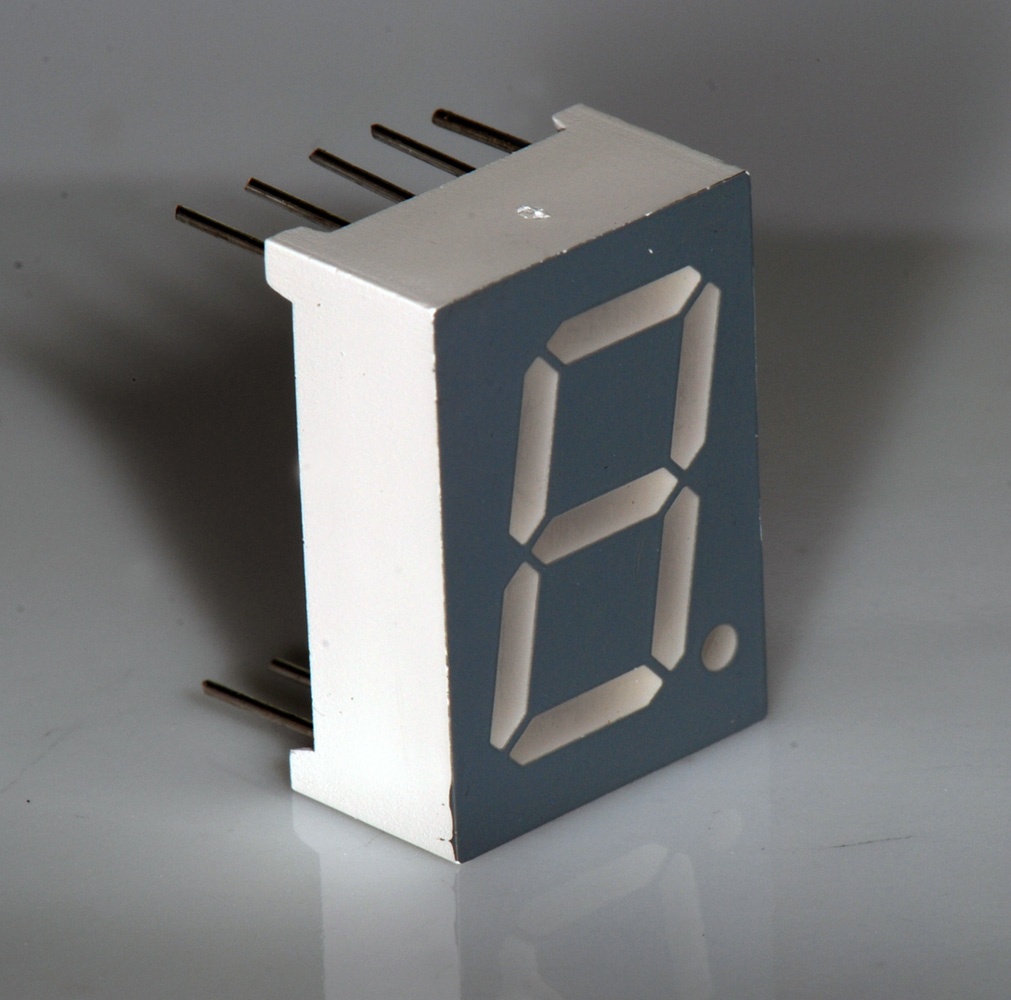
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of LEDs in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven-segment Display
A seven-segment display is a form of electronic display device for displaying decimal numerals that is an alternative to the more complex dot matrix displays. Seven-segment displays are widely used in digital clocks, electronic meters, basic calculators, and other electronic devices that display numerical information. History Seven-segment representation of figures can be found in patents as early as 1903 (in ), when Carl Kinsley invented a method of telegraphically transmitting letters and numbers and having them printed on tape in a segmented format. In 1908, F. W. Wood invented an 8-segment display, which displayed the number 4 using a diagonal bar (). In 1910, a seven-segment display illuminated by incandescent bulbs was used on a power-plant boiler room signal panel. They were also used to show the dialed telephone number to operators during the transition from manual to automatic telephone dialing. They did not achieve widespread use until the advent of LEDs in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nine-segment Display
A nine-segment display is a type of display based on nine segments that can be turned on or off according to the graphic pattern to be produced. It is an extension of the more common seven-segment display, having an additional two diagonal or vertical segments (one between the top and the middle, and the other between the bottom and the horizontal segments). It provides an efficient method of displaying alphanumeric characters. The letters displayed by a nine-segment display are not consistently uppercase or lowercase in shape. A common compromise is to use a lower-case "n" instead of "N". Depending on the design of the display segments, the use of the extra two segments may be avoided whenever possible, as in the Nixxo X-Page "tall" lowercase "r" and "y". Perhaps to avoid this awkward inconsistency, the Scope Geo N8T does not allow the use of uppercase or lowercase versions of the letters "J" (even though it could easily be displayed on a 7-segment display). Some other letters li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
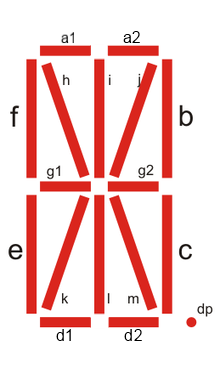
Fourteen-segment Display
A fourteen-segment display (FSD) (sometimes referred to as a starburst display or Union Jack display) is a type of display based on 14 segments that can be turned on or off to produce letters and numerals. It is an expansion of the more common seven-segment display, having an additional four diagonal and two vertical segments with the middle horizontal segment broken in half. A seven-segment display suffices for numerals and certain letters, but unambiguously rendering the ISO basic Latin alphabet requires more detail. A slight variation is the sixteen-segment display which allows additional legibility in displaying letters or other symbols. A decimal point or comma may be present as an additional segment, or pair of segments; the comma (used for triple-digit groupings or as a decimal separator in many regions) is commonly formed by combining the decimal point with a closely 'attached' leftwards-descending arc-shaped segment. Electronic alphanumeric displays may use LEDs, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixteen-segment Display
A sixteen-segment display (SISD) is a type of display based on sixteen segments that can be turned on or off to produce a graphic pattern. It is an extension of the more common seven-segment display, adding four diagonal and two vertical segments and splitting the three horizontal segments in half. Other variants include the fourteen-segment display which does not split the top or bottom horizontal segments, and the twenty-two-segment display that allows lower-case characters with descenders. Often a character generator is used to translate 7-bit ASCII character codes to the 16 bits that indicate which of the 16 segments to turn on or off. Applications Sixteen-segment displays were originally designed to display alphanumeric characters (Latin letters and Arabic digits). Later they were used to display Thai numerals and Persian characters. Non-electronic displays using this pattern existed as early as 1902. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
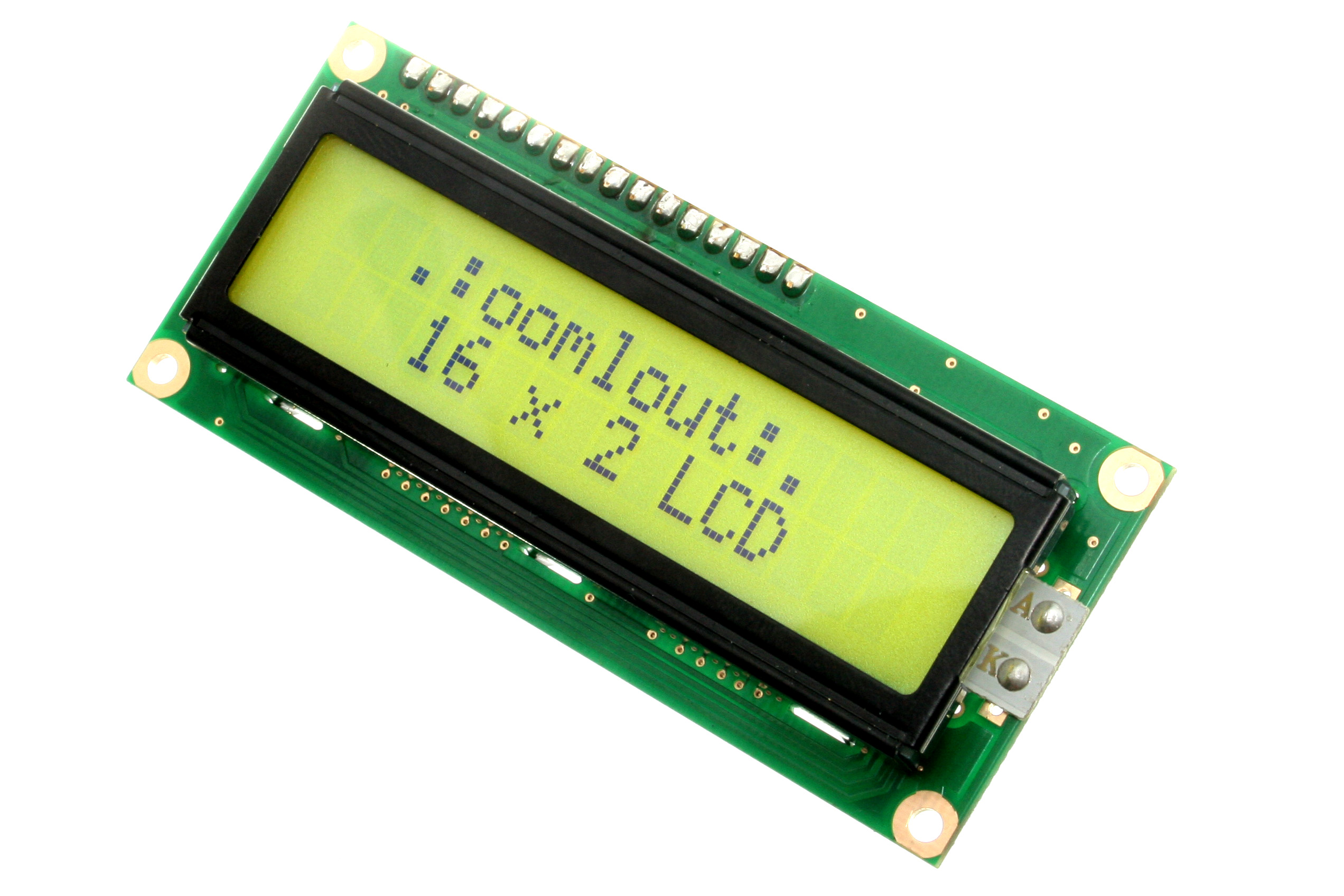
Dot Matrix Display
A dot-matrix display is a low cost electronic digital display device that displays information on machines such as clocks, watches, calculators, and many other devices requiring a simple alphanumeric (and/or graphic) display device of limited resolution. The display consists of a dot matrix of lights or mechanical indicators arranged in a rectangular configuration (other shapes are also possible, although not common) such that by switching on or off selected lights, text or graphics can be displayed. These displays are normally created with LCD, OLED, or Light-emitting diode, LED lights and can be found in some Thin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display, Thin Film Transistors. The Thin Film Transistors had an active display which allows the dot matrix to display different pixels with different colors at the same time. A dot matrix controller converts instructions from a processor into signals that turn on or off indicator elements in the matrix so that the required display is pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Fluorescent Display
A vacuum fluorescent display (VFD) is a display device once commonly used on consumer electronics equipment such as video cassette recorders, car radios, and microwave ovens. A VFD operates on the principle of cathodoluminescence, roughly similar to a cathode ray tube, but operating at much lower voltages. Each tube in a VFD has a phosphor-coated carbon anode that is bombarded by electrons emitted from the cathode filament.Chen, J., Cranton, W., & Fihn, M. (Eds.). (2016). Handbook of Visual Display Technology. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-14346-0 page 1610 onwards In fact, each tube in a VFD is a triode vacuum tube because it also has a mesh control grid. Unlike liquid crystal displays, a VFD emits very bright light with high contrast and can support display elements of various colors. Standard illumination figures for VFDs are around 640 cd/m2 with high-brightness VFDs operating at 4,000 cd/m2, and experimental units as high as 35,000 cd/m2 depending on the drive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |