|
Exploration Of Saturn
The exploration of Saturn has been performed solely by crewless probes. Three missions were flybys, which formed an extended foundation of knowledge about the system. The ''Cassini–Huygens'' spacecraft, launched in 1997, was in orbit from 2004 to 2017. Missions A list of previous and upcoming missions to the outer Solar System (including Saturn) can be found at the List of missions to the outer planets article. Flybys ''Pioneer 11'' flyby Saturn was first visited by ''Pioneer 11'' in September 1979. It flew within of the top of the planet's cloud layer. Low-resolution images were acquired of the planet and a few of its moons; the resolution of the images was not good enough to discern surface features. The spacecraft also studied the rings; among the discoveries were the thin F-ring and the fact that dark gaps in the rings are bright when viewed towards the Sun, or in other words, they are not empty of material. ''Pioneer 11'' also measured the temperature of Titan at 250 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cassini Saturn Orbit Insertion
Cassini may refer to: People * Cassini (surname) * Oleg Cassini (1913–2006), American fashion designer Cassini family: * Giovanni Domenico Cassini (1625–1712), Italian mathematician, astronomer, engineer, and astrologer * Jacques Cassini (1677–1756), French astronomer, son of Giovanni Domenico Cassini * César-François Cassini de Thury (1714–1784), French astronomer and cartographer, son of Jacques Cassini * Jean-Dominique, comte de Cassini (1748–1845), French astronomer, son of César-François Cassini de Thury * Alexandre Henri Gabriel de Cassini (1781–1832), French botanist and naturalist, son of Jean-Dominique de Cassini Planetary science * Cassini's laws on the motion of the Moon * Cassini Division, a gap in the rings of Saturn * ''Cassini–Huygens'', the space mission to examine Saturn and its moons, of which the ''Cassini'' orbiter was a part * Cassini (Martian crater) * Cassini (lunar crater) * 24101 Cassini, an asteroid * 24102 Jacquescassini, another aster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
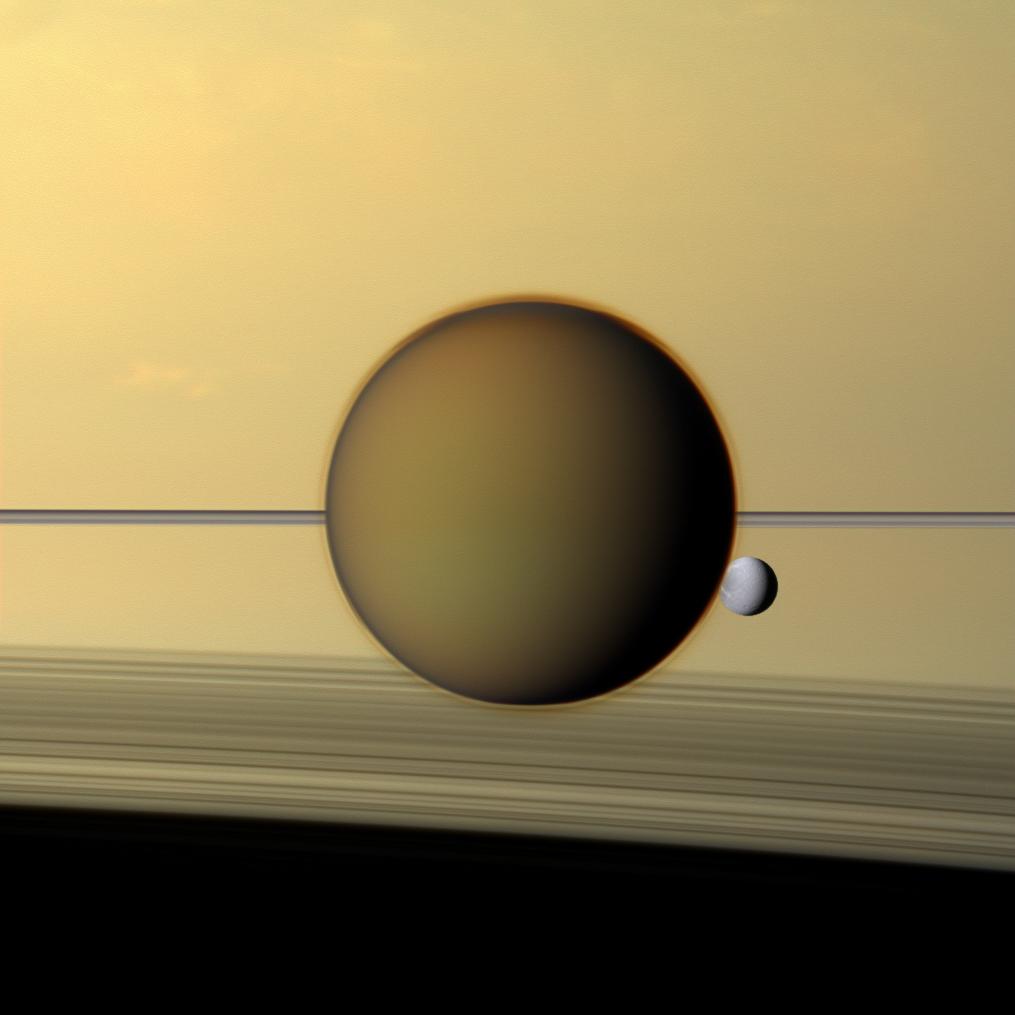
Enceladus
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn and the 18th-largest in the Solar System. It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan. It is covered by clean, freshly deposited snow hundreds of meters thick, making it one of the most reflective bodies of the Solar System. Consequently, its surface temperature at noon reaches only , far colder than a light-absorbing body would be. Despite its small size, Enceladus has a wide variety of surface features, ranging from old, heavily cratered regions to young, tectonically deformed terrain. Enceladus was discovered on August 28, 1789, by William Herschel, but little was known about it until the two Voyager spacecraft, '' Voyager 1'' and '' Voyager 2'', flew by Saturn in 1980 and 1981. In 2005, the spacecraft '' Cassini'' started multiple close flybys of Enceladus, revealing its surface and environment in greater detail. In particular, ''Cassini'' discovered water-rich plumes venting fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Life Investigation For Enceladus
Life Investigation For Enceladus (LIFE) was a proposed astrobiology mission concept that would capture icy particles from Saturn's moon Enceladus and return them to Earth, where they could be studied in detail for signs of life such as biomolecules. The LIFE orbiter concept was proposed by a team led by Peter Tsou to NASA's 13th Discovery Mission solicitation, but the mission was not selected by NASA for Phase-A design study. Mission concept Enceladus is a small icy moon with jets or geysers of water erupting from its surface that might be connected to active hydrothermal vents at its subsurface water ocean floor, where the moon's ocean meets the underlying rock, a prime habitat for life. The geysers could provide easy access for sampling the moon's subsurface ocean, and if there is microbial life in it, ice particles from the sea could contain the evidence astrobiologists need to identify them. The 15-year LIFE mission would use a 'Tanpopo' aerogel collector similar to the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enceladus Explorer
Enceladus Explorer (EnEx) is a planned interplanetary orbiter and lander mission equipped with a subsurface maneuverable ice melting probe suitable to assess the existence of life on Saturn's moon Enceladus. The astrobiology Enceladus Explorer project is funded by the German Aerospace Center (DLR), and is carried out by a research consortium of seven German universities. This collaborative project was started on 22 February 2012. Concept Enceladus is a small icy moon, seemingly similar in chemical makeup to comets, with jets or geysers of water erupting from its surface that might be connected to active hydrothermal vents at its subsurface water ocean floor, where the moon's ocean meets the underlying rock, a prime habitat for life. The geysers could provide easy access for sampling the moon's subsurface ocean, and if there is microbial life in it, ice particles from the sea could contain the evidence astrobiologists need to identify them. Water from the ocean is assumed to up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (, abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 35 locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. The DLR acts as the German space agency and is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries. As of 2020, the German Aerospace Center had a national budget of €1.348 billion. Overview DLR has approximately 10.000 employees at 30 locations in Germany. Institutes and facilities are spread over 13 sites, as well as offices in Brussels, Paris and Washington, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titan Mare Explorer
Titan Mare Explorer (TiME) is a proposed design for a lander for Saturn's moon Titan. TiME is a relatively low-cost, outer-planet mission designed to measure the organic constituents on Titan and would have performed the first nautical exploration of an extraterrestrial sea, analyze its nature and, possibly, observe its shoreline. As a Discovery-class mission it was designed to be cost-capped at US$425 million, not counting launch vehicle funding. It was proposed to NASA in 2009 by Proxemy Research as a scout-like pioneering mission, originally as part of NASA's Discovery Program. The TiME mission design reached the finalist stage during that Discovery mission selection, but was not selected, and despite attempts in the U.S. Senate failed to get earmark funding in 2013. A related Titan Submarine has also been proposed. Discovery-class finalist TiME was one of three Discovery Mission finalists that received US$3 million in May 2011 to develop a detailed concept study. The o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Journey To Enceladus And Titan
Journey to Enceladus and Titan (JET) is an astrobiology mission concept to assess the planetary habitability, habitability potential of Enceladus and Titan (moon), Titan, moons of Saturn. The JET orbiter concept was proposed in 2011 by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory to NASA's Discovery Program for its 13th mission, but it was not selected as a semi-finalist; Lucy (spacecraft), Lucy was selected on January 4, 2017. Concept Enceladus is a small icy moon, seemingly similar in chemical makeup to comets, with jets or geysers of water erupting from its surface that might be connected to active hydrothermal vents at its subsurface water ocean floor, where the moon's ocean meets the underlying rock, a prime habitat for life. The geysers could provide easy access for sampling the moon's subsurface ocean, and if there is Microorganism, microbial life in it, ice particles from the sea could contain the evidence astrobiologists need to identify them. An Organic compound, organic-rich world, Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Europa Jupiter System Mission
Europa may refer to: Places * Europa (Roman province), a province within the Diocese of Thrace * Europa (Seville Metro), Seville, Spain; a station on the Seville Metro * Europa City, Paris, France; a planned development * Europa Cliffs, Alexander Island, Antarctica * Europa Island, a small island in the Mozambique Channel which is a possession of France * Europa Point, Gibraltar; the southernmost point of Gibraltar * Europa Road, Gibraltar * Plaça d'Europa, Barcelona, Spain; a square * Europa, Missouri, US; a community * Europe, known as Europa in many European languages Celestial bodies * Europa (moon), a moon of Jupiter * 52 Europa, an asteroid Buildings and structures * Europa building, the seat of the European Council and Council of the European Union in Brussels, Belgium * Europa Hotel (other) * Europa Hut, a Swiss mountain hut * Europa Tower, Vilnius, Lithuania * Europa-Park, A theme park in Rust, Germany People * Europa of Macedon, the daughter of Philip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Enceladus (moon)
Enceladus is the sixth-largest moon of Saturn and the 18th-largest in the Solar System. It is about in diameter, about a tenth of that of Saturn's largest moon, Titan (moon), Titan. It is covered by clean, freshly deposited snow hundreds of meters thick, making it one of the most reflective bodies of the Solar System. Consequently, its surface temperature at noon reaches only , far colder than a light-absorbing body would be. Despite its small size, Enceladus has a wide variety of surface features, ranging from old, heavily impact crater, cratered regions to young, Tectonics, tectonically deformed terrain. Enceladus was discovered on August 28, 1789, by William Herschel, but little was known about it until the two Voyager program, Voyager spacecraft, ''Voyager 1'' and ''Voyager 2'', flew by Saturn in 1980 and 1981. In 2005, the spacecraft ''Cassini–Huygens, Cassini'' started multiple close flybys of Enceladus, revealing its surface and environment in greater detail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titan Saturn System Mission
Titan Saturn System Mission (TSSM) was a joint NASA– ESA proposal for an exploration of Saturn and its moons Titan and Enceladus, where many complex phenomena were revealed by '' Cassini''. TSSM was proposed to launch in 2020, get gravity assists from Earth and Venus, and arrive at the Saturn system in 2029. The 4-year prime mission would include a two-year Saturn tour, a 2-month Titan aero-sampling phase, and a 20-month Titan orbit phase. In 2009, a mission to Jupiter and its moons was given priority over ''Titan Saturn System Mission'', although TSSM will continue to be assessed for possible development and launch. Origin and status The Titan Saturn System Mission (TSSM) was officially created in January 2009 by the merging of the ESA's Titan and Enceladus Mission (TandEM) with NASA's Titan Explorer (2007) study, although plans to combine both concepts date at least back to early 2008. TSSM was competing against the Europa Jupiter System Mission (EJSM) proposal for fund ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gas Planet Size Comparisons
Gas is a state of matter that has neither a fixed volume nor a fixed shape and is a compressible fluid. A ''pure gas'' is made up of individual atoms (e.g. a noble gas like neon) or molecules of either a single type of atom ( elements such as oxygen) or from different atoms (compounds such as carbon dioxide). A ''gas mixture'', such as air, contains a variety of pure gases. What distinguishes gases from liquids and solids is the vast separation of the individual gas particles. This separation can make some gases invisible to the human observer. The gaseous state of matter occurs between the liquid and plasma states, the latter of which provides the upper-temperature boundary for gases. Bounding the lower end of the temperature scale lie degenerative quantum gases which are gaining increasing attention. High-density atomic gases super-cooled to very low temperatures are classified by their statistical behavior as either Bose gases or Fermi gases. For a comprehensive listing of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Titan (moon)
Titan is the largest moon of Saturn and the List of Solar System objects by size, second-largest in the Solar System. It is the only Natural satellite, moon known to have an atmosphere denser than the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's and is the only known object in space—other than Earth—on which there is clear evidence that stable bodies of liquid exist. Titan is one of seven List of gravitationally rounded objects of the Solar System, gravitationally rounded moons of Saturn and the second-most distant among them. Frequently described as a Planetary-mass moon, planet-like moon, Titan is 50% larger in diameter than Earth's Moon and 80% more Mass, massive. It is the second-largest moon in the Solar System after Jupiter's Ganymede (moon), Ganymede and is larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury; yet Titan is only 40% as massive as Mercury, because Mercury is mainly iron and rock while much of Titan is ice, which is less dense. Discovered in 1655 by the Dutch astronomer Christiaan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |