|
Etruscan Architecture
Etruscan architecture was created between about 900 BC and 27 BC, when the expanding civilization of ancient Rome finally absorbed Etruscan civilization. The Etruscans were considerable builders in stone, wood and other materials of temples, houses, tombs and city walls, as well as bridges and roads. The only structures remaining in quantity in anything like their original condition are tombs and walls, but through archaeology and other sources we have a good deal of information on what once existed. From about 630 BC, Etruscan architecture was heavily influenced by Greek architecture, which was itself developing through the same period. In turn it influenced Roman architecture, which in its early centuries can be considered as just a regional variation of Etruscan architecture. But increasingly, from about 200 BC, the Romans looked directly to Greece for their styling, while sometimes retaining Etruscan shapes and purposes in their buildings. The main monumental forms of Etru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tomba Dei Rilievi (Banditaccia)
The Tomb of the Reliefs () is an Etruscan tomb in the Banditaccia necropolis near Cerveteri, Italy. It was discovered in 1847 and has been dated to the end of the 4th century BC. It is a unique example of an Etruscan tomb which is decorated with stucco reliefs instead of the usual frescoes. Description The tomb belonged to the Matuna family according to inscriptions inside the chamber. The rectangular chamber is entered through a steeply descending stepped dromos. The center of the room is surrounded by a raised platform, which is separated by low ledges into 32 spaces to depose the dead. Above these are 12 oblong niches carved in the walls, which provided space for more deceased. The niches are modeled after beds with stucco pillows. The central niche in the rear wall is deeper, which allowed for a deceased couple to be placed side by side. Below this central niche are reliefs of Kerberos and an unidentified demon from the underworld. The demon has a fish tail and wields a ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Entablature
An entablature (; nativization of Italian , from "in" and "table") is the superstructure of moldings and bands which lies horizontally above columns, resting on their capitals. Entablatures are major elements of classical architecture, and are commonly divided into the architrave (the supporting member immediately above; equivalent to the lintel in post and lintel construction), the frieze (an unmolded strip that may or may not be ornamented), and the cornice (the projecting member below the pediment). The Greek and Roman temples are believed to be based on wooden structures, the design transition from wooden to stone structures being called petrification. Overview The structure of an entablature varies with the orders of architecture. In each order, the proportions of the subdivisions (architrave, frieze, cornice) are defined by the proportions of the column. In Roman and Renaissance interpretations, it is usually approximately a quarter of the height of the column. Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doric Order
The Doric order is one of the three orders of ancient Greek and later Roman architecture; the other two canonical orders were the Ionic and the Corinthian. The Doric is most easily recognized by the simple circular capitals at the top of the columns. Originating in the western Doric region of Greece, it is the earliest and, in its essence, the simplest of the orders, though still with complex details in the entablature above. The Greek Doric column was fluted, and had no base, dropping straight into the stylobate or platform on which the temple or other building stood. The capital was a simple circular form, with some mouldings, under a square cushion that is very wide in early versions, but later more restrained. Above a plain architrave, the complexity comes in the frieze, where the two features originally unique to the Doric, the triglyph and gutta, are skeuomorphic memories of the beams and retaining pegs of the wooden constructions that preceded stone Doric tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuscan Order
The Tuscan order (Latin ''Ordo Tuscanicus'' or ''Ordo Tuscanus'', with the meaning of Etruscan order) is one of the two classical orders developed by the Romans, the other being the composite order. It is influenced by the Doric order, but with un- fluted columns and a simpler entablature with no triglyphs or guttae. While relatively simple columns with round capitals had been part of the vernacular architecture of Italy and much of Europe since at least Etruscan architecture, the Romans did not consider this style to be a distinct architectural order (for example, the Roman architect Vitruvius did not include it alongside his descriptions of the Greek Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian orders). Its classification as a separate formal order is first mentioned in Isidore of Seville's 6th-century '' Etymologiae'' and refined during the Italian Renaissance. Sebastiano Serlio described five orders including a "Tuscan order", "the solidest and least ornate", in his fourth book of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corinthian Order
The Corinthian order (, ''Korinthiakós rythmós''; ) is the last developed and most ornate of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Ancient Roman architecture, Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order, which was the earliest, followed by the Ionic order. In Ancient Greek architecture, the Corinthian order follows the Ionic in almost all respects, other than the capitals of the columns, though this changed in Roman architecture. A Corinthian capital may be seen as an enriched development of the Ionic capital, though one may have to look closely at a Corinthian capital to see the Ionic volutes ("helices"), at the corners, perhaps reduced in size and importance, scrolling out above the two ranks of Acanthus (ornament), stylized acanthus leaves and stalks ("cauliculi" or ''caulicoles''), eight in all, and to notice that smaller volutes scroll inwards to meet each other on each side. The leaves may be quite stiff, schematic and dry, or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital (architecture), capital, which have been the subject of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
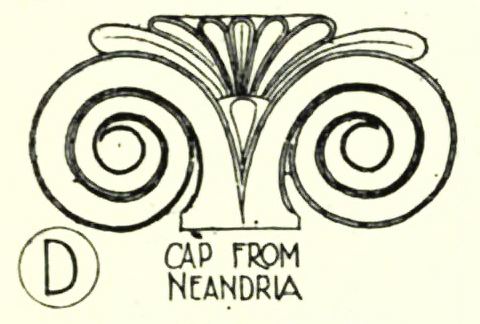
Aeolic Order
The Aeolic order or Aeolian order was an early classical order, order of Classical architecture. It has a strong similarity to the better known Ionic order, but differs in the Capital (architecture), capital, where a palmette rises between the two outer volutes, rather than them being linked horizontally by a form at the top of the capital. Many examples also show simplified details compared to the Ionic. "Proto-Aeolic" capitals of Southern Levant Decorated stone structures reminiscent of the Aeolic order, widely known as "Proto-Aeolic" or "Proto-Ionian" capitals, were especially common in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Capitals of this style were discovered in royal buildings and fortified city gates. They were built up for some ashlar masonry, ashlar masonries, an architectonic style reserved to Israelites, Israelite royal structures. One of them is 110 x 28 x 60 cm of dimension and also differs from the canon for its ornamental details, showing a triangular shape ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frontone A Del Grande Tempio Di Luni Con Concilio Degli Dei, 175-150 Ac
Frontone is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Pesaro e Urbino in the Italian region of Marche, located about west of Ancona and about southwest of Pesaro. Frontone borders the following municipalities: Cagli, Cantiano, Pergola, Scheggia e Pascelupo, Serra Sant'Abbondio. The town is home to a '' Rocca'' (castle), designed, among the others, by Francesco di Giorgio Martini Francesco di Giorgio Martini (1439–1501) was an Italian architect, engineer, painter, sculptor, and writer. As a painter, he belonged to the Sienese School. He was considered a visionary architectural theorist—in Nikolaus Pevsner's terms .... Climate References Cities and towns in the Marche {{Marche-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Florence
Florence ( ; ) is the capital city of the Italy, Italian region of Tuscany. It is also the most populated city in Tuscany, with 362,353 inhabitants, and 989,460 in Metropolitan City of Florence, its metropolitan province as of 2025. Florence was a centre of Middle Ages, medieval European trade and finance and one of the wealthiest cities of that era. It is considered by many academics to have been the birthplace of the Renaissance, becoming a major artistic, cultural, commercial, political, economic and financial center. During this time, Florence rose to a position of enormous influence in Italy, Europe, and beyond. Its turbulent political history includes periods of rule by the powerful House of Medici, Medici family and numerous religious and republican revolutions. From 1865 to 1871 the city served as the capital of the Kingdom of Italy. The Florentine dialect forms the base of Italian language, standard Italian and it became the language of culture throughout Italy due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talamone
Talamone (, ) is a town in Tuscany, on the west coast of central Italy, administratively a frazione of the comune of Orbetello, province of Grosseto, in the Tuscan Maremma. Talamone is easily reached from Via Aurelia, and is about from Grosseto and from Orbetello. Geography The village lies on a rocky promontory, which lies on the southern border of the Maremma nature reserve, in a dominant position along the whole stretch of coast arriving at Monte Argentario, Mount Argentario. The surrounding area is characterized by the presence of vegetation typical of Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean scrub and long sandy beaches, lined by pine trees. History According to Diodorus Siculus, the town was by the Argonauts named after the hero Telamon. However, this etymology is likely a mythological fabrication. It was an ancient and flourishing city already during the Etruscans, Etruscan period. It was the site of the Battle of Telamon in 225 BC between Roman and the Celtic armies. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luna (Etruria)
Luni is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the province of La Spezia, in the easternmost end of the Liguria region of northern Italy. It was founded by the Romans as Luna. It gives its name to Lunigiana, a region spanning eastern Liguria and northern Tuscany (province of Massa-Carrara). The commune was known as Ortonovo (from the name of one of its current ''frazione, frazioni'') until April 2017. It is now named after the ''frazione'' of Luni. Geography Located in a plain near the Tyrrhenian Sea and close to the borders with Tuscany, Luni is crossed by the river Magra (river), Magra and lies between Sarzana (7 km in north) and Carrara (5 km in south). It is 4 km far from Ortonovo, 15 km from Massa, Tuscany, Massa and 30 km from La Spezia. The village is served by National Highway 1 "Aurelia", crossed at Luni Mare by the Autostrada A12 (Italy), A12 motorway and counts a railway station on the Pisa–La Spezia–Genoa railway, Pisa-Genoa line. Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock consisting of carbonate minerals (most commonly calcite (CaCO3) or Dolomite (mineral), dolomite (CaMg(CO3)2) that have recrystallized under the influence of heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture, and is typically not Foliation (geology), foliated (Layered intrusion, layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphosed limestone, but its use in stonemasonry more broadly encompasses unmetamorphosed limestone. The extraction of marble is performed by quarrying. Marble production is dominated by four countries: China, Italy, India and Spain, which account for almost half of world production of marble and decorative stone. Because of its high hardness and strong wear resistance, and because it will not be deformed by temperature, marble is often used in Marble sculpture, sculpture and construction. Etymology The word "marble" derives from the Ancient Greek (), from (), "crystalline rock, shin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |