|
Erythrosuchid
Erythrosuchidae (meaning "red crocodiles" in Greek) are a family of large basal archosauriform carnivores that lived from the later Early Triassic (Olenekian) to the early Middle Triassic (Anisian). Naming The family Erythrosuchidae was named by David Meredith Seares Watson in 1917.D.M.S. Watson. 1917. "A sketch classification of the Pre-Jurassic tetrapod vertebrates". ''Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London'' 1917: 167–186 Description They were the apex predators of their day, with lengths of to almost . Their fossil remains are known to date from South Africa (Beaufort Group of the Karoo Basin), China, India and European Russia, from the Early to Middle Triassic. Erythrosuchids were unusually large and robust archosauromorphs. Several features set them apart from other archosauriformes and are also seen in later, more derived archosaurs. For example, they lack teeth on the palate, which are found in other early archosauriformes, such as '' Doswellia'' and eupar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosaur
Archosauria () or archosaurs () is a clade of diapsid sauropsid tetrapods, with birds and crocodilians being the only extant taxon, extant representatives. Although broadly classified as reptiles, which traditionally exclude birds, the cladistics, cladistic sense of the term includes all living and extinct relatives of birds and crocodilians such as non-avian dinosaurs, pterosaurs, phytosaurs, aetosaurs and rauisuchians as well as many marine reptile#Extinct groups, Mesozoic marine reptiles. Modern paleontologists define Archosauria as a crown group that includes the most recent common ancestor of living birds and crocodilians, and all of its descendants. The base of Archosauria splits into two clades: Pseudosuchia, which includes crocodilians and their extinct relatives; and Avemetatarsalia, which includes birds and their extinct relatives (such as non-avian dinosaurs and pterosaurs). Older definitions of the group Archosauria rely on shared morphology (biology), morphological ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
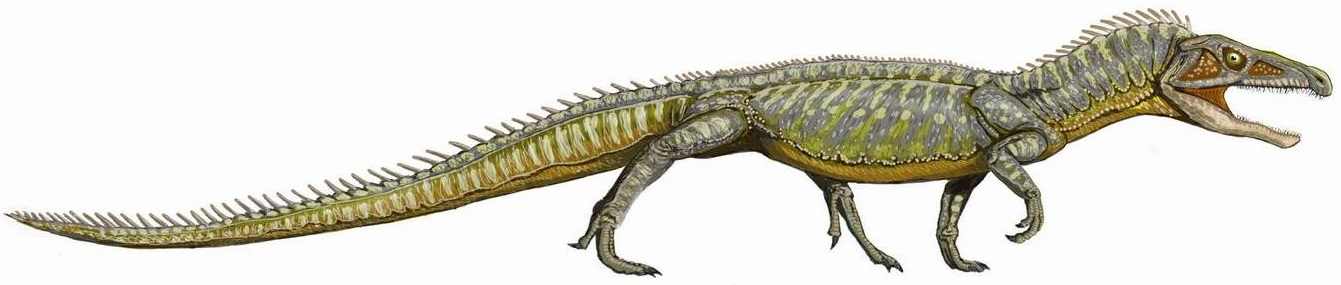
Erythrosuchus
''Erythrosuchus'' (from , 'red' and , 'crocodile') is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptiles from the early Triassic of South Africa. Remains have been found from the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo of South Africa. In the Late Triassic, the ecological niche left by ''Erythrosuchus'' was filled by archosaurs including ''Saurosuchus'' and ''Postosuchus''. Description ''Erythrosuchus'' was the largest predator of its time, and was around long. It walked on all fours and had limbs positioned semivertically under its body, unlike the more sprawling gait of most earlier reptiles. Its head was large and theropod-like, reaching a length of , and had sharp, conical teeth. ''Erythrosuchus'' was largest prehistoric animals, the largest erythrosuchid, but apart from its size, was largely similar in appearance to other related genera. It had a large head and comparatively short neck. One of the few distinguishing features of ''Erythrosuchus'' other th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterosuchid
Proterosuchidae is an early family of basal archosauriforms whose fossils are known from the Late Permian and the Early Triassic. The highest diversity of genera is known from European Russia, but fossils are also known from South Africa, India, China, Australia, Brazil and possibly Argentina. The name comes from Greek πρότερο- ("first") and σοῦχος ("crocodile"). Description They were slender, medium-sized (about long, largest specimens reached ), long-snouted and superficially crocodile-like animals, although they lacked the armoured scutes of true crocodiles, and their skeletal features are much more primitive. The limbs are short and indicate a sprawling posture, like contemporary lizards but unlike most later archosaurs. Their most characteristic feature is a distinct down-turning of the premaxilla (the front of the upper jaw, which overhangs the lower jaw). Evolutionary history The terminal Permian catastrophe, which killed off 95% of all types of life, c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauriform
Archosauriformes (Greek for 'ruling lizards', and Latin for 'form') is a clade of diapsid reptiles encompassing archosaurs and some of their close relatives. It was defined by Jacques Gauthier (1994) as the clade stemming from the last common ancestor of Proterosuchidae and Archosauria. Phil Senter (2005) defined it as the most exclusive clade containing '' Proterosuchus'' and Archosauria. Gauthier as part of the ''Phylonyms'' (2020) defined the clade as the last common ancestor of '' Gallus'', ''Alligator'', and '' Proterosuchus'', and all its descendants. Archosauriforms are a branch of archosauromorphs which originated in the Late Permian (roughly 252 million years ago) and persist to the present day as the two surviving archosaur groups: crocodilians and birds. Archosauriforms present several traits historically ascribed to the group Archosauria. These include serrated teeth set in deep sockets, a more active metabolism, and an antorbital fenestra (a hole in the skull in fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triassic
The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era and the seventh period of the Phanerozoic Eon. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic. The Triassic began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, which left the Earth's biosphere impoverished; it was well into the middle of the Triassic before life recovered its former diversity. Three categories of organisms can be distinguished in the Triassic record: survivors from the extinction event, new groups that flourished briefly, and other new groups that went on to dominate the Mesozoic Era. Reptiles, especially archosaurs, were the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilium (bone)
The ilium () (: ilia) is the uppermost and largest region of the coxal bone, and appears in most vertebrates including mammals and birds, but not bony fish. All reptiles have an ilium except snakes, with the exception of some snake species which have a tiny bone considered to be an ilium. The ilium of the human is divisible into two parts, the body and the wing; the separation is indicated on the top surface by a curved line, the arcuate line, and on the external surface by the margin of the acetabulum. The name comes from the Latin ('' ile'', ''ilis''), meaning "groin" or "flank". Structure The ilium consists of the body and wing. Together with the ischium and pubis, to which the ilium is connected, these form the pelvic bone, with only a faint line indicating the place of union. The body () forms less than two-fifths of the acetabulum; and also forms part of the acetabular fossa. The internal surface of the body is part of the wall of the lesser pelvis and gives o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spinal segment and the particular species. The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the vertebral body (also ''centrum'') is of bone and bears the load of the vertebral column. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles (pedicle of vertebral arch), two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava (ligaments of the spine). There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conduits for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premaxilla
The premaxilla (or praemaxilla) is one of a pair of small cranial bones at the very tip of the upper jaw of many animals, usually, but not always, bearing teeth. In humans, they are fused with the maxilla. The "premaxilla" of therian mammals has been usually termed as the incisive bone. Other terms used for this structure include premaxillary bone or ''os premaxillare'', intermaxillary bone or ''os intermaxillare'', and Goethe's bone. Human anatomy In human anatomy, the premaxilla is referred to as the incisive bone (') and is the part of the maxilla which bears the incisor teeth, and encompasses the anterior nasal spine and alar region. In the nasal cavity, the premaxillary element projects higher than the maxillary element behind. The palatal portion of the premaxilla is a bony plate with a generally transverse orientation. The incisive foramen is bound anteriorly and laterally by the premaxilla and posteriorly by the palatine process of the maxilla. It is formed from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxilla
In vertebrates, the maxilla (: maxillae ) is the upper fixed (not fixed in Neopterygii) bone of the jaw formed from the fusion of two maxillary bones. In humans, the upper jaw includes the hard palate in the front of the mouth. The two maxillary bones are fused at the intermaxillary suture, forming the anterior nasal spine. This is similar to the mandible (lower jaw), which is also a fusion of two mandibular bones at the mandibular symphysis. The mandible is the movable part of the jaw. Anatomy Structure The maxilla is a paired bone - the two maxillae unite with each other at the intermaxillary suture. The maxilla consists of: * The body of the maxilla: pyramid-shaped; has an orbital, a nasal, an infratemporal, and a facial surface; contains the maxillary sinus. * Four processes: ** the zygomatic process ** the frontal process ** the alveolar process ** the palatine process It has three surfaces: * the anterior, posterior, medial Features of the maxilla include: * t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triradiate Pelvic Girdle
The triradiate pelvic girdle is a shared feature common to archosaurs. The pelvis has three prongs, with an elongate pubis and ischium. This feature first appeared in the Erythrosuchidae, large basal archosaurian predators of the early Triassic The Triassic ( ; sometimes symbolized 🝈) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is t ... period. References * Benton, M. J. (2000), ''Vertebrate Paleontology'', 2nd Ed. p. 136; (2004) 3rd edition, Blackwell Science Ltd Reptile anatomy {{vertebrate-anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ischium
The ischium (; : ischia) is a paired bone forming the lower and back part of the hip bone. Situated below the ilium (bone), ilium and behind the pubis (bone), pubis, it is one of three regions whose fusion creates the coxal bone. The superior portion of this region forms approximately one-third of the acetabulum. Structure The ischium is made up of three parts–the body, the superior ramus and the inferior ramus. The body contains a prominent ischial spine, spine, which serves as the origin for the superior gemellus muscle. The indentation inferior to the spine is the lesser sciatic notch. Continuing down the posterior side, the ischial tuberosity is a thick, rough-surfaced prominence below the lesser sciatic notch. This is the portion ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubis (bone)
In vertebrates, the pubis or pubic bone () forms the lower and anterior part of each side of the hip bone. The pubis is the most forward-facing ( ventral and anterior) of the three bones that make up the hip bone. The left and right pubic bones are each made up of three sections; a superior ramus, an inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic bone is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat – the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubis is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body of pubis has: * a superior border or the pubic crest * a pubic tubercle at the lateral end of the pubic crest * three surfaces (anterior, posterior and medial). The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic bone. The bodies of the left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphysis. The r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |