|
Erechtheion
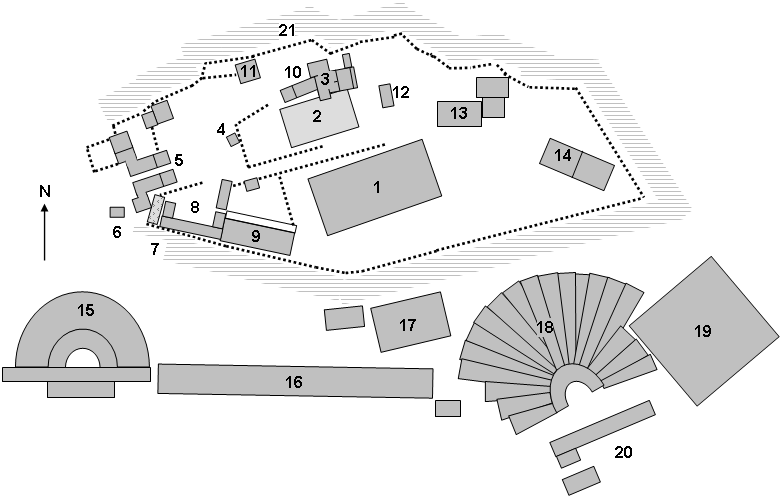
The Erechtheion (, latinized as Erechtheum ; , ) or Temple of Athena Polias is an ancient Greek Ionic temple on the north side of the Acropolis, Athens, which was primarily dedicated to the goddess Athena. The Ionic building, which housed the statue of Athena Polias, has in modern scholarship been called the Erechtheion (the sanctuary of Erechtheus or Poseidon) in the belief that it encompassed two buildings mentioned by the Greek-Roman geographer Pausanias: the Temple of Athena Polias and the Erechtheion. However, whether the Erechtheion referred to by Pausanias and other sources is indeed the Ionic temple or an entirely different building has become a point of contention in recent decades, with various scholars ruling out that Athena and Erechtheus were worshipped in a single building. Alternative suggested locations of the true Erechtheion include the structures on the Acropolis conventionally identified as the Arrephorion, the Sanctuary of Zeus Polieus, the Sanctuary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Greek Architecture
Ancient Greek architecture came from the Greeks, or Hellenes, whose Ancient Greece, culture flourished on the Greek mainland, the Peloponnese, the Aegean Islands, and in colonies in Asia Minor, Anatolia and Italy for a period from about 900 BC until the 1st century AD, with the earliest remaining architectural works dating from around 600 BC. Ancient Greek architecture is best known for its Ancient Greek temple, temples, many of which are found throughout the region, with the Parthenon regarded, now as in ancient times, as the prime example. Most remains are very incomplete ruins, but a number survive substantially intact, mostly outside modern Greece. The second important type of building that survives all over the Hellenic world is the Theatre of Ancient Greece#Characteristics of the buildings, open-air theatre, with the earliest dating from around 525–480 BC. Other architectural forms that are still in evidence are the processional gateway (''propylon''), the public square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Acropolis Of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens (; ) is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, Greece, and contains the remains of several Ancient Greek architecture, ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. The word ''Acropolis'' is . The term acropolis is generic and there are many other acropoleis in Greece. During ancient times the Acropolis of Athens was also more properly known as Cecropia, after the legendary serpent-man Cecrops I, Cecrops, the supposed first Athenian king. While there is evidence that the hill was inhabited as early as the 4th millennium BC, it was Pericles (–429 BC) in the fifth century BC who coordinated the construction of the buildings whose present remains are the site's most important ones, including the Parthenon, the Propylaia_(Acropolis_of_Athens), Propylaea, the Erechtheion and the Temple of Athena Nike. The Parthenon and the other buildings were seriously damaged during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Old Temple Of Athena
The Old Temple of Athena or the Archaios Neos () was an archaic Greek limestone Doric temple on the Acropolis of Athens probably built in the second half of the sixth-century BCE, and which housed the xoanon of Athena Polias. The existence of an archaic temple to Athena had long been conjectured from literary references until the discovery of substantial building foundations under the raised terrace between the Erechtheion and Parthenon in 1886 confirmed it. While it is uncontroversial that a temple stood on the central acropolis terrace in the late archaic period and was burnt down in the Achaemenid destruction of Athens, Persian invasion of 480 BC, nevertheless questions of its nature, name, reconstruction and duration remain unresolved. Evidence Prior to the archaeological discoveries of the late 19th century, the existence of the archaic temple on the acropolis was known only from literary testimonia, and the few remains from the archaic buildings which have been visible c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ancient Greek Temple
Greek temples (, semantically distinct from Latin language, Latin , "temple") were structures built to house deity statues within Greek sanctuaries in ancient Greek religion. The temple interiors did not serve as meeting places, since the Ancient Greek religion#Sacrifice, sacrifices and rituals dedicated to the deity took place outside them, within the wider precinct of the sanctuary, which might be large. Temples were frequently used to store votive offerings. They are the most important and most widespread surviving building type in Greek architecture. In the Hellenistic Greece, Hellenistic kingdoms of Southwest Asia and of North Africa, buildings erected to fulfill the functions of a temple often continued to follow the local traditions. Even where a Greek influence is visible, such structures are not normally considered as Greek temples. This applies, for example, to the Parthia, Graeco-Parthian and Bactrian temples, or to the Ptolemaic Egypt, Ptolemaic examples, which follow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Arrephorion
The Arrephorion or House of the Arrephoroi is a building conjectured to have been on the Acropolis of Athens based on a passage in Pausanias. The discovery of the foundations of a substantial building on the north-west edge of the Acropolis has led to the identification of this structure with the Arrephorion. Pausanias reports that: I was much amazed at something which is not generally known, and so I will describe the circumstances. Two maidens dwell not far from the temple of Athena Polias, called by the Athenians Bearers of the Sacred Offerings. For a time they live with the goddess, but when the festival comes round they perform at night the following rites. Having placed on their heads what the priestess of Athena gives them to carry—neither she who gives nor they who carry have any knowledge what it is—the maidens descend by the natural underground passage that goes across the adjacent precincts, within the city, of Aphrodite in the Gardens. They leave down below what t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ionic Order
The Ionic order is one of the three canonic classical order, orders of classical architecture, the other two being the Doric order, Doric and the Corinthian order, Corinthian. There are two lesser orders: the Tuscan order, Tuscan (a plainer Doric), and the rich variant of Corinthian called the composite order. Of the three classical canonic orders, the Corinthian order has the narrowest columns, followed by the Ionic order, with the Doric order having the widest columns. The Ionic capital is characterized by the use of volutes. Ionic columns normally stand on a base which separates the shaft of the column from the stylobate or platform while the cap is usually enriched with egg-and-dart. The ancient architect and architectural historian Vitruvius associates the Ionic with feminine proportions (the Doric representing the masculine). Description Capital The major features of the Ionic order are the volutes of its capital (architecture), capital, which have been the subject of mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Erechtheus
Erechtheus (; ) in Greek mythology was a king of Athens, the founder of the ''polis'' and, in his role as god, attached to Poseidon, as "Poseidon Erechtheus". The name Erichthonius is carried by a son of Erechtheus, but Plutarch conflated the two names in the myth of the begetting of Erechtheus. Erechtheus I Athenians thought of themselves as ''Erechtheidai'', the "sons of Erechtheus". In Homer's ''Iliad'' (2. 547–48) Erechtheus is the son of "grain-giving Earth", reared by Athena. The earth-born son was sired by Hephaestus, whose semen Athena wiped from her thigh with a fillet of wool cast to earth, by which Gaia was made pregnant. In the contest for patronage of Athens between Poseidon and Athena, the salt spring on the Acropolis where Poseidon's trident struck was known as the ''sea of Erechtheus''. Erechtheus II, king of Athens Family The second Erechtheus was given a historicizing genealogy as son and heir to King Pandion I of Athens by Zeuxippe, this Pandion be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Temple Of Roma And Augustus
The Temple of Roma (personification), Roma and Augustus was a monopteral circular Ionic order, Ionic temple built on the Acropolis of Athens , likely coincident with Augustus' second visit to Athens. The structure was axially aligned with the eastern entrance of the Parthenon, placed eastward. The temple, which asserted the divinity of Rome and the Roman imperial cult, Imperial cult in the context of the religious centre of the Acropolis, was a propaganda monument erected at a time of tension between Rome and Athens. Its ruins remain on the Acropolis. __NOTOC__ Description The Pentelic marble temple was at its greatest diameter , and likely measured in height. The building had one step and a stylobate on which its nine columns stood. It had no interior wall, making it a monopteros, and might have been the frame or setting for a statue or other cult object. In style it recalls the columns of the Erechtheion with elaborately carved floral motifs at the top of the shaft, making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Athens
Athens ( ) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. A significant coastal urban area in the Mediterranean, Athens is also the capital of the Attica (region), Attica region and is the southernmost capital on the European mainland. With its urban area's population numbering over 3.6 million, it is the List of urban areas in the European Union, eighth-largest urban area in the European Union (EU). The Municipality of Athens (also City of Athens), which constitutes a small administrative unit of the entire urban area, had a population of 643,452 (2021) within its official limits, and a land area of . Athens is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years, and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BCE. According to Greek mythology the city was named after Athena, the ancient Greek goddess of wisdom, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sanctuary Of Zeus Polieus
The Sanctuary of Zeus Polieus was a walled open-air sanctuary dedicated to Zeus Polieus (city protector) around 500 BC on the Acropolis of Athens, sited to the Erechtheion's east. None of its foundations have been discovered and its trapezoid plan and many entrances have been worked out from rock cuttings on the Acropolis. The eastern area of the sanctuary is thought to have housed the oxen for the annual Bouphonia or ox-sacrificing. Its main entrance had a pediment Pediments are a form of gable in classical architecture, usually of a triangular shape. Pediments are placed above the horizontal structure of the cornice (an elaborated lintel), or entablature if supported by columns.Summerson, 130 In an .... Pausanias described the Homarium at Aegium in the 2nd century: : n the Akropolis of Athens :There are statues of Zeus, one made by Leokhares and one called Polieus (Of the City, the customary mode of sacrificing to whom I will give without adding the traditional re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ottoman Greece
The vast majority of the territory of present-day Greece was at some point incorporated within the Ottoman Empire. The period of Ottoman rule in Greece, lasting from the mid-15th century until the successful Greek War of Independence broke out in 1821 and the First Hellenic Republic was proclaimed in 1822, is known in Greece as Turkocracy (). Some regions, like the Ionian islands and various temporary Republic of Venice, Venetian possessions of the Stato da Mar, were not incorporated in the Ottoman Empire. The Mani Peninsula in the Peloponnese was not fully integrated into the Ottoman Empire, but was under Ottoman suzerainty. The Eastern Roman Empire, which ruled most of the Greek-speaking world for over 1100 years, had been fatally weakened since the Fourth Crusade of 1204. Having defeated the Serbs, the Ottomans fall of Constantinople, captured Constantinople in 1453 and soon advanced southwards capturing Athens in 1456 and the Peloponnese in 1460. By the early 16th century, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |