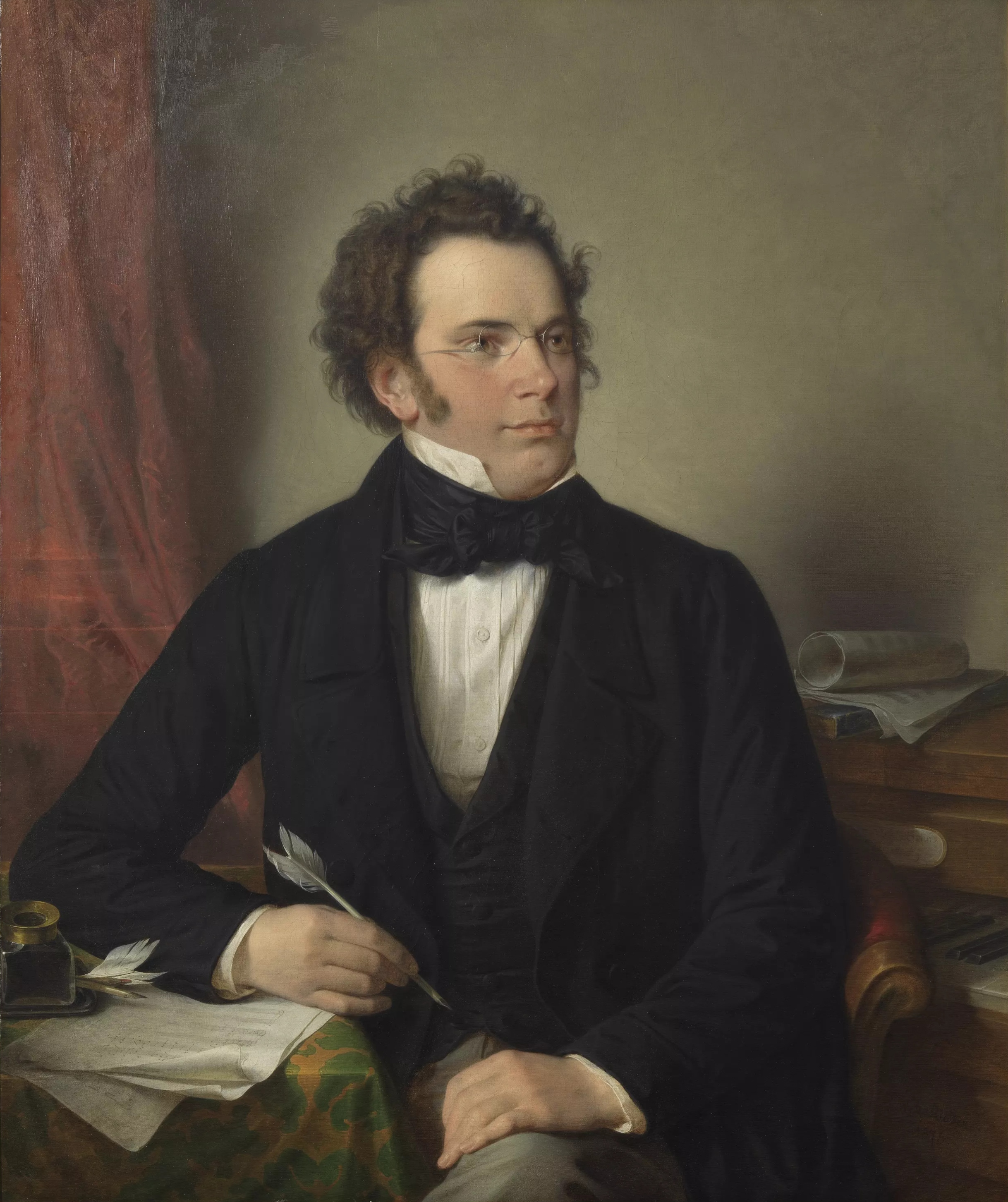|
Entr'acte At The Theatre Of Nicolet - Carlson 1966 P167
(or , ;Since 1932–35 the recommends this spelling, with no apostrophe, so historical, ceremonial and traditional uses (such as the 1924 René Clair film title) are still spelled . and ', , and ) means 'between the acts'. It can mean a pause between two parts of a stage production, synonymous to an intermission (this is nowadays the more common meaning in French), but it more often (in English) indicates a piece of music performed between acts of a theatrical production. But despite this, an entr'acte is often paired with a longer intermission, as an intermission is usually "between acts." However, there can also be an entr'acte on its own, usually between the two acts without an intermission. In the case of stage musicals, the serves as the overture of act 2 (and sometimes acts 3 and 4, as in ''Carmen''). In films that were meant to be shown with an intermission, there was frequently a specially recorded on the soundtrack between the first and second half of the film, al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Académie Française
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and Skills, skill, north of Ancient Athens, Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the Gymnasium (ancient Greece), gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive Grove (nature), grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacques Offenbach
Jacques Offenbach (; 20 June 18195 October 1880) was a German-born French composer, cellist and impresario. He is remembered for his nearly 100 operettas of the 1850s to the 1870s, and his uncompleted opera ''The Tales of Hoffmann''. He was a powerful influence on later composers of the operetta genre, particularly Franz von Suppé, Johann Strauss II and Arthur Sullivan. His best-known works were continually revived during the 20th century, and many of his operettas continue to be staged in the 21st. ''The Tales of Hoffmann'' remains part of the standard opera repertory. Born in Cologne, Kingdom of Prussia, the son of a synagogue hazzan, cantor, Offenbach showed early musical talent. At the age of 14, he was accepted as a student at the Paris Conservatoire; he found academic study unfulfilling and left after a year, but remained in Paris. From 1835 to 1855 he earned his living as a cellist, achieving international fame, and as a conductor. His ambition, however, was to compose c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosamunde
''Rosamunde, Fürstin von Zypern'' (''Rosamunde, Princess of Cyprus'') is a play by Helmina von Chézy, which is primarily remembered for the incidental music which Franz Schubert composed for it. Music and play premiered in Vienna's Theater an der Wien on 20 December 1823. The play ''Rosamunde, Fürstin von Zypern'' (''Rosamunde, Princess of Cyprus'') is a play in four acts by Helmina von Chézy, which is primarily known for the incidental music which Franz Schubert composed for it. The premiere of the play took place on 20 December 1823 in Vienna at the Theater an der Wien. The text version of the original play by von Chézy is lost. A modified version in five acts was discovered in the State Library of Württemberg and was published in 1996. Fragmentary autograph sources relating to the original the play have been recovered. Plot The story concerns the attempt of Rosamunde, who was brought up incognito as a shepherdess by the mariner's widow Axa, to reclaim her throne. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmina Von Chézy
Helmina von Chézy (26 January 178328 January 1856), née Wilhelmine Christiane von Klencke, was a German journalist, poet and playwright. She is known for writing the libretto for Carl Maria von Weber's opera '' Euryanthe'' (1823) and the play ''Rosamunde'', for which Franz Schubert composed incidental music. Life Helmina was born in Berlin, the daughter of Prussian officer Carl Friedrich von Klencke and his wife Caroline Louise von Klencke (1754–1802), daughter of Anna Louisa Karsch and herself a poet. The marriage of her parents had already broken up at her birth and she was partly raised by her grandmother. She started writing at the age of 14. Married the first time in 1799, she divorced the next year and upon the death of her mother moved to Paris, where she worked as a correspondent for several German papers. From 1803 to 1807 she edited her own ''Französische Miszellen'' ("French Miscellanea") journal, commenting on political issues, which earned her trouble with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Ensemble
A musical ensemble, also known as a music group, musical group, or a band is a group of people who perform Instrumental music, instrumental and/or vocal music, with the ensemble typically known by a distinct name. Some music ensembles consist solely of instrumentalists, such as the jazz quartet or the orchestra. Other music ensembles consist solely of singers, such as choirs and doo wop, doo-wop groups. In both popular music and classical music, there are ensembles in which both instrumentalists and singers perform, such as the Band (rock and pop), rock band or the Baroque chamber group for basso continuo (harpsichord and cello) and one or more singers. In classical music, trios or quartets either blend the sounds of musical instrument families (such as piano, strings (music), strings, and wind instruments) or group instruments from the same instrument family, such as string ensembles (e.g., string quartet) or wind ensembles (e.g., wind quintet). Some ensembles blend the sounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don Giovanni
''Don Giovanni'' (; K. 527; full title: , literally ''The Rake Punished, or Don Giovanni'') is an opera in two acts with music by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart to an Italian libretto by Lorenzo Da Ponte. Its subject is a centuries-old Spanish legend about a libertine as told by playwright Tirso de Molina in his 1630 play '' El burlador de Sevilla y convidado de piedra''. It is a ''dramma giocoso'' blending comedy, melodrama and supernatural elements (although the composer entered it into his catalogue simply as ''opera buffa''). It was premiered by the Prague Italian opera at the National Theatre (of Bohemia), now called the Estates Theatre, on 29 October 1787. ''Don Giovanni'' is regarded as one of the greatest operas of all time and has proved a fruitful subject for commentary in its own right; critic Fiona Maddocks has described it as one of Mozart's "trio of masterpieces with librettos by Da Ponte". Composition and premiere The opera was commissioned after the success of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 1756 – 5 December 1791) was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period (music), Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition and proficiency from an early age resulted in List of compositions by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, more than 800 works representing virtually every Western classical genre of his time. Many of these compositions are acknowledged as pinnacles of the symphony, symphonic, concerto, concertante, chamber music, chamber, operatic, and choir, choral repertoires. Mozart is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers in the history of Classical music, Western music, with his music admired for its "melodic beauty, its formal elegance and its richness of harmony and texture". Born in Salzburg, Mozart showed Child prodigy, prodigious ability from his earliest childhood. At age five, he was already competent on keyboard and violin, had begun to compose, and performed before European r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Querelle Des Bouffons
The ("Quarrel of the Comic Actors"), also known as the ("War of the Comic Actors"), was the name given to a battle of musical philosophies that took place in Paris between 1752 and 1754. The controversy concerned the relative merits of French and Italian opera. It was also known as the ("War of the Corners"), with those favoring French opera in the King's corner, and those favoring Italian opera in the Queen's corner. It was sparked by the reaction of literary Paris to a performance of Giovanni Battista Pergolesi's short intermezzo ''La serva padrona'' at the Académie royale de musique in Paris on 1 August 1752. ''La serva padrona'' was performed by an itinerant Italian troupe of comic actors, known as ''buffoni'' (''bouffons'' in French, hence the name of the quarrel). In the controversy that followed, critics such as Jean-Jacques Rousseau and Friedrich Melchior Grimm, along with other writers associated with the ''Encyclopédie'', praised Italian opera buffa. They att ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opera Seria
''Opera seria'' (; plural: ''opere serie''; usually called ''dramma per musica'' or ''melodramma serio'') is an Italian musical term which refers to the noble and "serious" style of Italian opera that predominated in Europe from the 1710s to about 1770. The term itself was rarely used at the time and only attained common usage once ''opera seria'' was becoming unfashionable and beginning to be viewed as something of a historical genre. The popular rival to ''opera seria'' was ''opera buffa,'' the 'comic' opera that took its cue from the improvisatory commedia dell'arte. An opera seria had a historical or Biblical subject, whereas an opera buffa had a contemporary subject. Italian ''opera seria'' (invariably to Italian libretto, libretti) was produced not only in Italy but almost throughout Europe, and beyond (see Opera in Latin America, Opera in Cuba e. g.). Among the main centres in Europe were the Royal court, court operas based in Warsaw (since 1628), Bavarian State Opera, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Battista Pergolesi
Giovanni Battista Draghi (; 4 January 1710 – 16 or 17 March 1736), usually referred to as Giovanni Battista Pergolesi (), was an Italian Baroque composer, violinist, and organist, leading exponent of the Baroque; he is considered one of the greatest Italian musicians of the first half of the 18th century and one of the most important representatives of the Neapolitan school. Despite his short life and few years of activity (he died of tuberculosis at the age of 26), he managed to create works of high artistic value and historical importance, such as ''La serva padrona'' (''The Maid Turned Mistress''), which played an important role in the development and diffusion of the opera buffa in Europe, and '' L'Olimpiade'', considered one of the best of the opera seria of the first half of the 18th century, and the '' Stabat Mater'', among the most important works of sacred music of all time. Biography Born in Jesi in what is now the Province of Ancona (but was then part of the Papa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opera Buffa
Opera buffa (, "comic opera"; : ''opere buffe'') is a genre of opera. It was first used as an informal description of Italian comic operas variously classified by their authors as ''commedia in musica'', ''commedia per musica'', ''dramma bernesco'', ''dramma comico'', ''divertimento giocoso''. Especially associated with developments in Naples in the first half of the 18th century, whence its popularity spread to Rome and northern Italy, ''buffa'' was at first characterized by everyday settings, local dialects, and simple vocal writing (the basso buffo is the associated voice type), the main requirement being clear diction and facility with patter song, patter. ''The New Grove Dictionary of Opera'' considers ''La Cilla'' (music by Michelangelo Faggioli, text by , 1706) and Luigi Ricci (composer), Luigi and Federico Ricci's'' Crispino e la comare'' (1850) to be the first and last appearances of the genre, although the term is still occasionally applied to newer work (for example E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Serva Padrona
''La serva padrona'' (''The Maid Turned Mistress'') is a 1733 intermezzo by Giovanni Battista Pergolesi (1710–1736) to a libretto by Gennaro Federico, after the Play (theatre), play by Jacopo Angello Nelli. It is some 40 minutes long, in two parts without overture, and was written as light-hearted staged entertainment between the acts of Pergolesi's serious opera ''Il prigionier superbo''. More specifically each of the two parts, set in the same dressing room, played during an intermission of the three-act opera to amuse people who remained in their seats. Federico's libretto was also set by Giovanni Paisiello, in 1781. Performance history ''La serva padrona'' and the opera seria it punctuates were premiered at the Teatro San Bartolomeo on 6 September 1733, the first performances there after an earthquake the previous year in Naples had closed all theatres. Both were written for the birthday of Holy Roman Empress Elisabeth Christine of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel a few days earlier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |