|
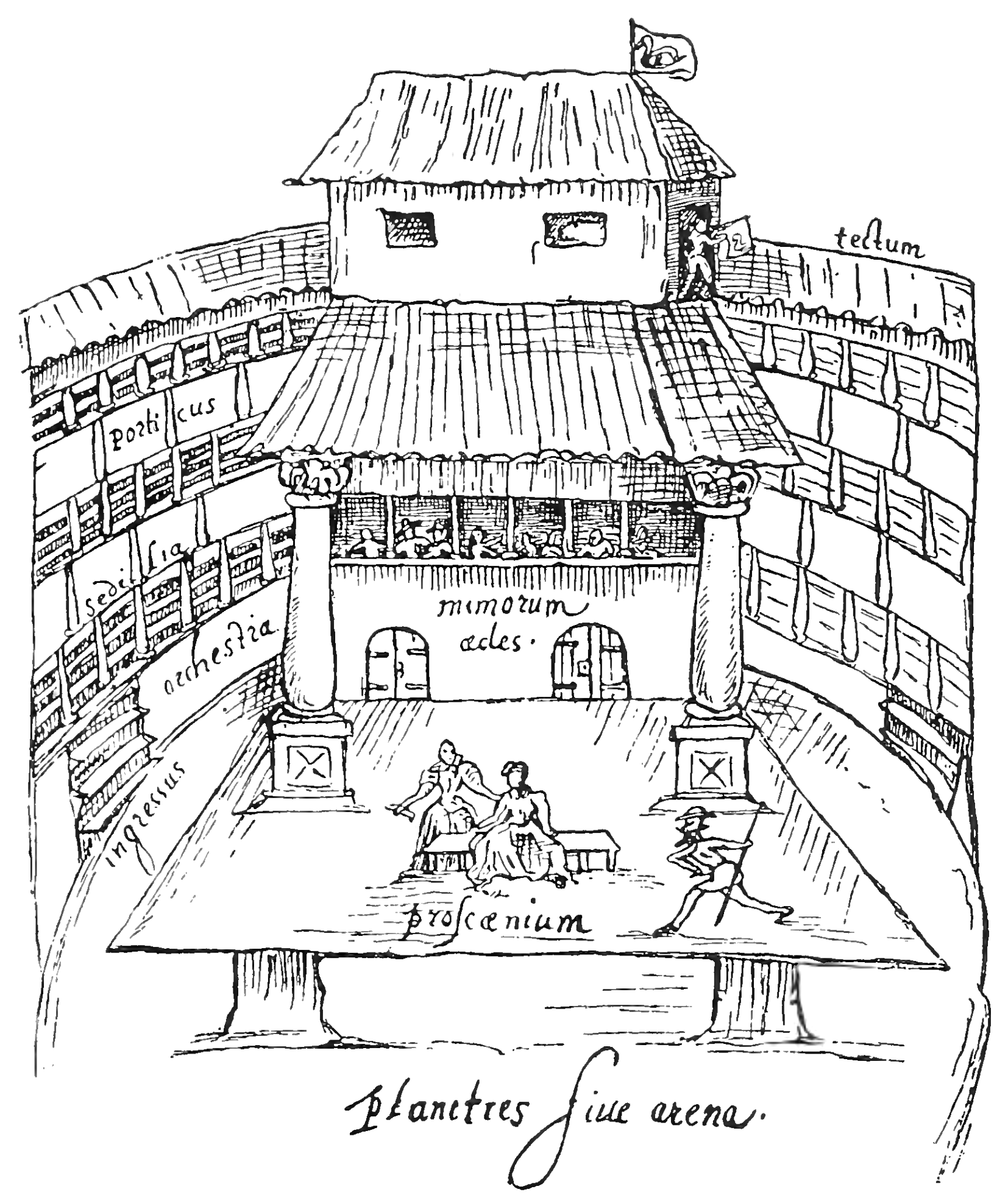
English Renaissance Theatre
The English Renaissance theatre or Elizabethan theatre was the theatre of England from 1558 to 1642. Its most prominent playwrights were William Shakespeare, Christopher Marlowe and Ben Jonson. Background The term ''English Renaissance theatre'' encompasses the period between 1562—following a performance of ''Gorboduc'', the first English play using blank verse, at the Inner Temple during the Christmas season of 1561—and the ban on theatrical plays enacted by the English Parliament in 1642. In a strict sense "Elizabethan" only refers to the period of Queen Elizabeth's reign (1558–1603). ''English Renaissance theatre'' may be said to encompass ''Elizabethan theatre'' from 1562 to 1603, '' Jacobean theatre'' from 1603 to 1625, and '' Caroline theatre'' from 1625 to 1642. Along with the economics of the profession, the character of the drama changed towards the end of the period. Under Elizabeth, the drama was a unified expression as far as social class was concerned: th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Swan Cropped
''The'' is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nathan Field
Nathan Field (also spelled Feild occasionally; 17 October 1587 – 1620) was an English dramatist and actor. Life His father was the Puritan preacher John Field, and his brother Theophilus Field became the Bishop of Llandaff. One of his brothers, named Nathaniel, often confused with the actor, became a printer. Nathan's father opposed London's public entertainments: he delivered a sermon that attributed Divine judgment to the collapse of the public seating area, during a bear baiting on a Sunday, at Beargarden in 1583, which resulted in several deaths. Nathan presumably did not intend a career in the theatre; he was a student of Richard Mulcaster at St. Paul's School in the late 1590s. At some point before 1600, he was impressed by Nathaniel Giles, the master of Elizabeth's choir and one of the managers of the new troupe of boy players at Blackfriars Theatre, called alternately the Children of the Chapel Royal and the Blackfriars Children. He remained in this profession ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mummers' Play
Mummers' plays are folk plays performed by troupes of amateur actors, traditionally all male, known as mummers or guisers (also by local names such as ''rhymers'', ''pace-eggers'', ''soulers'', ''tipteerers'', ''wrenboys'', and ''galoshins''). Historically, mummers' plays consisted of informal groups of costumed community members that visited from house to house on various holidays. Today the term refers especially to a play in which a number of characters are called on stage, two of whom engage in a combat, the loser being revived by a doctor character. This play is sometimes found associated with a sword dance though both also exist in Britain independently. Plays may be performed in the street or during visits to houses and pubs. They are generally performed seasonally, often at Christmas, Easter or on Plough Monday, more rarely on Halloween or All Souls' Day, and often with a collection of money. The practice may be compared with other customs such as those of Halloween, Bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Of Misrule
In England, the Lord of Misrule – known in Scotland as the Abbot of Unreason and in France as the ''Prince des Sots'' – was an officer sortition, appointed by lot during Christmastide to preside over the Feast of Fools. The Lord of Misrule was generally a peasant or sub-deacon appointed to be in charge of Christmas revelries, which often included drunkenness and wild partying. The Catholic Church in England held a similar festival involving a boy bishop. This custom was abolished by Henry VIII in 1541, restored by the Catholic Mary I and again abolished by Protestant Elizabeth I, though here and there it lingered on for some time longer. In continental Europe, it was suppressed by the Council of Basel in 1431, but was revived in some places from time to time, even as late as the eighteenth century. In the Tudor period, the Lord of Misrule (sometimes called the Abbot of Misrule or the King of Misrule) is mentioned a number of times by contemporary documents refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feast Of Fools
The Feast of Fools or Festival of Fools (Latin: ''festum fatuorum'', ''festum stultorum'') was a feast day on January 1 celebrated by the clergy in Europe during the Middle Ages, initially in Southern France, but later more widely. During the Feast, participants would elect either a false Bishop, false Archbishop, or false Pope. Ecclesiastical ritual would also be parodied, and higher and lower-level clergy would change places. The lack of surviving documents or accounts, as well as changing cultural and religious norms, has considerably obscured the modern understanding of the Feast, which originated in proper liturgical observance, and has more to do with other examples of medieval liturgical drama, though there is some connection with the earlier pagan (Roman) feasts of Saturnalia and Kalends or the later bourgeois in Sotie. Over the course of a week, the ceremonies would be led by different people in positions of power within the church. On December 26, St. Stephen's Day, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern
The early modern period is a Periodization, historical period that is defined either as part of or as immediately preceding the modern period, with divisions based primarily on the history of Europe and the broader concept of modernity. There is no exact date that marks the beginning or end of the period and its extent may vary depending on the area of history being studied. In general, the early modern period is considered to have lasted from around the start of the 16th century to the start of the 19th century (about 1500–1800). In a European context, it is defined as the period following the Middle Ages and preceding the advent of modernity; but the dates of these boundaries are far from universally agreed. In the context of World history (field), global history, the early modern period is often used even in contexts where there is no equivalent "medieval" period. Various events and historical transitions have been proposed as the start of the early modern period, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Medieval
The late Middle Ages or late medieval period was the period of European history lasting from 1300 to 1500 AD. The late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renaissance). Around 1350, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and plagues, including the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it had been before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. France and England experienced serious peasant uprisings, such as the Jacquerie and the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict, the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was temporarily shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively, those events are sometimes called the crisis of the late Middle Ages. Despite the crises, the 14th c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Drama
Academic drama refers to a theatrical movement that emerged in the mid 16th century during the Renaissance. Dedicated to the study of classical dramas for the purpose of higher education, universities in England began to produce the plays of Sophocles, Euripides, and Seneca the Younger (among others) in the Greek and Roman languages, as well as neoclassical dramas. These classical and neoclassical productions were performed by young scholars at universities in Cambridge and Oxford. Other European countries, such as Spain and Italy, adapted classical plays into a mixture of Latin and vernacular dramas. These Spanish and Italian adaptations were used in teaching morals in schools and colleges. The intellectual development of dramas in schools, universities, and Inns of Court in Europe allowed the emergence of the great playwrights of the late 16th century. At Oxford University The history of academic drama at Oxford University may be traced back to the mid 16th century. While th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cynthia’s Revels
''Cynthia's Revels, or The Fountain of Self-Love'' is a late Elizabethan stage play, a satire written by Ben Jonson. The play was one element in the ''Poetomachia'' or War of the Theatres between Jonson and rival playwrights John Marston and Thomas Dekker. Performance The play was first performed in 1600 at the Blackfriars Theatre by the Children of the Chapel, one of the troupes of boy actors active in that era. The Children acted the play at the English Royal Court during the 1600/01 Christmas season – though it was not a success with the audience there. Publication The play was entered into the Stationers' Register on 23 May 1601, with the title ''Narcissus the Fountain of Self-Love.'' It was published in quarto later that year by the bookseller Walter Burre, under the title ''The Fountain of Self-Love, or Cynthia's Revels.'' The play next appeared in print when it was included in the first folio collection of Jonson's works in 1616. A prefatory note to the folio text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midas (Lyly Play)
''Midas'' is an Elizabethan era stage play, a comedy written by John Lyly. It is arguably the most overtly and extensively allegorical of Lyly's allegorical plays. Performance and production ''Midas'' was entered into the Stationers' Register on 4 October 1591; it was first published in 1592 in a quarto printed by Thomas Scarlet for Joan Broome. She was the widow of William Broome, the bookseller who issued reprints of Lyly's ''Campaspe'' and '' Sapho and Phao'' in 1591; the widow Broome herself published the first editions of Lyly's '' Endymion'' (1591) and '' Gallathea'' (1592). ''Midas'' was probably acted by the Children of Paul's, Lyly's regular company through most of his playwriting career. The title page of the first edition states that the play was performed at Court on Twelfth Night, probably on 6 January 1590. John Dover Wilson proposed that Lyly himself may have played the role of Midas; but this is a speculation unsupported by evidence. "Obviously" the play w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endymion (play)
''Endymion, the Man in the Moon'' is an Elizabethan era comedy by John Lyly, written circa 1588. The action of the play centers around a young courtier, Endymion, who is sent into an endless slumber by Tellus, his former lover, because he has spurned her to worship the ageless Queen Cynthia. The prose is characterised by Euphuism, Lyly's highly ornate, formalised style, meant to convey the intelligence and wit of the speaker. ''Endymion'' has been called "without doubt, the boldest in conception and the most beautiful in execution of all Lyly's plays." Lyly makes allusions to ancient Greek and Roman texts and traditional English folklore throughout the play. While the title and characters are references to the myth of Endymion, the plot sharply deviates from the classical story and highlights contemporary issues in Elizabeth I's court through its allegorical framework. Characters * Endymion- a young man * Cynthia- the queen * Eumenides- Endymion's friend * Tellus- lady-in-w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallathea
''Gallathea'' or ''Galatea'' is an English literature#Elizabethan era, Elizabethan era stage play, a comedy by John Lyly. The first record of the play's performance was at Palace of Placentia, Greenwich Palace on New Year's Day, 1588 where it was performed before Queen Elizabeth I and her court by the Children of Paul's, Children of St Paul's, a troupe of boy actors. At this point in his literary career, Lyly had already achieved success with his prose romance Euphues and was a writer in residence at Blackfriars Theatre, Blackfriars theatre. The play is set in a village on the Lincolnshire shore of the Humber estuary and in the neighboring woods. It features a host of characters including Greek deities, nymphs, Fairy, fairies, and some shepherds. Plot The play opens in a small village somewhere in Lincolnshire with the shepherd Tyterus informing his daughter Gallathea of Neptune's demands. Every five years, the village must sacrifice the fairest virgin to Neptune (mythology), Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |