|
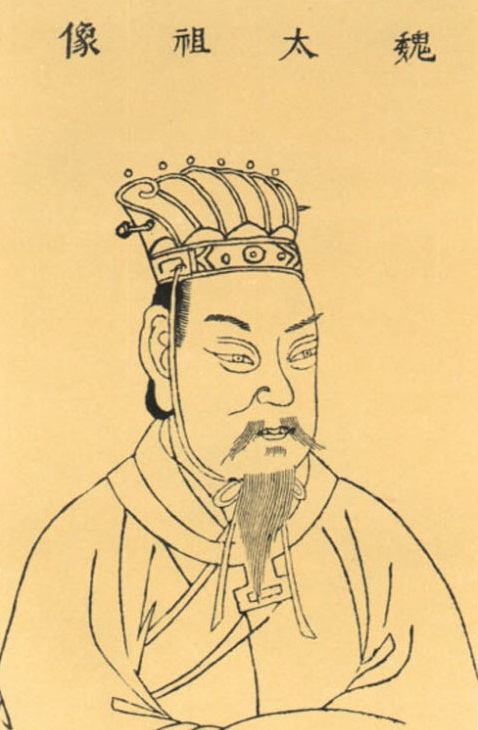
Emperor Taizong Of Song
Zhao Jiong (20 November 939 – 8 May 997), known as Zhao Guangyi from 960 to 977 and Zhao Kuangyi before 960, also known by his temple name as the Emperor Taizong of Song, was the second emperor of the Song dynasty of China. He reigned from 976 to his death in 997. He was a younger brother of his predecessor Emperor Taizu of Song, Emperor Taizu, and the father of his successor Emperor Zhenzong. Why Emperor Taizong succeeded his brother rather than Emperor Taizu's grown sons (Zhao Dezhao and Zhao Defang, who both died in their twenties during his reign) is not entirely understood by later historians. According to official history, his succession was confirmed by Emperor Taizu on their mother Empress Dowager Du's deathbed as a result of her instruction. A popular story dating back from at least the 11th century suggests that Emperor Taizong murdered his brother in the dim candlelight when the sound of an axe was allegedly heard. Whatever the truth, Zhao Guangyi had been prefect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao (surname)
Zhao (; ) is a Chinese surname, Chinese-language surname. The name is first in the ''Hundred Family Surnames'' – the traditional list of all Chinese surnames – because it was the emperor's surname of the Song dynasty (960–1279) when the list was compiled. The first line of the poem is 趙錢孫李 (Zhao, Qian (surname), Qian, Sun (surname), Sun, Li (surname 李), Li). Zhao may be Romanization, romanized as "Chiu" from the Cantonese pronunciation, and is romanized in Taiwan and Hong Kong as "Chao (surname), Chao" in the Wade–Giles system. It is romanized as Vietnamese name, Vietnamese family name "Triệu" among the Chinese diaspora in Vietnam. Zhao is cognate to List of Korean surnames, Korean family name "Cho (Korean surname), Cho" (조) in Korea. The romanization is shared with the much rarer family name Zhào (兆). Evolution of the Zhao clan Modern culture In Lu Xun's novel ''The True Story of Ah Q'', Ah Q said he belonged to the same clan as Mr. Zhao, who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tang Dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, c=唐朝), or the Tang Empire, was an Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907, with an Wu Zhou, interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. Historians generally regard the Tang as a high point in Chinese civilisation, and a Golden age (metaphor), golden age of cosmopolitan culture. Tang territory, acquired through the military campaigns of its early rulers, rivalled that of the Han dynasty. The House of Li, Li family founded the dynasty after taking advantage of a period of Sui decline and precipitating their final collapse, in turn inaugurating a period of progress and stability in the first half of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty was formally interrupted during 690–705 when Empress Wu Zetian seized the throne, proclaiming the Wu Zhou dynasty and becoming the only legitimate Chinese empress regnant. The An Lushan rebellion (755 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irredentism
Irredentism () is one State (polity), state's desire to Annexation, annex the territory of another state. This desire can be motivated by Ethnicity, ethnic reasons because the population of the territory is ethnically similar to or the same as the population of the parent state. Historical reasons may also be responsible, i.e., that the territory previously formed part of the parent state. Difficulties in applying the concept to concrete cases have given rise to academic debates about its precise definition. Disagreements concern whether either or both ethnic and historical reasons have to be present and whether non-state actors can also engage in irredentism. A further dispute is whether attempts to absorb a full neighboring state are also included. There are various types of irredentism. For typical forms of irredentism, the parent state already exists before the territorial conflict with a neighboring state arises. There are also forms of irredentism in which the parent state is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China Proper
China proper, also called Inner China, are terms used primarily in the West in reference to the traditional "core" regions of China centered in the southeast. The term was first used by Westerners during the Manchu people, Manchu-led Qing dynasty to describe the distinction between the historical "Han lands" ( zh, t=漢地, i.e. regions long dominated by the majority Han Chinese, Han population) and the "frontier" regions of China where more ethnic minorities in China, non-Han ethnic minorities and newer foreign immigrants (e.g. Russians) reside, sometimes known as "Outer China". There is no fixed extent for China ''proper'', as many administrative, cultural, and linguistic shifts have occurred in History of China, Chinese history. One definition refers to the original area of Chinese civilization, the Zhongyuan, Central Plain (in the North China Plain); another to the Eighteen Provinces of the Qing dynasty. There was no direct translation for "China ''proper''" in the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Han
The Northern Han ( zh, t=北漢, s=北汉, p=Běi Hàn) was a dynastic state of China and one of the Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period. It was founded by Liu Min (Emperor Shizu) as a continuation of the Later Han dynasty founded by his brother Liu Zhiyuan (Emperor Gaozu). The Northern Han lasted from 951 to 979, when it was conquered by the Northern Song dynasty. Founding of the Northern Han The short-lived state of Later Han fell in 950 because of Guo Wei, a powerful military governor's ''de facto'' coup. Liu Min founded the Northern Han Kingdom, sometimes referred to as the Eastern Han, in 951 claiming that he was the legitimate heir to the imperial throne of Later Han. Liu Min immediately restored the traditional relationship with the Khitans, who had founded the Liao dynasty. Sources conflict as to the origin of the Later Han and Northern Han emperors; some indicate sinicized Shatuo ancestry while some traditional historical sour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qian Chu
Qian Chu (29 September 929 – 7 October 988), courtesy name Wende, known as Qian Hongchu before 960, also known by his posthumous name as the King Zhongyi of Wuyue, was the last king of Wuyue during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period of China. He reigned from 947 until 978, when he surrendered his kingdom to the Northern Song dynasty. Life Qian Chu came to power after his brother, Qian Zong, was deposed in a coup d'état. At the time, Wuyue was at its largest territorial extent, ruling 13 in modern-day Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Shanghai, and Fujian. Throughout its history, Wuyue maintained a policy of nominally submitting to the successive dominant northern regimes. Unlike the other small states in the south, the Wuyue kings never declared themselves Emperor. In return, the northern regimes respected Wuyue's autonomy and conferred upon its kings high honours, one of which was the title of "Commander of All Horses and Soldiers Under Heaven". Indeed, Qian Chu changed his name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wuyue
Wuyue (; ) was a Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic state of China and one of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period#Ten Kingdoms, Ten Kingdoms during the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period of History of China, Chinese history. It was ruled by the Qian (surname), Qian clan of Haiyan County, Zhejiang, Haiyan (海鹽錢氏), whose family name remains widespread in the kingdom's former territory. Founding Beginning in 887, the Qian (surname), Qian family provided military leaders (or ''jiedushi'') to the Tang dynasty. Qian Liu was named Prince of Zhejiang, Yue in 902, with the title of Prince of Jiangsu, Wu added two years later. In 907, when the Tang dynasty fell and was replaced in the north by the Later Liang (Five Dynasties), Later Liang, military leaders in the south formed their own kingdoms. Qian Liu used his position to proclaim himself the King of Wuyue. This signaled the beginning of the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms period which would last until the foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chen Hongjin
Chen Hongjin () (914–985), courtesy name Jichuan (), formally Duke Zhongshun of Qi (), was a warlord late in the Chinese Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, who controlled Qingyuan Circuit (headquartered in modern Quanzhou, Fujian). After a series of conquests by the Song dynasty, Chen, who was a vassal to Song, believed that it would be wise for him to surrender his realm, and did so. He subsequently remained honored as a Song general until his death. Background and service under Liu Congxiao Chen Hongjin was born in 914.'' History of Song'', vol. 483. His ancestors were said to be originally from Linhuai (臨淮, in modern Suqian, Jiangsu), but had relocated south and settled at Xianyou (仙遊, in modern Putian, Fujian), and thus Chen was said to be from Xianyou.''Spring and Autumn Annals of the Ten Kingdoms''vol. 93 Chen was said to be ambitious and studious in his youth, particularly spending attention to military strategies. When he grew older, he was known f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qingyuan Jiedushi
Qingyuan Circuit () was a '' de facto'' independent entity and circuit late in China's Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdoms Period, renamed to Pinghai Circuit () in 964. It was an office created in 949 by Southern Tang's second emperor Li Jing for the warlord Liu Congxiao, who nominally submitted to him but virtually controlled Quan Prefecture (泉州, comprising modern Quanzhou, Xiamen and Putian) and Zhang Prefecture (漳州, comprising modern Zhangzhou, Xinluo and Zhangping). Prefectures in ''de facto'' independence from the Southern Tang state.''Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 288. (Zhang Prefecture was, at times during the circuit's existence, also known as Nan Prefecture (.'' History of Song'', vol. 483. Starting in 960, in addition to being nominally submissive to Southern Tang, the Qingyuan Circuit was also nominally submissive to the Song, which had itself become Southern Tang's nominal suzerain.'' Xu Zizhi Tongjian'', vol. 1. After demise of Congxiao, the circuit was briefl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Councilor
The grand chancellor (, among other titles), also translated as counselor-in-chief, chancellor, chief councillor, chief minister, imperial chancellor, lieutenant chancellor and prime minister, was the highest-ranking executive official in the imperial Chinese government. The term was known by many different names throughout Chinese history, and the exact extent of the powers associated with the position fluctuated greatly, even during a particular dynasty. Professor Zhu Zongbin of Peking University outlined the role of "grand chancellor" as one with the power to oversee all jurisdictional matters, the right to decide and to draft edicts with other ministers, and the position of chief advisor to the emperor. This extended even to the ability to criticize the emperor's edicts and decisions. Thus, the grand chancellor served as the emperor's chief of staff and main political advisor, often exercising power second only to the emperor. In practice, the grand chancellor was often a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Official History
An official history is a work of history which is sponsored, authorised or endorsed by its subject. The term is most commonly used for histories which are produced for a government. The term also applies to commissions from non-state bodies including histories of commercial companies. An official biography (one written with the permission, cooperation and sometimes the participation of its subject or heirs) is an authorised biography. Official histories frequently have the advantage that the author has had access to archives, been allowed to interview subjects and use other primary sources closed to independent historians. Because of the close relationship between author and subject, such works may be (or be perceived to be) partisan in tone and to lack historical objectivity. Such bias varies and some official histories have been called exercises in propaganda; in other cases the authors have retained a measure of independence. Early official histories There is a tradition of hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |