|
Elias Loomis
Elias Loomis (August 7, 1811 – August 15, 1889) was an American mathematician. He served as a professor of mathematics and natural philosophy at Case Western Reserve University, Western Reserve College (now Case Western Reserve University), the New York University, University of the City of New York and Yale University. During his tenure at Western Reserve College in 1838, he established the Loomis Observatory, currently the second oldest observatory in the United States. Life and work Loomis was born in Willington, Connecticut in 1811. He graduated at Yale College in 1830, was a tutor there for three years (1833–36), and then spent the next year in scientific investigation in Paris. On his return, Loomis served as professor of mathematics and natural philosophy for eight years (1836–44) at Case Western Reserve University, Western Reserve College in Hudson, Ohio, Hudson, Ohio, now Case Western Reserve University. During his tenure, he opened up the Loomis Observatory i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Willington, Connecticut
Willington is a New England town, town in Tolland County, Connecticut, Tolland County, Connecticut, United States. The town is part of the Capitol Planning Region, Connecticut, Capitol Planning Region. The population was 5,566 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Willimantic River borders the town on the west. Willington is approximately 25 miles northeast of Hartford, Connecticut, Hartford on Interstate 84 in Connecticut, Interstate 84, which also provides a connection to Boston, Massachusetts, Boston, via the Massachusetts Turnpike. Providence, Rhode Island, Providence, RI is accessible via U.S. Route 44#Connecticut, U.S. Route 44. Larger communities nearby include Coventry, Connecticut, Coventry, Stafford, Connecticut, Stafford, Tolland, Connecticut, Tolland, and Willimantic, Connecticut, Willimantic. The University of Connecticut is located in adjacent Mansfield, Connecticut, Mansfield. A new public library (formerly located within Hall Memorial School) opened i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Alexander Wylie (missionary)
Alexander Wylie (Traditional Chinese: 偉烈亞力, Simplified Chinese: 伟烈亚力) (6 April 181510 February 1887), was a British Protestant Christian missionary to China. He is known for his translation work and scholarship during the late Qing Dynasty. Early life Wylie was born in London, and went to school at Drumlithie, Kincardineshire, and at Chelsea, London, Chelsea. While apprenticed to a cabinet-maker, Wylie picked up a Chinese grammar book written in Latin language, Latin (the ''Notitia linguae sinicae'' by Joseph Henri Marie de Prémare). China After having mastered Latin, he went on to make such good progress in Chinese that, in 1846, James Legge engaged him to superintend the London Missionary Society's press in Shanghai. In this position, he acquired a wide knowledge of Chinese religion and civilisation, and especially of mathematics, enabling him to demonstrate in his paper ''Jottings on the Science of the Chinese'' that William George Horner, Sir George Horner' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's rotation, Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the North magnetic pole, Magnetic North Pole. The North Pole is by definition the northernmost point on the Earth, lying antipode (geography), antipodally to the South Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° North, as well as the direction of true north. At the North Pole all directions point south; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the North Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, counterclockwise is east and clockwise is west. The North Pole is at the center of the Northern Hemisphere. The nearest land is usually said to be Kaffeklubben Island, off the northern coast of Greenland about away, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
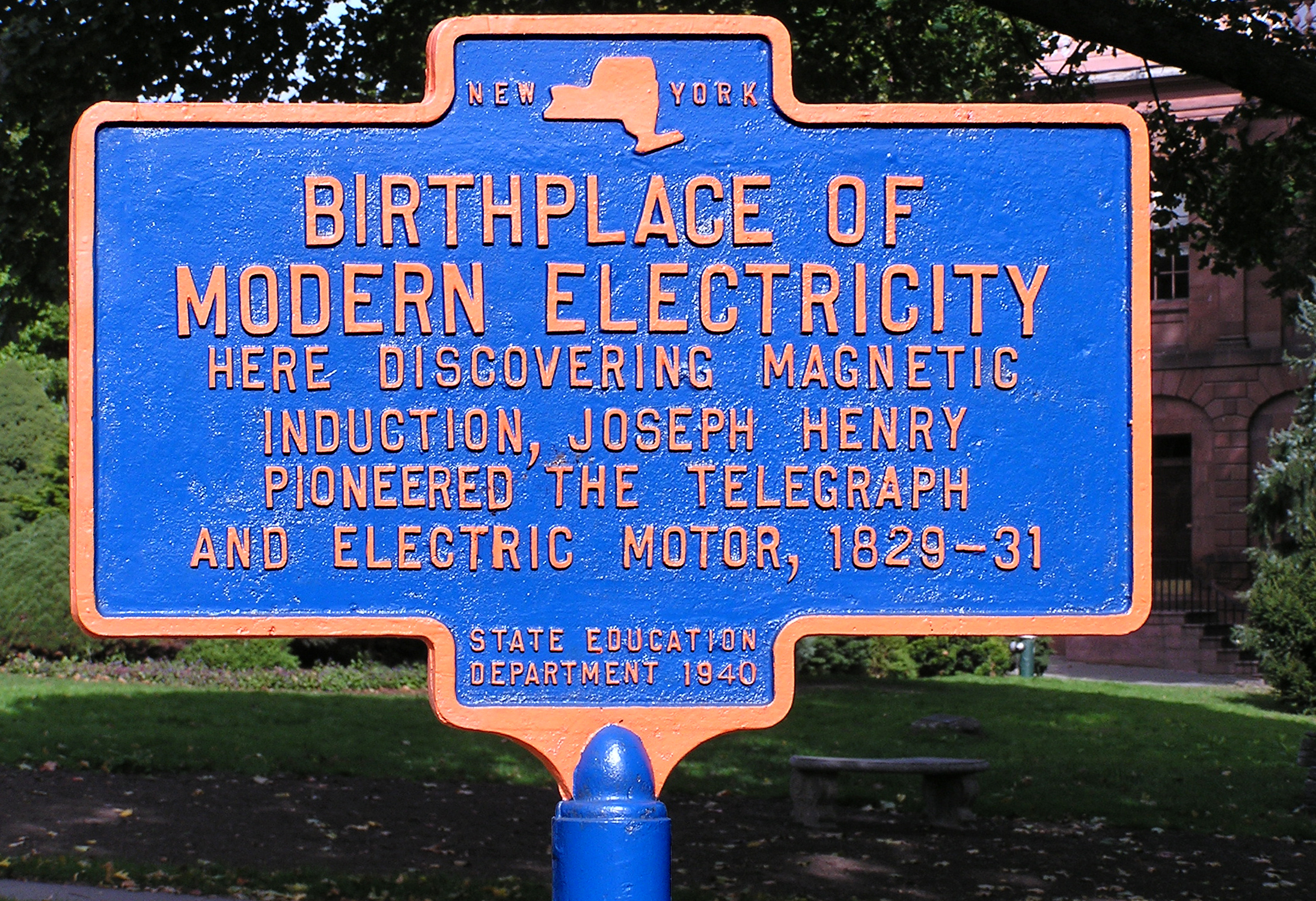
Joseph Henry
Joseph Henry (December 17, 1797– May 13, 1878) was an American physicist and inventor who served as the first secretary of the Smithsonian Institution. He was the secretary for the National Institute for the Promotion of Science, a precursor of the Smithsonian Institution. He also served as president of the National Academy of Sciences from 1868 to 1878. While building electromagnets, Henry discovered the electromagnetism, electromagnetic phenomenon of self-inductance. He also discovered mutual inductance independently of Michael Faraday, though Faraday was the first to make the discovery and publish his results. Henry developed the electromagnet into a practical device. He invented a precursor to the electric doorbell (specifically a bell that could be rung at a distance via an electric wire, 1831) and electric relay (1835). His work on the electromagnetic relay was the basis of the practical electrical telegraph, invented separately by Samuel Morse, Samuel F. B. Morse and Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Aurora (astronomy)
An aurora ( aurorae or auroras), also commonly known as the northern lights (aurora borealis) or southern lights (aurora australis), is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly observed in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of radiant lights that appear as curtains, rays, spirals or dynamic flickers covering the entire sky. Auroras are the result of disturbances in the Earth's magnetosphere caused by enhanced speeds of solar wind from coronal holes and coronal mass ejections. These disturbances alter the trajectories of charged particles in the magnetospheric plasma. These particles, mainly electrons and protons, precipitate into the upper atmosphere ( thermosphere/exosphere). The resulting ionization and excitation of atmospheric constituents emit light of varying color and complexity. The form of the aurora, occurring within bands around both polar regions, is also dependent on the amount of accelera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Terrestrial Magnetism
The ''Journal of Geophysical Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It is the flagship journal of the American Geophysical Union. It contains original research on the physical, chemical, and biological processes that contribute to the understanding of the Earth, Sun, and Solar System. It has seven sections: A (Space Physics), B (Solid Earth), C (Oceans), D (Atmospheres), E (Planets), F (Earth Surface), and G (Biogeosciences). All current and back issues are available online for subscribers. History The journal was originally founded under the name ''Terrestrial Magnetism'' by the American Geophysical Union's president Louis Agricola Bauer in 1896. It was renamed to ''Terrestrial Magnetism and Atmospheric Electricity'' in 1899 and in 1948 it acquired its current name. In 1980, three specialized sections were established: ''A: Space Physics'', ''B: Solid Earth'', and ''C: Oceans''. Subsequently, further sections have been added: ''D: Atmospheres'' in 1984, ''E: Planets'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Geomagnetic Storm
A geomagnetic storm, also known as a magnetic storm, is a temporary disturbance of the Earth's magnetosphere that is driven by interactions between the magnetosphere and large-scale transient Plasma (physics), plasma and magnetic field structures that originate on or near the Sun. The structures that produce geomagnetic storms include interplanetary coronal mass ejections (CME) and corotating interaction regions (CIR). The former often originate from solar active regions, while the latter originate at the boundary between high- and low-speed streams of solar wind. The frequency of geomagnetic storms increases and decreases with the sunspot cycle. During solar maximum, solar maxima, geomagnetic storms occur more often, with the majority driven by CMEs. When these structures reach Earth, the increase in the solar wind pressure initially compresses the magnetosphere. The solar wind's magnetic field interacts with the Earth's magnetic field and transfers an increased energy into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
United States National Academy Of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the National Academy of Medicine (NAM). As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and continuing achievements in original research. Election to the National Academy is one of the highest honors in the scientific field in the United States. Members of the National Academy of Sciences serve '' pro bono'' as "advisers to the nation" on science, engineering, and medicine. The group holds a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code. Congress legislated and President Abraham Lincoln signed an Act of Congress (1863) establishing the National Academy of Sciences as an independent, trusted nongovernmental institution, created for the purpose of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |