|
Elektron (company)
Elektron is a Swedish developer and manufacturer of musical instruments founded in 1998, as well as having its headquarters, R&D and production in Gothenburg, Sweden. They produce mainly electronic musical instruments, but have also made effects units and software. Since 2012, there have been branch offices in Los Angeles and in Tokyo. Musicians who use Elektron instruments include Panda Bear, Timbaland, The Knife, Sophie Xeon, Depeche Mode, 8 Bit Weapon, and Autechre. Early years Elektron started working on its first electronic instrument in 1997. At the time, it was a school project, a mandatory course part of the Computer Science program at the Chalmers University of Technology in Gothenburg, Sweden. The three founders were Daniel Hansson, Anders Gärder and Mikael Räim. Hansson recalls: "There were a number of projects to choose from: build a digital landline phone, a bicycle trip computer, or a beeper. None of that seemed fun or challenging enough, so I suggested we bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Instruments
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted to make musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can be considered a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. A person who plays a musical instrument is known as an '' instrumentalist''. The history of musical instruments dates to the beginnings of human culture. Early musical instruments may have been used for rituals, such as a horn to signal success on the hunt, or a drum in a religious ceremony. Cultures eventually developed composition and performance of melodies for entertainment. Musical instruments evolved in step with changing applications and technologies. The exact date and specific origin of the first device considered a musical instrument, is widely disputed. The oldest object identified by scholars as a musical instrument, is a simple flute, dated back 50,000–60,000 years. Many scholars date early flutes to about 40,000 years ago. Many hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elektron Overbridge
{{disambiguation ...
Elektron may refer to: * Elektron (alloy), a magnesium alloy * Elektron (company), a musical instrument company * Elektron (ISS), a Russian oxygen generator * Elektron (resin) or amber, a fossilised resin * Elektron (satellite), a series of four Soviet particle physics satellites See also * Electron, a subatomic particle * Electron (other) * Tron (other) ''Tron'' is a 1982 science fiction film produced by Walt Disney Productions. Tron may also refer to: Tron franchise * Tron (franchise), ''Tron'' (franchise), an American science fiction media franchise begun with the 1982 film ''Tron'' * Tron (ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reverberation
In acoustics, reverberation (commonly shortened to reverb) is a persistence of sound after it is produced. It is often created when a sound is reflection (physics), reflected on surfaces, causing multiple reflections that build up and then decay as the sound is absorbed by the surfaces of objects in the space – which could include furniture, people, and air. This is most noticeable when the sound source stops but the reflections continue, their amplitude decreasing, until zero is reached. Reverberation is frequency dependent: the length of the decay, or reverberation time, receives special consideration in the architectural design of spaces which need to have specific reverberation times to achieve optimum performance for their intended activity. In comparison to a distinct echo, that is detectable at a minimum of 50 to 100 millisecond, ms after the previous sound, reverberation is the occurrence of reflections that arrive in a sequence of less than approximately 50 ms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delay (audio Effect)
Delay is an audio signal processing technique that records an input signal to a storage medium and then plays it back after a period of time. When the delayed playback is electronic mixer, mixed with the live audio, it creates an echo-like effect, whereby the original audio is heard followed by the delayed audio. The delayed signal may be played back multiple times, or fed back into the recording, to create the sound of a repeating, decaying echo. Delay effects range from a subtle echo effect to a pronounced blending of previous sounds with new sounds. Delay effects can be created using tape loops, an approach developed in the 1940s and 1950s and used by artists including Elvis Presley and Buddy Holly. Analog effects units were introduced in the 1970s; digital effects pedals in 1984; and audio plug-in software in the 2000s. History The first delay effects were achieved using tape loops improvised on reel-to-reel audio tape recording systems. By shortening or lengthening the loo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
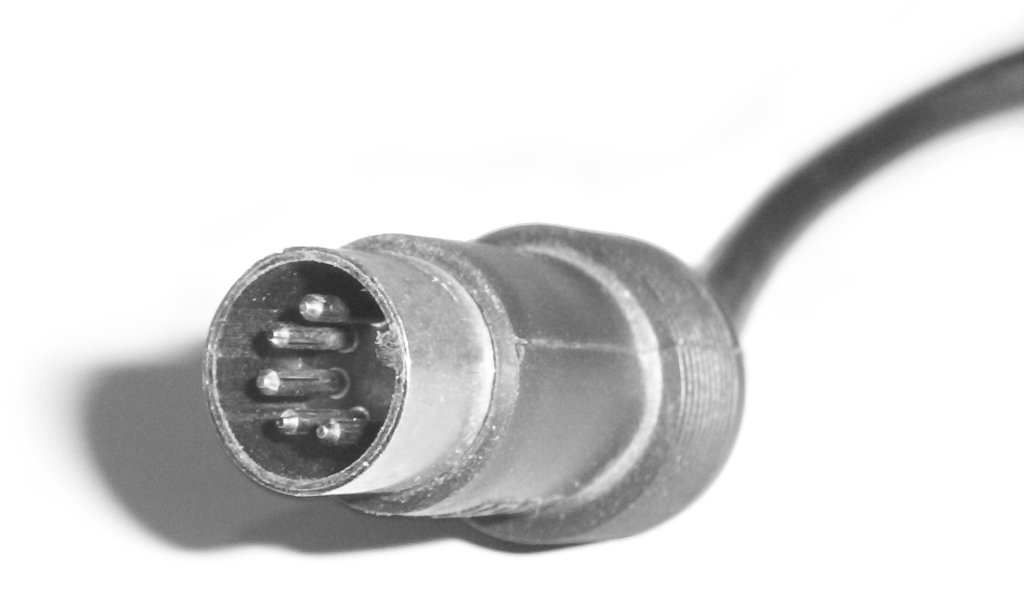
DIN Sync
DIN sync, also called Sync24, is a synchronization interface for electronic musical instruments. It was introduced in 1980 by Roland Corporation and has been superseded by MIDI. Definition and history DIN sync was introduced in 1980 by Roland Corporation with the release of the TR-808 drum machine. The intended use was the synchronization of music sequencers, drum machines, arpeggiators and similar devices. It was superseded by MIDI in the mid-to-late 1980s. DIN sync consists of two signals, clock (tempo) and run/stop. Both signals are TTL compatible, meaning the low state is 0 V and the high state is about +5 V. The clock signal is a low-frequency pulse wave suggesting the tempo. Instead of measuring the waveform's frequency, the machine receiving the signal merely has to count the number of pulses to work out when to increment its position in the music. Roland equipment uses 24 pulses per quarter note, known as Sync24. Therefore, a Roland-compatible dev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CV/gate
CV/gate (an abbreviation of ''control voltage/gate'') is an analog method of controlling synthesizers, drum machines, and similar equipment with external sequencers. The control voltage typically controls pitch and the gate signal controls note on-off. This method was widely used in the epoch of analog modular synthesizers and CV/Gate music sequencers, since the introduction of the Roland MC-8 Microcomposer in 1977 through to the 1980s, when it was eventually superseded by the MIDI protocol (introduced in 1983), which is more feature-rich, easier to configure reliably, and more readily supports polyphony. The advent of digital synthesizers also made it possible to store and retrieve voice "patches" – eliminating patch cables and (for the most part) control voltages. However, numerous companies – including Doepfer, who designed a modular system for Kraftwerk in 1992, Buchla, MOTM, Analogue Systems, and others continue to manufacture modular synthesizers that are incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Step Sequencer
A music sequencer (or audio sequencer or simply sequencer) is a device or application software that can record, edit, or play back music, by handling note and performance information in several forms, typically CV/Gate, MIDI, or Open Sound Control, and possibly audio and automation data for digital audio workstations (DAWs) and plug-ins. Overview Modern sequencers The advent of Musical Instrument Digital Interface (MIDI) in the 1980s gave programmers the opportunity to design software that could more easily record and play back sequences of notes played or programmed by a musician. As the technology matured, sequencers gained more features, such as the ability to record multitrack audio. Sequencers used for audio recording are called digital audio workstations (DAWs). Many modern sequencers can be used to control virtual instruments implemented as software plug-ins. This allows musicians to replace expensive and cumbersome standalone synthesizers with their software equ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elektron Analog Four
{{disambiguation ...
Elektron may refer to: * Elektron (alloy), a magnesium alloy * Elektron (company), a musical instrument company * Elektron (ISS), a Russian oxygen generator * Elektron (resin) or amber, a fossilised resin * Elektron (satellite), a series of four Soviet particle physics satellites See also * Electron, a subatomic particle * Electron (other) * Tron (other) ''Tron'' is a 1982 science fiction film produced by Walt Disney Productions. Tron may also refer to: Tron franchise * Tron (franchise), ''Tron'' (franchise), an American science fiction media franchise begun with the 1982 film ''Tron'' * Tron (ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CompactFlash
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994. CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the early memory card formats, surpassing Miniature Card and SmartMedia. Subsequent formats, such as MMC/ SD, various Memory Stick formats, and xD-Picture Card offered stiff competition. Most of these cards are smaller than CompactFlash while offering comparable capacity and speed. Proprietary memory card formats for use in professional audio and video, such as P2 and SxS, are faster, but physically larger and more costly. CompactFlash's popularity is declining as CFexpress is taking over. As of 2022, both Canon and Nikon's newest high end cameras, e.g. the Canon EOS R5, Canon EOS R3, and Nikon Z 9 use CFexpress cards for the higher performance required to record 8K video. Traditional CompactFlash cards use the Parallel ATA interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MIDI
Musical Instrument Digital Interface (; MIDI) is an American-Japanese technical standard that describes a communication protocol, digital interface, and electrical connectors that connect a wide variety of electronic musical instruments, computers, and related audio devices for playing, editing, and recording music. A single MIDI cable can carry up to sixteen channels of MIDI data, each of which can be routed to a separate device. Each interaction with a key, button, knob or slider is converted into a MIDI event, which specifies musical instructions, such as a note's pitch, timing and velocity. One common MIDI application is to play a MIDI keyboard or other controller and use it to trigger a digital sound module (which contains synthesized musical sounds) to generate sounds, which the audience hears produced by a keyboard amplifier. MIDI data can be transferred via MIDI or USB cable, or recorded to a sequencer or digital audio workstation to be edited or played back. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crossfader
In audio engineering, a fade is a gradual increase or decrease in the level of an audio signal. The term can also be used for film cinematography or theatre lighting in much the same way (see fade (filmmaking) and fade (lighting)). In sound recording and reproduction a song may be gradually reduced to silence at its end (fade-out), or may gradually increase from silence at the beginning (fade-in). Fading-out can serve as a recording solution for pieces of music that contain no obvious ending. Quick fade-ins and -outs can also be used to change the characteristics of a sound, such as to soften the attack in vocal plosives and percussion sounds. Professional turntablists and DJs in hip hop music use faders on a DJ mixer, notably the horizontal crossfader, in a rapid fashion while simultaneously manipulating two or more record players (or other sound sources) to create ''scratching'' and develop beats. Club DJs in house music and techno use DJ mixers, two or more sound s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |