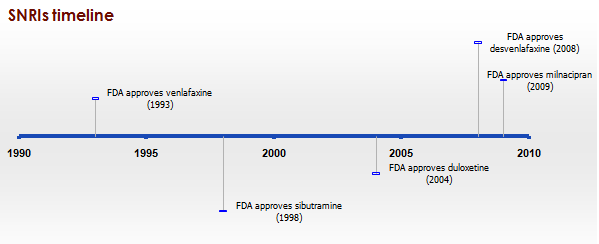
|
Effexor
Venlafaxine, sold under the brand name Effexor among others, is an antidepressant medication of the serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class. It is used to treat major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. Studies have shown that venlafaxine improves post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) as a recommended first-line treatment. It may also be used for chronic neuropathic pain. It is taken orally (swallowed by mouth). It is also available as the salt venlafaxine besylate (venlafaxine benzenesulfonate monohydrate) in an extended-release formulation (Venbysi XR). Common side effects include loss of appetite, constipation, dry mouth, dizziness, sweating, insomnia, drowsiness and sexual problems. Severe side effects include an increased risk of suicide, mania, and serotonin syndrome. Antidepressant withdrawal syndrome may occur if stopped. A meta-analysis of randomized trials in depression found an increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin–norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor
Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant medications used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, social phobia, chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopause, menopausal symptoms. Off-label uses include treatments for attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD). SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they reuptake inhibitor, inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs), which act upon single neurotransmitters. The human serotonin transporter (SERT) and noradrenaline transporter (NAT) are membrane transport proteins that are responsible for the reuptake of serotonin and noradrenaline from the Chemical synapse, synapti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidepressant
Antidepressants are a class of medications used to treat major depressive disorder, anxiety disorders, chronic pain, and addiction. Common side effects of antidepressants include Xerostomia, dry mouth, weight gain, dizziness, headaches, akathisia, sexual dysfunction, and emotional blunting. There is an increased risk of Suicidal ideation, suicidal thinking and Suicide, behavior when taken by children, adolescents, and young adults. Antidepressant discontinuation syndrome, Discontinuation syndrome, which resembles recurrent Depression (mood), depression in the case of the Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, SSRI class, may occur after stopping the intake of any antidepressant. Research regarding the effectiveness of antidepressants for depression in adults is controversial and has found both benefits and drawbacks. Meanwhile, evidence of benefit in children and adolescents is unclear, even though antidepressant use has considerably increased in children and adolescents in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational worry about events or activities. Worry often interferes with daily functioning. Individuals with GAD are often overly concerned about everyday matters such as health, finances, death, family, relationship concerns, or work difficulties."What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?" National Institute of Mental Health. Accessed 28 May 2008. Symptoms may include excessive worry, restlessness, trouble sleeping, exhaustion, irritability, sweating, and trembling. Symptoms must be con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Anxiety Disorder
Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is an anxiety disorder characterized by excessive, uncontrollable and often irrational worry about events or activities. Worry often interferes with daily functioning. Individuals with GAD are often overly concerned about everyday matters such as health, finances, death, family, relationship concerns, or work difficulties."What Is Generalized Anxiety Disorder?" National Institute of Mental Health. Accessed 28 May 2008. Symptoms may include excessive worry, restlessness, , exhaustion, irritability, sweating, and |
Migraine
Migraine (, ) is a complex neurological disorder characterized by episodes of moderate-to-severe headache, most often unilateral and generally associated with nausea, and light and sound sensitivity. Other characterizing symptoms may include vomiting, cognitive dysfunction, allodynia, and dizziness. Exacerbation or worsening of headache symptoms during physical activity is another distinguishing feature. Up to one-third of people with migraine experience aura, a premonitory period of sensory disturbance widely accepted to be caused by cortical spreading depression at the onset of a migraine attack. Although primarily considered to be a headache disorder, migraine is highly heterogenous in its clinical presentation and is better thought of as a spectrum disease rather than a distinct clinical entity. Disease burden can range from episodic discrete attacks to chronic disease. Migraine is believed to be caused by a mixture of environmental and genetic factors that influe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetic Neuropathy
Diabetic neuropathy includes various types of nerve damage associated with diabetes mellitus. The most common form, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, affects 30% of all diabetic patients. Studies suggests that cutaneous nerve branches, such as the sural nerve, are involved in more than half of patients with diabetes 10 years after the diagnosis and can be detected with high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Symptoms depend on the site of nerve damage and can include motor changes such as weakness; sensory symptoms such as numbness, tingling, or pain; or autonomic changes such as urinary symptoms. These changes are thought to result from a microvascular disease, microvascular injury involving small blood vessels that supply nerves (vasa nervorum). Relatively common conditions which may be associated with diabetic neuropathy include distal symmetric polyneuropathy; Oculomotor nerve palsy, third, Fourth nerve palsy, fourth, or Sixth nerve palsy, sixth cranial nerve palsy; mononeuro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Off-label Use
Off-label use is the use of pharmaceutical drugs for an unapproved indication or in an unapproved age group, dosage, or route of administration. Both prescription drugs and over-the-counter drugs (OTCs) can be used in off-label ways, although most studies of off-label use focus on prescription drugs. Off-label use is very common and generally legal unless it violates ethical guidelines or safety regulations. The ability to prescribe drugs for uses beyond the officially approved indications is commonly used to good effect by healthcare providers. For example, methotrexate is commonly used off-label because its immunomodulatory effects relieve various disorders. However, off-label use can entail health risks and differences in legal liability. Marketing of pharmaceuticals for off-label use is usually prohibited. Indications and labeling laws An '' indication'' is when a drug is medically appropriate for a given condition; an approved indication is when a government drug regula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasomotor Symptoms
Hot flushes are a form of flushing, often caused by the changing hormone levels that are characteristic of menopause. They are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to 30 minutes for each occurrence. Signs and symptoms Hot flashes, a common symptom of menopause and perimenopause, are typically experienced as a feeling of intense heat with sweating and rapid heartbeat, and may typically last from two to thirty minutes for each occurrence, ending just as rapidly as they began. The sensation of heat usually begins in the face or chest, although it may appear elsewhere such as the back of the neck, and it can spread throughout the whole body. Some people feel as if they are going to faint. In addition to being an internal sensation, the surface of the skin, especially on the face, becomes hot to the touch. This is the origin of the alternative term "hot flush", since the sensation of heat is often ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Social Phobia
Social anxiety disorder (SAD), also known as social phobia, is an anxiety disorder characterized by sentiments of fear and anxiety in social situations, causing considerable distress and impairing ability to function in at least some aspects of daily life. These fears can be triggered by perceived or actual scrutiny from others. Individuals with social anxiety disorder fear negative evaluations from other people. Physical symptoms often include excessive blushing, excessive sweating, trembling, palpitations, rapid heartbeat, muscle tension, shortness of breath, and nausea. Panic attacks can also occur under intense fear and discomfort. Some affected individuals may use alcohol or other drugs to reduce fears and inhibitions at social events. It is common for those with social phobia to self-medicate in this fashion, especially if they are undiagnosed, untreated, or both; this can lead to alcohol use disorder, eating disorders or other kinds of substance use disorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mania
Mania, also known as manic syndrome, is a Psychiatry, psychiatric Abnormality (behavior), behavioral syndrome defined as a state of Abnormality (behavior), abnormally elevated arousal, affect (psychology), affect, and energy level. During a manic episode, an individual will experience Emotional lability, rapidly changing emotions and moods, highly influenced by surrounding Stimulus (psychology), stimuli. Although mania is often conceived of as a "mirror image" to depression (mood), depression, the heightened mood (psychology), mood can be Dysphoria, dysphoric as well as Euphoria, euphoric. As the mania intensifies, irritability can be more pronounced and result in anxiety or anger. The symptoms of mania include elevated mood (either euphoric or irritable), Flight of Ideas, flight of ideas, pressure of speech, increased energy, decreased "need" and desire for sleep, and psychomotor agitation, hyperactivity. They are most plainly evident in fully developed hypomanic states, however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time when Menstruation, menstrual periods permanently stop, marking the end of the Human reproduction, reproductive stage for the female human. It typically occurs between the ages of 45 and 55, although the exact timing can vary. Menopause is usually a natural change related to a decrease in circulating blood estrogen levels. It can occur earlier in those who smoke tobacco. Other causes include surgery that removes both ovaries, some types of chemotherapy, or anything that leads to a decrease in hormone levels. At the physiological level, menopause happens because of a decrease in the ovaries' production of the hormones estrogen and progesterone. While typically not needed, measuring hormone levels in the blood or urine can confirm a diagnosis. Menopause is the opposite of menarche, the time when periods start. In the years before menopause, a woman's periods typically become irregular, which means that periods may be longer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |