|
Edward Yourdon
Edward Nash Yourdon (April 30, 1944 – January 20, 2016) was an American software engineer, computer consultant, author and lecturer, and software engineering methodology pioneer. He was one of the lead developers of the structured analysis techniques of the 1970s and a co-developer of both the Yourdon/Whitehead method for object-oriented analysis/design in the late 1980s and the Coad/Yourdon methodology for object-oriented analysis/design in the 1990s. Biography Yourdon obtained his B.S. in applied mathematics from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in 1965, and did graduate work in electrical engineering and computer science at MIT and the Polytechnic Institute of New York. In 1964 Yourdon started working at Digital Equipment Corporation developing FORTRAN programs for the PDP-5 minicomputer and later assembler for the PDP-8. In the late 1960s and early 1970s he worked at a small consulting firm and as an independent consultant. In 1974 Yourdon founded his ow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structured Systems Analysis And Design Method
Structured systems analysis and design method (SSADM) is a systems approach to the analysis and design of information systems. SSADM was produced for the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency, a UK government office concerned with the use of technology in government, from 1980 onwards. Overview SSADM is a waterfall method for the analysis and design of information systems. SSADM can be thought to represent a pinnacle of the rigorous document-led approach to system design, and contrasts with more contemporary agile methods such as DSDM or Scrum. SSADM is one particular implementation and builds on the work of different schools of structured analysis and development methods, such as Peter Checkland's soft systems methodology, Larry Constantine's structured design, Edward Yourdon's Yourdon Structured Method, Michael A. Jackson's Jackson Structured Programming, and Tom DeMarco's structured analysis. The names "Structured Systems Analysis and Design Method" and " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Science
Computer science is the study of computation, information, and automation. Computer science spans Theoretical computer science, theoretical disciplines (such as algorithms, theory of computation, and information theory) to Applied science, applied disciplines (including the design and implementation of Computer architecture, hardware and Software engineering, software). Algorithms and data structures are central to computer science. The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of computational problem, problems that can be solved using them. The fields of cryptography and computer security involve studying the means for secure communication and preventing security vulnerabilities. Computer graphics (computer science), Computer graphics and computational geometry address the generation of images. Programming language theory considers different ways to describe computational processes, and database theory concerns the management of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDP-5
The PDP-5 was Digital Equipment Corporation's first 12-bit computer, introduced in 1963. History An earlier 12-bit computer, named LINC has been described as the first minicomputer and also "the first modern personal computer." It had 2,048 12-bit words, and the first LINC was built in 1962. DEC's founder, Ken Olsen, had worked with both it and a still earlier computer, the 18-bit 64,000-word TX-0, at MIT's Lincoln Laboratory. Neither of these machines was mass-produced. Applicability Although the LINC computer was intended primarily for laboratory use, the PDP-5's 12-bit system had a far wider range of use. An example of DEC's "The success of the PDP-5 ... proved that a market for minicomputers did exist" is: * "Data-processing computers have accomplished for mathematicians what the wheel did for transportation" * "Very reliable data was obtained with ..." * "A PDP-5 computer was used very successfully aboard EvergreenU. S. Coast Guard Oceanographic Vessel — ''Ever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Web 2
Web 2.0 (also known as participative (or participatory) web and social web) refers to websites that emphasize user-generated content, usability, ease of use, participatory culture, and interoperability (i.e., compatibility with other products, systems, and devices) for end users. The term was coined by Darcy DiNucci in 1999 and later popularized by Tim O'Reilly and Dale Dougherty at the first Web 2.0 Summit, Web 2.0 Conference in 2004. Although the term mimics the numbering of software versions, it does not denote a formal change in the nature of the World Wide Web, but merely describes a general change that occurred during this period as interactive websites proliferated and came to overshadow the older, more static websites of the original Web. A Web 2.0 website allows users to interact and collaborate through social media dialogue as creators of user-generated content in a virtual community. This contrasts the first generation of #Web 1.0, Web 1.0-era websites where people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Engineering Methodologies
In software engineering, a software development process or software development life cycle (SDLC) is a process of planning and managing software development. It typically involves dividing software development work into smaller, parallel, or sequential steps or sub-processes to improve design and/or product management. The methodology may include the pre-definition of specific deliverables and artifacts that are created and completed by a project team to develop or maintain an application. Most modern development processes can be vaguely described as agile. Other methodologies include waterfall, prototyping, iterative and incremental development, spiral development, rapid application development, and extreme programming. A life-cycle "model" is sometimes considered a more general term for a category of methodologies and a software development "process" is a particular instance as adopted by a specific organization. For example, many specific software development processes fit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Project Management
Project management is the process of supervising the work of a Project team, team to achieve all project goals within the given constraints. This information is usually described in project initiation documentation, project documentation, created at the beginning of the development process. The primary constraints are Scope (project management), scope, time and budget. The secondary challenge is to operations research, optimize the Resource allocation, allocation of necessary inputs and apply them to meet predefined objectives. The objective of project management is to produce a complete project which complies with the client's objectives. In many cases, the objective of project management is also to shape or reform the client's brief to feasibly address the client's objectives. Once the client's objectives are established, they should influence all decisions made by other people involved in the project– for example, project managers, designers, contractors and subcontractors ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of North Texas
The University of North Texas (UNT) is a public university, public research university located in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. Its main campus is in Denton, Texas, Denton, with a satellite campus in Frisco, Texas, Frisco. It serves as the flagship of the University of North Texas System, which also includes universities in Dallas and Fort Worth, Texas, Fort Worth. UNT offers 114 bachelor's degree, bachelor's, 97 master's degree, master's, and 39 doctoral degree, doctoral programs. Founded in 1890, it was the 48th largest university in the United States by enrollment in 2023. UNT is classified as an "R1: Doctoral University – Very High Research Activity" by the Carnegie Classification of Institutions of Higher Education, Carnegie system, the highest Carnegie designation for U.S. research institutions. UNT is also designated an Emerging Research University by the State of Texas and is one of four universities supported by the Texas University Fund (TUF). Created with an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EWeek
''eWeek'' (''Enterprise Newsweekly'', stylized as ''eWEEK''), formerly ''PCWeek'', is a technology and business magazine. Previously owned by Ziff Davis, then sold to QuinStreet. Nashville, Tennessee marketing company TechnologyAdvice acquired eWeek in 2020. The print edition ceased in 2012, "and eWeek became an all-digital publication"), at which time Quinstreet acquired the magazine from Internet company Ziff Davis, along with Baseline.com, ChannelInsider.com, CIOInsight.com, and WebBuyersGuide.com. ''eWeek'' was started under the name ''PCWeek'' on Feb. 28, 1984. The magazine was called ''PCWeek'' until 2000, during which time it covered the rise of business computing in America; as ''eWeek'', it increased its online presence and covers more kinds of worldwide technologies. History The magazine was started by Ziff Davis Ziff Davis, Inc. is an American digital media and internet company. Founded in 1927 by William Bernard Ziff Sr. and Bernard George Davis, the comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
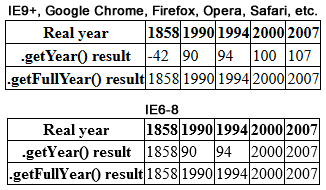
Year 2000 Problem
The term year 2000 problem, or simply Y2K, refers to potential computer errors related to the Time formatting and storage bugs, formatting and storage of calendar data for dates in and after the year 2000. Many Computer program, programs represented four-digit years with only the final two digits, making the year 2000 indistinguishable from 1900. Computer systems' inability to distinguish dates correctly had the potential to bring down worldwide infrastructures for computer-reliant industries. In the years leading up to the turn of the millennium, the public gradually became aware of the "Y2K scare", and individual companies predicted the global damage caused by the bug would require anything between $400 million and $600 billion to rectify. A lack of clarity regarding the potential dangers of the bug led some to stock up on food, water, and firearms, purchase backup generators, and withdraw large sums of money in anticipation of a computer-induced Global catastrophic risk, ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerald Weinberg
Gerald Marvin Weinberg (October 27, 1933 – August 7, 2018) was an American computer scientist, author and teacher of the psychology and anthropology of computer software development. His most well-known books are ''The Psychology of Computer Programming'' and ''Introduction to General Systems Thinking''. Biography Gerald Weinberg was born and raised in Chicago. He attended Omaha Central High School in Omaha, Nebraska. In 1963 he received a PhD in Communication Sciences from the University of Michigan.Gerald M. Weinberg at dorsethouse.com. Accessed June 5, 2009.Jerry Weinberg. Author, Teacher, Consultant at linkedin.com. Accessed June 5, 2009.< ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grace Hopper
Grace Brewster Hopper (; December 9, 1906 – January 1, 1992) was an American computer scientist, mathematician, and United States Navy rear admiral. She was a pioneer of computer programming. Hopper was the first to devise the theory of machine-independent programming languages, and used this theory to develop the FLOW-MATIC programming language and COBOL, an early high-level programming language still in use today. She was also one of the first programmers on the Harvard Mark I computer. She is credited with writing the first computer manual, "A Manual of Operation for the Automatic Sequence Controlled Calculator." Before joining the Navy, Hopper earned a Ph.D. in both mathematics and mathematical physics from Yale University and was a professor of mathematics at Vassar College. She left her position at Vassar to join the United States Navy Reserve during World War II. Hopper began her computing career in 1944 as a member of the Harvard Mark I team, led by Howard H. Aiken. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Martin (author)
James Martin (19 October 1933 – 24 June 2013) was an English information technology consultant and author, known for his work on information technology engineering. Biography James Martin was born on 19 October 1933 in Ashby-de-la-Zouch, England. He earned a degree in physics at Keble College, Oxford. Martin joined IBM in 1959, and from the 1980s on, established several IT consultancy firms. Starting in 1981 with Dixon Doll and Tony Carter he establisheDMW (Doll Martin Worldwide)in London, UK, which was later renamed James Martin Associates (JMA), which was (partly) bought by Texas Instruments Software in 1991. He later co-founded Database Design Inc. (DDI), in Ann Arbor, Michigan, to promulgate his database design techniques and to develop tools to help implement them. After becoming the market leader in information technology engineering software, DDI was renamed KnowledgeWare and eventually purchased by Fran Tarkenton, who took it public. Martin was awarded an honora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |