|
Ecuadorian–Peruvian War
The Ecuadorian–Peruvian War, known locally as the War of '41 (), was a South American border war fought between 5–31 July 1941. It was the first of three military conflicts between Ecuador and Peru during the 20th century. During the war, Peru occupied the western Ecuadorian province of El Oro and parts of the Andean province of Loja. Although the war took place during World War II, it is unrelated to that conflict, as neither country was supported by either the Allies or the Axis. A ceasefire agreement between the two countries came into effect on 31 July 1941. Both countries signed the Rio Protocol on 29 January 1942, and Peruvian forces subsequently withdrew. Enmity over the territorial dispute continued after 1942, and the border disputes were not entirely resolved until the Cenepa War of 1995 and the signing of the Brasilia Presidential Act agreement in October 1998. Background The territorial dispute between Ecuador and Peru dated from before Ecuador's ind ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuadorian–Peruvian Territorial Dispute
The Ecuadorian–Peruvian territorial dispute was a territorial dispute between Ecuador and Peru, which, until 1928, also included Colombia.Ecuador and Colombia signed the Muñoz Vernaza-Suárez Treaty in 1916, ending their dispute, while Peru and Colombia's Salomon-Lozano Treaty became effective in 1928 The dispute had its origins on each country's interpretation of what Real cédula, Real Cedulas Spain used to precisely define its colonial territories in the Americas. After independence, all of Spain's colonial territories signed and agreed to proclaim their limits in the basis of the principle of ''uti possidetis juris'', which regarded the Spanish borders of 1810 as the borders of the new republics. However, conflicting claims and disagreements between the newly formed countries eventually escalated to the point of armed conflicts on several occasions. The dispute ''de jure'' had come to an end in the aftermath of the Ecuadorian–Peruvian War with the signing of the Rio de Ja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Institute Of Peace
The United States Institute of Peace (USIP) is an American independent, nonprofit, national institute funded by the U.S. Congress and tasked with promoting conflict resolution and prevention worldwide. See alsPDF on USIP website. It provides research, analysis, and training to individuals in diplomacy, mediation, and other peace-building measures. Following years of proposals for a national peace academy, USIP was established in 1984 by congressional legislation signed into law by President Ronald Reagan. It is officially nonpartisan and independent, receiving funding only through a congressional appropriation to prevent outside influence. The institute is governed by a bipartisan board of directors with 15 members, which must include the United States Secretary of Defense, secretary of defense, the United States Secretary of State, secretary of state, and the president of the National Defense University (Washington, D.C.), National Defense University. The remaining 12 members are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Colombia–Peru War
The Gran Colombian–Peruvian War () of 1828 and 1829 was the first international conflict fought by the Republic of Peru, which had gained its independence from Spain in 1821, and Gran Colombia, that existed between 1819 and 1830. Causes The issues that led to war were Gran Colombian claims, dating from colonial times, concerning control of the territories of Jaén and Maynas. The Royal Audience of Quito () was established in 1563 by a royal decree of the King of Spain. Its territories included, to the north, Pasto, Popayán, Cali, Buenaventura, and Buga in what is now Colombia. The Royal Audience of Quito was initially part of the Viceroyalty of Peru until 1717, when it became part of the Viceroyalty of New Granada. Borders at the time were imprecise, especially in the eastern unsettled areas, beyond the Andean cordillera, because of a lack of geographical knowledge and the low importance accorded to these unpopulated and largely inaccessible territories. The first c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brazil
Brazil, officially the Federative Republic of Brazil, is the largest country in South America. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, fifth-largest country by area and the List of countries and dependencies by population, seventh-largest by population, with over 212 million people. The country is a federation composed of 26 Federative units of Brazil, states and a Federal District (Brazil), Federal District, which hosts the capital, Brasília. List of cities in Brazil by population, Its most populous city is São Paulo, followed by Rio de Janeiro. Brazil has the most Portuguese-speaking countries, Portuguese speakers in the world and is the only country in the Americas where Portuguese language, Portuguese is an Portuguese-speaking world, official language. Bounded by the Atlantic Ocean on the east, Brazil has a Coastline of Brazil, coastline of . Covering roughly half of South America's land area, it Borders of Brazil, borders all other countries and ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country primarily located in South America with Insular region of Colombia, insular regions in North America. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Caribbean Sea to the north, Venezuela to the east and northeast, Brazil to the southeast, Peru and Ecuador to the south and southwest, the Pacific Ocean to the west, and Panama to the northwest. Colombia is divided into 32 Departments of Colombia, departments. The Capital District of Bogotá is also the List of cities in Colombia by population, country's largest city hosting the main financial and cultural hub. Other major urban areas include Medellín, Cali, Barranquilla, Cartagena, Colombia, Cartagena, Santa Marta, Cúcuta, Ibagué, Villavicencio and Bucaramanga. It covers an area of 1,141,748 square kilometers (440,831 sq mi) and has a population of around 52 million. Its rich cultural heritage—including language, religion, cuisine, and art—reflects its history as a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
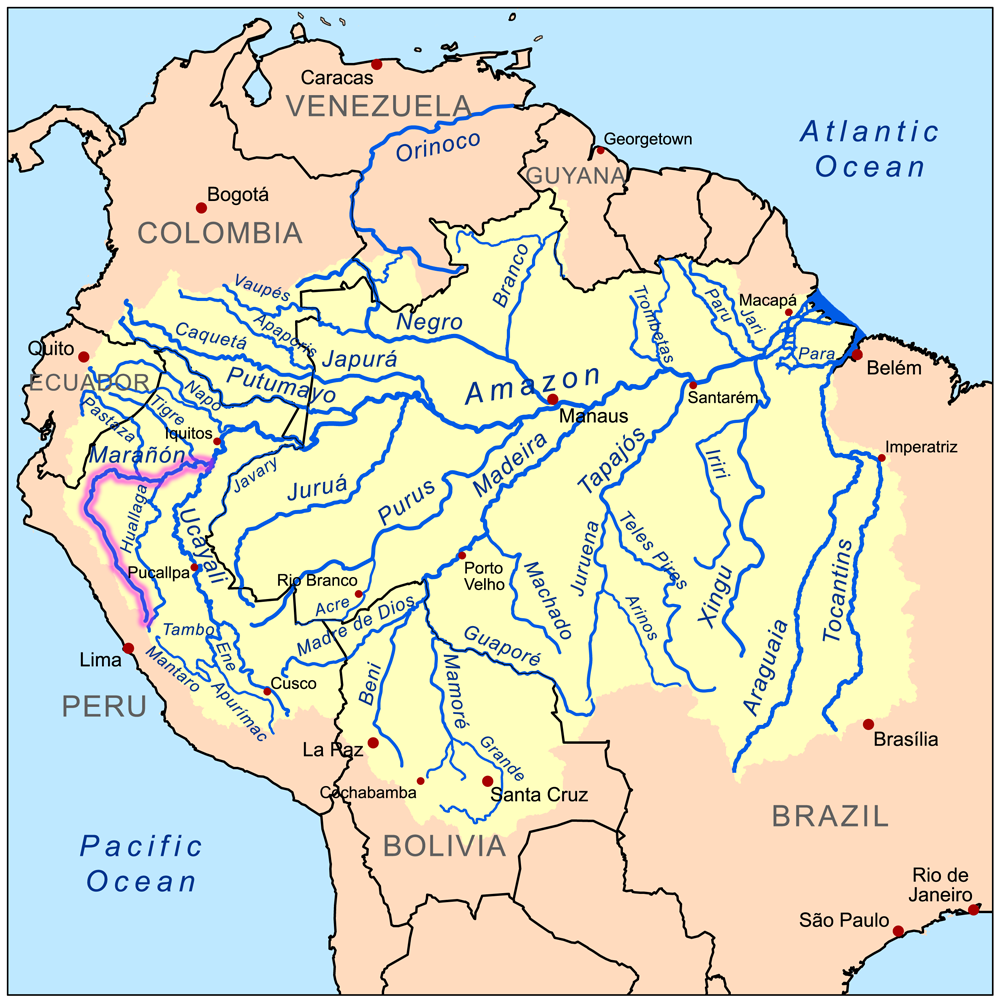
Marañón River
The Marañón River (, , ) is the principal or mainstem source of the Amazon River, arising about 160 km (100 miles) to the northeast of Lima, Peru, and flowing northwest across plateaus 3,650 m (12,000 feet) high, it runs through a deeply eroded Andean valley, along the eastern base of the Cordillera of the Andes, as far as 5° 36′ southern latitude; from where it makes a great bend to the northeast, and cuts through the jungle Ande in its midcourse, until at the Pongo de Manseriche it flows into the flat Amazon basin. Although historically, the term "Marañón River" often was applied to the river all the way to the Atlantic Ocean, nowadays the Marañón River is generally thought to end at the confluence with the Ucayali River, after which most cartographers label the ensuing waterway the Amazon River. As the Marañón passes through high jungle in its midcourse, it is marked by a series of unnavigable rapids and falls. The Marañón was the subject of a landmark legal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), also known as Greater Colombia and officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish language, Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and parts of Central America from 1819 to 1831. It included present-day Colombia, mainland Ecuador (i.e. excluding the Galápagos Islands), Panama, and Venezuela, along with the Caribbean coasts of Nicaragua and Costa Rica, parts of northern Peru, northwestern Brazil, and Guyana–Venezuela territorial dispute, claimed the Essequibo region. The terms Gran Colombia and Greater Colombia are used historiography, historiographically to distinguish it from the current Colombia, Republic of Colombia, which is also the official name of the former state. However, Diplomatic recognition, international recognition of the legitimacy of the Gran Colombian state ran afoul of European opposition to the independence of states in the Americas. Austrian Empire, Austria, Bourb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala Conflict Data Program
The Uppsala Conflict Data Program (UCDP) is a data collection program on organized violence, based at Uppsala University in Sweden. The UCDP is a leading provider of data on organized violence and armed conflict, and it is the oldest ongoing data collection project for civil war, with a history of almost 40 years. UCDP data are systematically collected and have global coverage, comparability across cases and countries, and long time series. Data are updated annually and are publicly available, free of charge. Furthermore, preliminary data on events of organized violence in Africa is released on a monthly basis. The UCDP's data is published annually in the ''Journal of Peace Research.'' The UCDP also makes its data publicly available through its interactive websiteUCDP website Background The UCDP began recording information on ongoing violent conflicts in the 1980s. It became clear that more systematic and global data on armed conflicts was necessary for conducting research in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |