|
Eclipse Season
An eclipse season is a period, roughly every six months, when eclipses occur. Eclipse seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of the Orbit of the Moon, Moon's orbital plane (orbital inclination, tilted five degrees to the ecliptic, Earth's orbital plane), just as Earth's Season, weather seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's axial tilt, tilted axis as it orbits around the Sun. During the season, the "lunar nodes" – the line where the Moon's orbital plane intersects with the ecliptic, Earth's orbital plane – align with the Sun and Earth, such that a solar eclipse is formed during the new moon phase and a lunar eclipse is formed during the full moon phase. Only two (or occasionally three) eclipse seasons occur during each year, and each season lasts about 35 days and repeats just short of six months (173 days) later, thus two full eclipse seasons always occur each year. Either two or three eclipses happen each eclipse season. During the eclipse seaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse Vs New Or Full Moons, Annotated
An eclipse is an astronomical event which occurs when an astronomical object or spacecraft is temporarily obscured, by passing into the shadow of another body or by having another body pass between it and the viewer. This alignment of three celestial objects is known as a ''syzygy''. An eclipse is the result of either an '' occultation'' (completely hidden) or a ''transit'' (partially hidden). A "deep eclipse" (or "deep occultation") is when a small astronomical object is behind a bigger one. "What is a deep eclipse? The smaller star is behind the bigger star" The term ''eclipse'' is most often used to describe either a solar eclipse, when the Moon's shadow crosses the Earth's surface, or a lunar eclipse, when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow. However, it can also refer to such events beyond the Earth–Moon system: for example, a planet moving into the shadow cast by one of its moons, a moon passing into the shadow cast by its host planet, or a moon passing into th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saros (astronomy)
The saros () is a period of exactly 223 synodic months, 18 years 11 days and 8 hours, that can be used to predict eclipses of the solar eclipse, Sun and lunar eclipse, Moon. One saros period after an eclipse, the Sun, Earth, and Moon return to approximately the same relative geometry, a near straight line, and a nearly identical eclipse will occur, in what is referred to as an eclipse cycle. Every eclipse has an associated saros series and all succeeding or preceding eclipses have a different saros series associated with them - as the eclipse of the same series occurs or occurred with a gap of one saros only. Solar and lunar eclipses have different saros series. A series of eclipses that are separated by one saros is called a ''saros series''. It corresponds to: *6,585.321347 solar days *18.029 years *223 synodic months *241.999 draconic months *18.999 eclipse years (38 eclipse seasons of 173.31 days) *238.992 anomalistic months *241.029 sidereal months The 19 eclipse years means ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Eclipse Of June 21, 2020
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun ** Solar eclipse, an eclipse of a sun in which it is obstructed by the moon ** Solar System, the planetary system made up by the Sun and the objects orbiting it * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from '' Mesmer'', 2017 * "Solar", a song by Sault from '' Air'', 2022 * ”Solar”, a song by Stam1na from '' Taival'', 2018 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
June 2020 Lunar Eclipse
A penumbral lunar eclipse occurred at the Moon’s descending node of orbit on Friday, June 5, 2020, with an umbral magnitude of −0.4036. A lunar eclipse occurs when the Moon moves into the Earth's shadow, causing the Moon to be darkened. A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs when part or all of the Moon's near side passes into the Earth's penumbra. Unlike a solar eclipse, which can only be viewed from a relatively small area of the world, a lunar eclipse may be viewed from anywhere on the night side of Earth. Occurring about 2.8 days after perigee (on June 2, 2020, at 23:40 UTC), the Moon's apparent diameter was larger. This eclipse was the second of four penumbral lunar eclipses in 2020, with the others occurring on January 10, July 5, and November 30. Visibility The eclipse was completely visible over east Africa, eastern Europe, Asia, and Australia, seen rising over west Africa, Europe, and eastern South America and setting over northeast Asia and the western Pacific Ocean. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse Cycle
Eclipses may occur repeatedly, separated by certain intervals of time: these intervals are called eclipse cycles. The series of eclipses separated by a repeat of one of these intervals is called an eclipse series. Eclipse conditions Eclipses may occur when Earth and the Moon are aligned with the Sun, and the shadow of one body projected by the Sun falls on the other. So at new moon, when the Moon is in conjunction (astronomy), conjunction with the Sun, the Moon may pass in front of the Sun as viewed from a narrow region on the surface of Earth and cause a solar eclipse. At full moon, when the Moon is in Astronomical opposition, opposition to the Sun, the Moon may pass through the shadow of Earth, and a lunar eclipse is visible from the night half of Earth. The conjunction and opposition of the Moon together have a special name: syzygy (astronomy), syzygy (Greek language, Greek for "junction"), because of the importance of these lunar phases. An eclipse does not occur at every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year
A year is a unit of time based on how long it takes the Earth to orbit the Sun. In scientific use, the tropical year (approximately 365 Synodic day, solar days, 5 hours, 48 minutes, 45 seconds) and the sidereal year (about 20 minutes longer) are more exact. The modern calendar year, as reckoned according to the Gregorian calendar, approximates the tropical year by using a system of leap years. The term 'year' is also used to indicate other periods of roughly similar duration, such as the lunar year (a roughly 354-day cycle of twelve of the Moon's phasessee lunar calendar), as well as periods loosely associated with the calendar or astronomical year, such as the seasonal year, the fiscal year, the academic year, etc. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by changes in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar climate, subpolar regions around the planet, four ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Month
A month is a unit of time, used with calendars, that is approximately as long as a natural phase cycle of the Moon; the words ''month'' and ''Moon'' are cognates. The traditional concept of months arose with the cycle of Moon phases; such lunar months ("lunations") are Lunar month#Synodic month, synodic months and last approximately 29.53 days, making for roughly 12.37 such months in one Earth year. From excavated tally sticks, researchers have deduced that people counted days in relation to the Moon's phases as early as the Paleolithic age. Synodic months, based on the Moon's orbital period with respect to the Earth–Sun line, are still the basis of many calendars today and are used to divide the year. Calendars that developed from the Roman calendar system, such as the internationally used Gregorian calendar, divide the year into 12 months, each of which lasts between 28 and 31 days. The names of the months were Anglicized from various Latin names and events important to Rome, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eclipse Cycle
Eclipses may occur repeatedly, separated by certain intervals of time: these intervals are called eclipse cycles. The series of eclipses separated by a repeat of one of these intervals is called an eclipse series. Eclipse conditions Eclipses may occur when Earth and the Moon are aligned with the Sun, and the shadow of one body projected by the Sun falls on the other. So at new moon, when the Moon is in conjunction (astronomy), conjunction with the Sun, the Moon may pass in front of the Sun as viewed from a narrow region on the surface of Earth and cause a solar eclipse. At full moon, when the Moon is in Astronomical opposition, opposition to the Sun, the Moon may pass through the shadow of Earth, and a lunar eclipse is visible from the night half of Earth. The conjunction and opposition of the Moon together have a special name: syzygy (astronomy), syzygy (Greek language, Greek for "junction"), because of the importance of these lunar phases. An eclipse does not occur at every ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Orbit
A circular orbit is an orbit with a fixed distance around the barycenter; that is, in the shape of a circle. In this case, not only the distance, but also the speed, angular speed, Potential energy, potential and kinetic energy are constant. There is no periapsis or apoapsis. This orbit has no Radial orbit, radial version. Listed below is a circular orbit in astrodynamics or celestial mechanics under standard assumptions. Here the centripetal force is the gravitational force, and the axis mentioned above is the line through the Center of mass, center of the central mass perpendicular to the orbital plane. Circular acceleration :wikt:transverse, Transverse acceleration (perpendicular to velocity) causes a change in direction. If it is constant in magnitude and changing in direction with the velocity, circular motion ensues. Taking two derivatives of the particle's coordinates concerning time gives the centripetal acceleration : a\, = \frac \, = where: *v\, is Kinetic e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lunar Month
In lunar calendars, a lunar month is the time between two successive syzygies of the same type: new moons or full moons. The precise definition varies, especially for the beginning of the month. Variations In Shona, Middle Eastern, and European traditions, the month starts when the young crescent moon first becomes visible, at evening, after conjunction with the Sun one or two days before that evening (e.g., in the Islamic calendar). In ancient Egypt, the lunar month began on the day when the waning moon could no longer be seen just before sunrise. Others run from full moon to full moon. Yet others use calculation, of varying degrees of sophistication, for example, the Hebrew calendar, the Chinese calendar, or the ecclesiastical lunar calendar. Calendars count integer days, so months may be 29 or 30 days in length, in some regular or irregular sequence. Lunar cycles are prominent, and calculated with great precision in the ancient Hindu Panchangam calendar, widely us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coplanar
In geometry, a set of points in space are coplanar if there exists a geometric plane that contains them all. For example, three points are always coplanar, and if the points are distinct and non-collinear, the plane they determine is unique. However, a set of four or more distinct points will, in general, not lie in a single plane. Two lines in three-dimensional space are coplanar if there is a plane that includes them both. This occurs if the lines are parallel, or if they intersect each other. Two lines that are not coplanar are called skew lines. Distance geometry provides a solution technique for the problem of determining whether a set of points is coplanar, knowing only the distances between them. Properties in three dimensions In three-dimensional space, two linearly independent vectors with the same initial point determine a plane through that point. Their cross product is a normal vector to that plane, and any vector orthogonal to this cross product through the in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
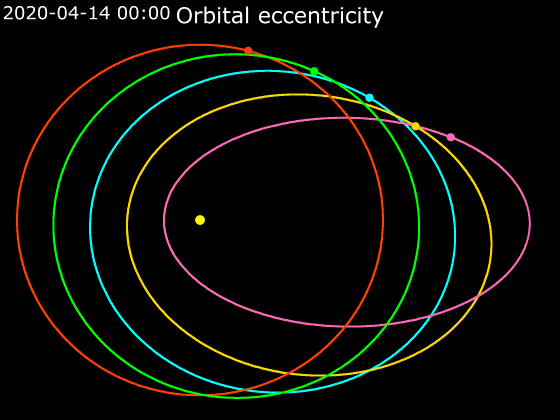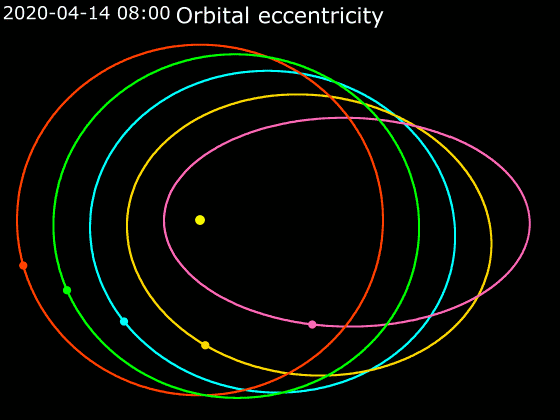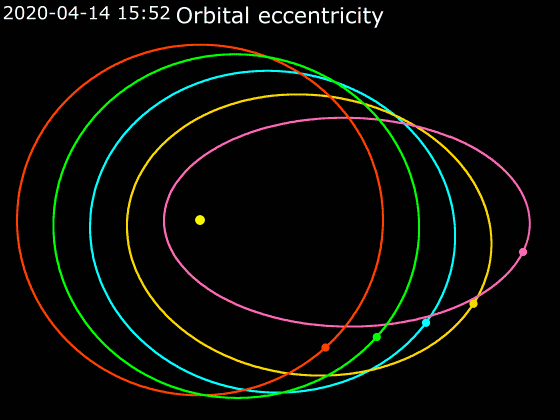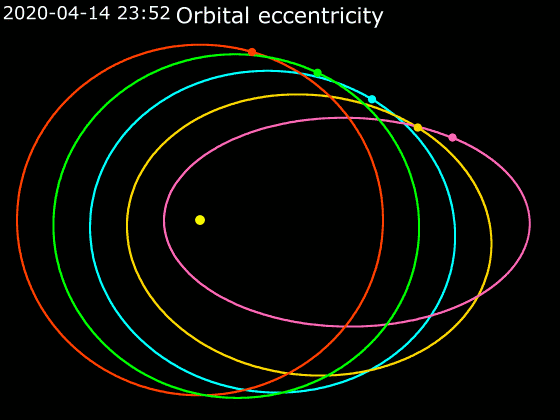
Elliptic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptical orbit or eccentric orbit is an orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. Some orbits have been referred to as "elongated orbits" if the eccentricity is "high" but that is not an explanatory term. For the simple two body problem, all orbits are ellipses. In a gravitational two-body problem, both bodies follow similar elliptical orbits with the same orbital period around their common barycenter. The relative position of one body with respect to the other also follows an elliptic orbit. Examples of elliptic orbits include Hohmann transfer orbits, Molniya orbits, and tundra orbits. Velocity Under standard assumptions, no other forces acting except two spherically symmetrical bodies (m_1) and (m_2), the orbital speed (v\,) of one body traveling along an elliptical orbit can be computed from the vis-viva equation as: :v = \sqrt where: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |