|
ELAVL4
HuD otherwise known as ELAV-like protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''ELAVL4'' gene. The HuD/ELAVL4 protein is an RNA-binding protein. HuD contains three RNA recognition motif, RRM Protein domain, protein domains, enabling RNA binding. HuD is expressed only in neurons and it binds to AU-rich element-containing mRNAs. As a result of this interaction the half-life of the transcript is increased. HuD is important in neurons during brain development and plasticity. Interactions HuD (protein) has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with NXF1. References Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Recognition Motif
RNA recognition motif, RNP-1 is a putative RNA-binding domain of about 90 amino acids that are known to bind single-stranded RNAs. It was found in many eukaryotic proteins. The largest group of single strand RNA-binding protein is the eukaryotic RNA recognition motif (RRM) family that contains an eight amino acid RNP-1 consensus sequence. RRM proteins have a variety of RNA binding preferences and functions, and include heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins ( hnRNPs), proteins implicated in regulation of alternative splicing (SR, U2AF2, Sxl), protein components of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (U1 and U2 snRNPs), and proteins that regulate RNA stability and translation ( PABP, La, Hu). The RRM in heterodimeric splicing factor U2 snRNP auxiliary factor appears to have two RRM-like domains with specialised features for protein recognition. The motif also appears in a few single stranded DNA binding proteins. The typical RRM consists of four anti-parallel beta-strands and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
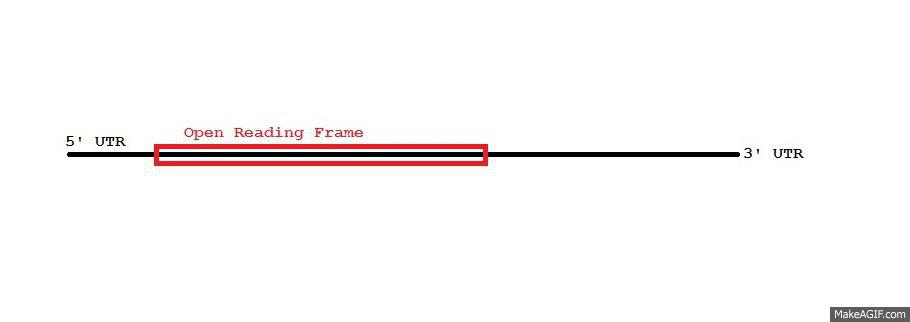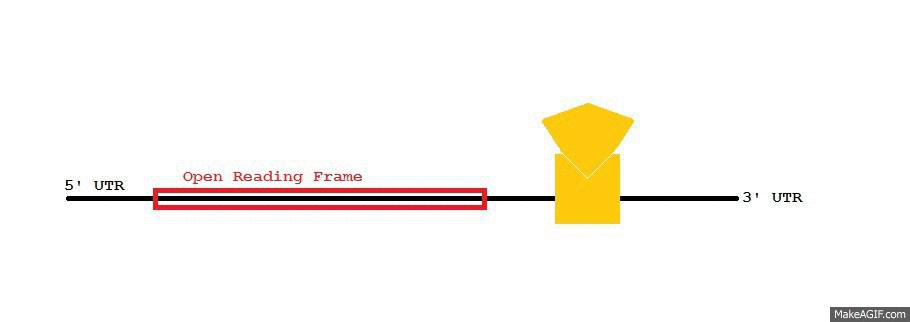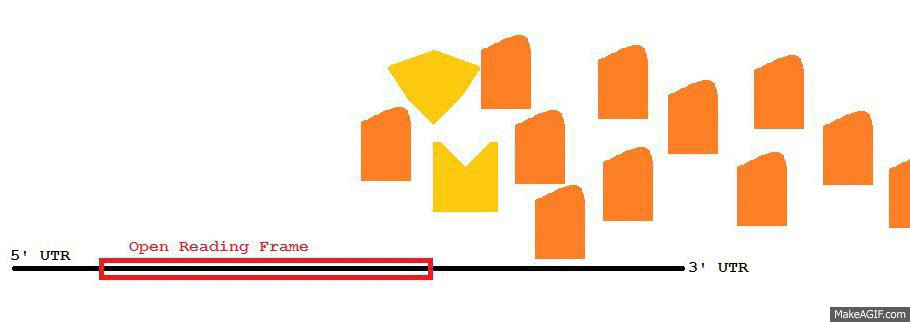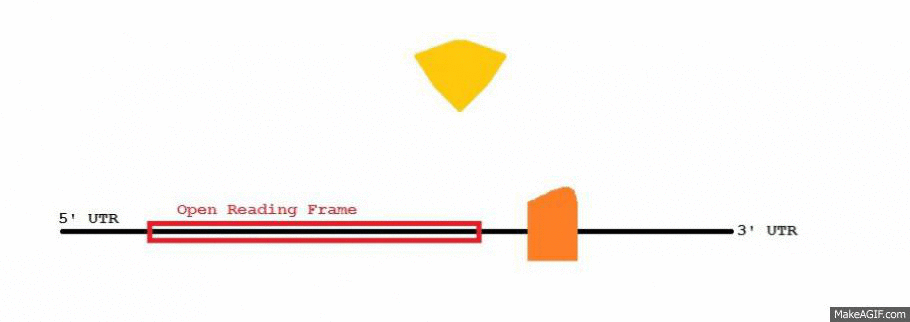
AU-rich Element
Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements (AU-rich elements; AREs) are found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of many messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that code for proto-oncogenes, nuclear transcription factors, and cytokines. AREs are one of the most common determinants of RNA stability in mammalian cells and can also modulate mRNA translation. The function of AREs was originally discovered by Shaw and Kamen in 1985, when Gray Shaw transferred the ARE from the 3' UTR of the human GM-CSF gene into the 3' UTR of a rabbit beta-globin gene. Shaw postulated that the conserved GM-CSF sequences must have a function as they were very similar to the conserved 3' UTR sequences that he had previously observed in mouse IFN-alpha genes. A comparison of the mouse and human cDNAs encoding TNF (aka cachectin) in 1986 revealed that the TNF genes also shared an unusual conserved TTATTTAT sequence in their 3'UTRs, leading to speculation of a regulatory function that might be acting either at the DNA transcription ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residue (biochemistry), residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including Enzyme catalysis, catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, Cell signaling, responding to stimuli, providing Cytoskeleton, structure to cells and Fibrous protein, organisms, and Intracellular transport, transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the Nucleic acid sequence, nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific Protein structure, 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called pep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene has two meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity. The molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and non-coding genes. During gene expression (the synthesis of Gene product, RNA or protein from a gene), DNA is first transcription (biology), copied into RNA. RNA can be non-coding RNA, directly functional or be the intermediate protein biosynthesis, template for the synthesis of a protein. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring, is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits from one generation to the next. These genes make up different DNA sequences, together called a genotype, that is specific to every given individual, within the gene pool of the population (biology), population of a given species. The genotype, along with environmental and developmental factors, ultimately determines the phenotype ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA-binding Protein
RNA-binding proteins (often abbreviated as RBPs) are proteins that bind to the double or single stranded RNA in cell (biology), cells and participate in forming ribonucleoprotein complexes. RBPs contain various structural motifs, such as RNA recognition motif (RRM), dsRNA binding domain, zinc finger and others. They are cytoplasmic and cell nucleus, nuclear proteins. However, since most mature RNA is exported from the nucleus relatively quickly, most RBPs in the nucleus exist as complexes of protein and Precursor mRNA, pre-mRNA called heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles (hnRNPs). RBPs have crucial roles in various cellular processes such as: cellular function, transport and localization. They especially play a major role in post-transcriptional control of RNAs, such as: RNA splicing, splicing, polyadenylation, mRNA stabilization, mRNA Subcellular localization, localization and Translation (biology), translation. Eukaryote, Eukaryotic cells express diverse RBPs with unique RN ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Domain
In molecular biology, a protein domain is a region of a protein's Peptide, polypeptide chain that is self-stabilizing and that Protein folding, folds independently from the rest. Each domain forms a compact folded Protein tertiary structure, three-dimensional structure. Many proteins consist of several domains, and a domain may appear in a variety of different proteins. Molecular evolution uses domains as building blocks and these may be recombined in different arrangements to create proteins with different functions. In general, domains vary in length from between about 50 amino acids up to 250 amino acids in length. The shortest domains, such as zinc fingers, are stabilized by metal ions or Disulfide bond, disulfide bridges. Domains often form functional units, such as the calcium-binding EF-hand, EF hand domain of calmodulin. Because they are independently stable, domains can be "swapped" by genetic engineering between one protein and another to make chimera (protein), chimeric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NXF1
Nuclear RNA export factor 1, also known as NXF1 or TAP, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''NXF1'' gene. Function This gene is one member of a family of nuclear RNA export factor genes. Common domain features of this family are a noncanonical RNP-type RNA-binding domain (RBD), 4 leucine-rich repeats (LRRs), a nuclear transport factor 2 (NTF2)-like domain that allows heterodimerization with NTF2-related export protein-1 ( NXT1), and a ubiquitin-associated domain that mediates interactions with nucleoporins. Alternative splicing results in transcript variants. The LRRs and NTF2-like domains are required for export activity. The encoded protein of this gene shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm and binds in vivo to poly(A)+ RNA. It is the vertebrate homologue of the yeast protein Mex67p. The encoded protein overcomes the mRNA export block caused by the presence of saturating amounts of CTE (constitutive transport element) RNA of type D retroviruses. A variant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |