|
Dynamic Stochastic General Equilibrium
Dynamic stochastic general equilibrium modeling (abbreviated as DSGE, or DGE, or sometimes SDGE) is a macroeconomic method which is often employed by monetary and fiscal authorities for policy analysis, explaining historical time-series data, as well as future forecasting purposes. DSGE econometric modelling applies general equilibrium theory and microeconomic principles in a tractable manner to postulate economic phenomena, such as economic growth and business cycles, as well as policy effects and market shocks. Terminology As a practical matter, people often use the term "DSGE models" to refer to a particular class of econometric, quantitative models of business cycles or economic growth called real business cycle (RBC) models.Christiano (2018) Considered to be classically quantitative, DSGE models were initially proposed by Kydland & Prescott, and Long & Plosser;Long & Plosser (1983) whereby Charles Plosser described RBC models as a precursor for DSGE modeling. As mentioned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroeconomics
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole. For example, using interest rates, taxes, and government spending to regulate an economy's growth and stability. This includes regional, national, and global economies. According to a 2018 assessment by economists Emi Nakamura and Jón Steinsson, economic "evidence regarding the consequences of different macroeconomic policies is still highly imperfect and open to serious criticism." Macroeconomists study topics such as Gross domestic product, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), unemployment (including Unemployment#Measurement, unemployment rates), national income, price index, price indices, output (economics), output, Consumption (economics), consumption, inflation, saving, investment (macroeconomics), investment, Energy economics, energy, international trade, and international finance. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Business-cycle Theory
Real business-cycle theory (RBC theory) is a class of new classical macroeconomics models in which business-cycle fluctuations are accounted for by real (in contrast to nominal) shocks. Unlike other leading theories of the business cycle, RBC theory sees business cycle fluctuations as the efficient response to exogenous changes in the real economic environment. That is, the level of national output necessarily maximizes ''expected'' utility, and governments should therefore concentrate on long-run structural policy changes and not intervene through discretionary fiscal or monetary policy designed to actively smooth out economic short-term fluctuations. According to RBC theory, business cycles are therefore "real" in that they do not represent a failure of markets to clear but rather reflect the most efficient possible operation of the economy, given the structure of the economy. RBC theory is associated with freshwater economics (the Chicago School of Economics in the neocl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiscal Multiplier
In economics, the fiscal multiplier (not to be confused with the money multiplier) is the ratio of change in national income arising from a change in government spending. More generally, the exogenous spending multiplier is the ratio of change in national income arising from any autonomous change in spending (including private investment spending, consumer spending, government spending, or spending by foreigners on the country's exports). When this multiplier exceeds one, the enhanced effect on national income may be called the multiplier effect. The mechanism that can give rise to a multiplier effect is that an initial incremental amount of spending can lead to increased income and hence increased consumption spending, increasing income further and hence further increasing consumption, etc., resulting in an overall increase in national income greater than the initial incremental amount of spending. In other words, an initial change in aggregate demand may cause a change in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
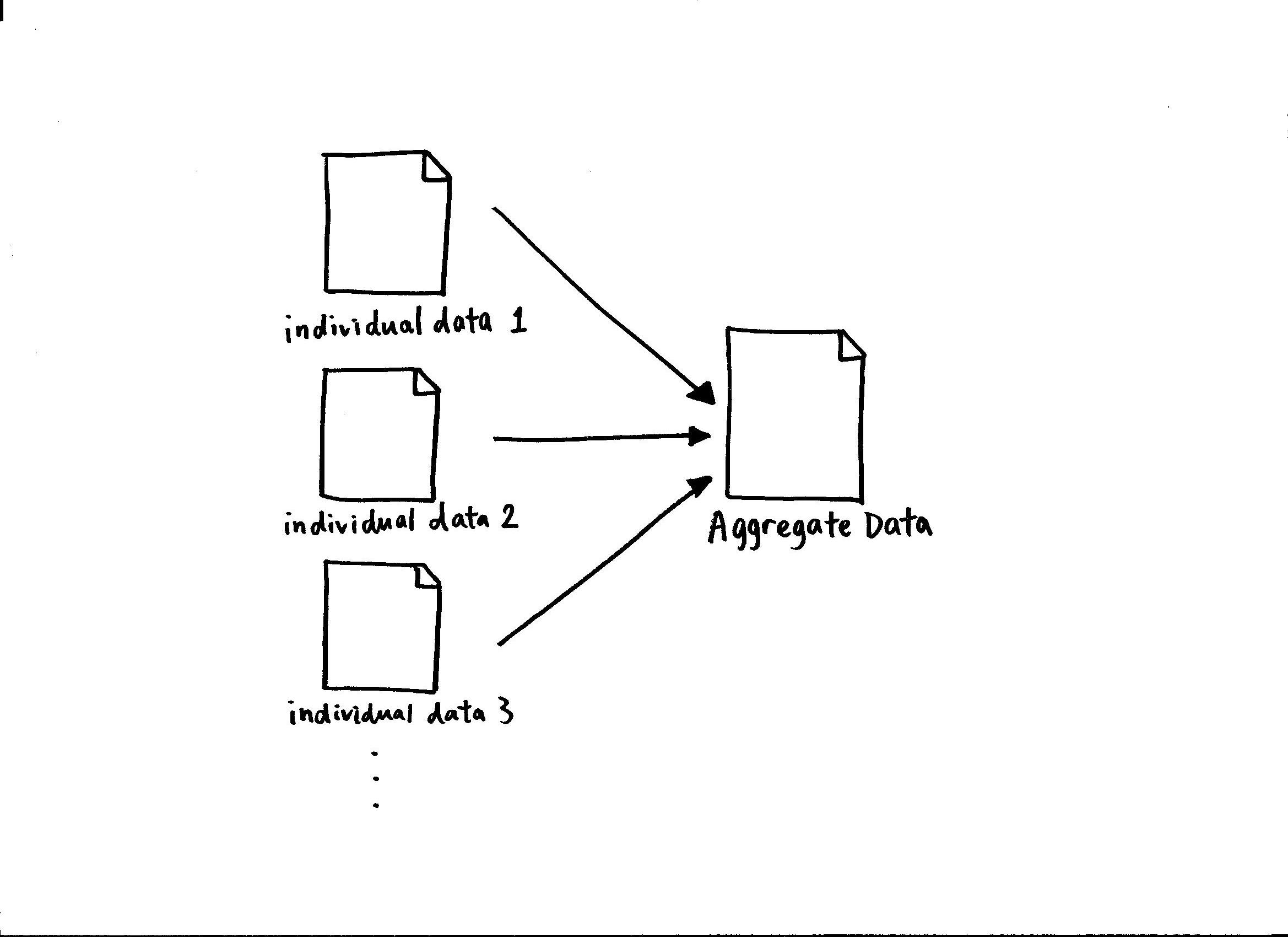
Aggregate Data
Aggregate data is high-level data which is acquired by combining individual-level data. For instance, the output of an industry is an aggregate of the firms’ individual outputs within that industry. Aggregate data are applied in statistics, data warehouses, and in economics. There is a distinction between aggregate data and individual data. Aggregate data refers to individual data that are averaged by geographic area, by year, by service agency, or by other means. Individual data are disaggregated individual results and are used to conduct analyses for estimation of subgroup differences. Aggregate data are mainly used by researchers and analysts, policymakers, banks and administrators for multiple reasons. They are used to evaluate policies, recognise trends and patterns of processes, gain relevant insights, and assess current measures for strategic planning. Aggregate data collected from various sources are used in different areas of studies such as comparative political ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Lucas Jr
Robert Emerson Lucas Jr. (born September 15, 1937) is an American economist at the University of Chicago, where he is currently the John Dewey Distinguished Service Professor Emeritus in Economics and the College. Widely regarded as the central figure in the development of the new classical approach to macroeconomics, he received the Nobel Prize in Economics in 1995 "for having developed and applied the hypothesis of rational expectations, and thereby having transformed macroeconomic analysis and deepened our understanding of economic policy". He has been characterized by N. Gregory Mankiw as "the most influential macroeconomist of the last quarter of the 20th century." As of 2020, he ranks as the 11th most cited economist in the world. Biography Lucas was born in 1937 in Yakima, Washington, and was the eldest child of Robert Emerson Lucas and Jane Templeton Lucas. Lucas received his B.A. in History in 1959 from the University of Chicago. Lucas attended the University of Cali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Consumption (economics)
Consumption is the act of using resources to satisfy current needs and wants. It is seen in contrast to investing, which is spending for acquisition of ''future'' income. Consumption is a major concept in economics and is also studied in many other social sciences. Different schools of economists define consumption differently. According to mainstream economists, only the final purchase of newly produced goods and services by individuals for immediate use constitutes consumption, while other types of expenditure — in particular, fixed investment, intermediate consumption, and government spending — are placed in separate categories (see consumer choice). Other economists define consumption much more broadly, as the aggregate of all economic activity that does not entail the design, production and marketing of goods and services (e.g. the selection, adoption, use, disposal and recycling of goods and services). Economists are particularly interested in the relationship bet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equity Premium Puzzle
The equity premium puzzle refers to the inability of an important class of economic models to explain the average equity risk premium (ERP) provided by a diversified portfolio of U.S. equities over that of U.S. Treasury Bills, which has been observed for more than 100 years. There is significant disparity between returns produced by stocks compared to returns produced by government treasury bills. The equity premium puzzle addresses the difficulty in understanding and explaining this disparity. This disparity is calculated using the equity risk premium: The equity risk premium is equal to the difference between equity returns and returns from government bonds. It is equal to around 5% to 8% in the United States. The risk premium represents the compensation awarded to the equity holder for taking on a higher risk by investing in equities rather than government bonds. However, the 5% to 8% premium is considered to be an implausibly high difference and the equity premium puzzle ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exogenous Variable
In an economic model, an exogenous variable is one whose measure is determined outside the model and is imposed on the model, and an exogenous change is a change in an exogenous variable.Mankiw, N. Gregory. ''Macroeconomics'', third edition, 1997.Varian, Hal R., ''Microeconomic Analysis'', third edition, 1992.Chiang, Alpha C. ''Fundamental Methods of Mathematical Economics'', third edition, 1984. In contrast, an endogenous variable is a variable whose measure is determined by the model. An endogenous change is a change in an endogenous variable in response to an exogenous change that is imposed upon the model. The term endogeneity in econometrics has a related but distinct meaning. An endogenous random variable is correlated with the error term in the econometric model, while an exogenous variable is not. Examples In the LM model of interest rate determination, the supply of and demand for money determine the interest rate contingent on the level of the money supply, so th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Information
In economics, perfect information (sometimes referred to as "no hidden information") is a feature of perfect competition. With perfect information in a market, all consumers and producers have complete and instantaneous knowledge of all market prices, their own utility, and own cost functions. In game theory, a sequential game has perfect information if each player, when making any decision, is perfectly informed of all the events that have previously occurred, including the "initialization event" of the game (e.g. the starting hands of each player in a card game).Archived aGhostarchiveand thWayback Machine Perfect information defined at 0:25, with academic sources and . Perfect information is importantly different from complete information, which implies common knowledge of each player's utility functions, payoffs, strategies and "types". A game with perfect information may or may not have complete information. Games where some aspect of play is ''hidden'' from opponents - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transaction Cost
In economics and related disciplines, a transaction cost is a cost in making any economic trade when participating in a market. Oliver E. Williamson defines transaction costs as the costs of running an economic system of companies, and unlike production costs, decision-makers determine strategies of companies by measuring transaction costs and production costs. Transaction costs are the total costs of making a transaction, including the cost of planning, deciding, changing plans, resolving disputes, and after-sales. Therefore, the transaction cost is one of the most significant factors in business operation and management. Oliver E. Williamson's ''Transaction Cost Economics'' popularized the concept of transaction costs. Douglass C. North argues that institutions, understood as the set of rules in a society, are key in the determination of transaction costs. In this sense, institutions that facilitate low transaction costs, boost economic growth.North, Douglass C. 1992. “Tran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complete Market
In economics, a complete market (aka Arrow-Debreu market or complete system of markets) is a market with two conditions: # Negligible transaction costs and therefore also perfect information, # there is a price for every asset in every possible state of the world In such a market, the complete set of possible bets on future states of the world can be constructed with existing assets without friction. Here, goods are state-contingent; that is, a good includes the time and state of the world in which it is consumed. For instance, an umbrella tomorrow if it rains is a distinct good from an umbrella tomorrow if it is clear. The study of complete markets is central to state-preference theory. The theory can be traced to the work of Kenneth Arrow (1964), Gérard Debreu (1959), Arrow & Debreu (1954) and Lionel McKenzie (1954). Arrow and Debreu were awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economics (Arrow in 1972, Debreu in 1983), largely for their work in developing the theory of complete ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorman Polar Form
Gorman polar form is a functional form for indirect utility functions in economics. Motivation Standard consumer theory is developed for a single consumer. The consumer has a utility function, from which his demand curves can be calculated. Then, it is possible to predict the behavior of the consumer in certain conditions, price or income changes. But in reality, there are many different consumers, each with his own utility function and demand curve. How can we use consumer theory to predict the behavior of an entire society? One option is to represent an entire society as a single "mega consumer", which has an aggregate utility function and aggregate demand curve. But in what cases is it indeed possible to represent an entire society as a single consumer? Formally: consider an economy with n consumers, each of whom has a demand function that depends on his income m^i and the price system: :x^i(p,m^i) The aggregate demand of society is, in general, a function of the price syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |