|
Disused London Underground Stations
The London Underground is a public rapid transit system in the United Kingdom that serves a large part of Greater London and adjacent parts of the home counties of Essex, Hertfordshire and Buckinghamshire. It has many closed stations, while other stations were planned but never opened for public use. Some stations were closed down because a scarcity of passengers made them uneconomic; some became redundant after lines were re-routed or replacements were built; and others are no longer served by the Underground but remain open to National Rail main line services. Many stations were planned as parts of new lines or extensions to existing ones but were later abandoned. Some closed station buildings are still standing, converted for other uses or abandoned, while others have been demolished and their sites redeveloped. A number of stations, while still open, have closed platforms or sections, such as the Jubilee line platforms at Charing Cross. The interiors and platforms of a few clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent ceremonial counties of England, counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground passenger railway. Opened on 10 January 1863, it is now part of the Circle line (London Underground), Circle, District line, District, Hammersmith & City line, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric locomotive, electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines, and in 2020/21 was used for 296 million passenger journeys, making it List of metro systems, one of the world's busiest metro systems. The 11 lines collectively handle up to 5 million passenger journeys a day and serve 272 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
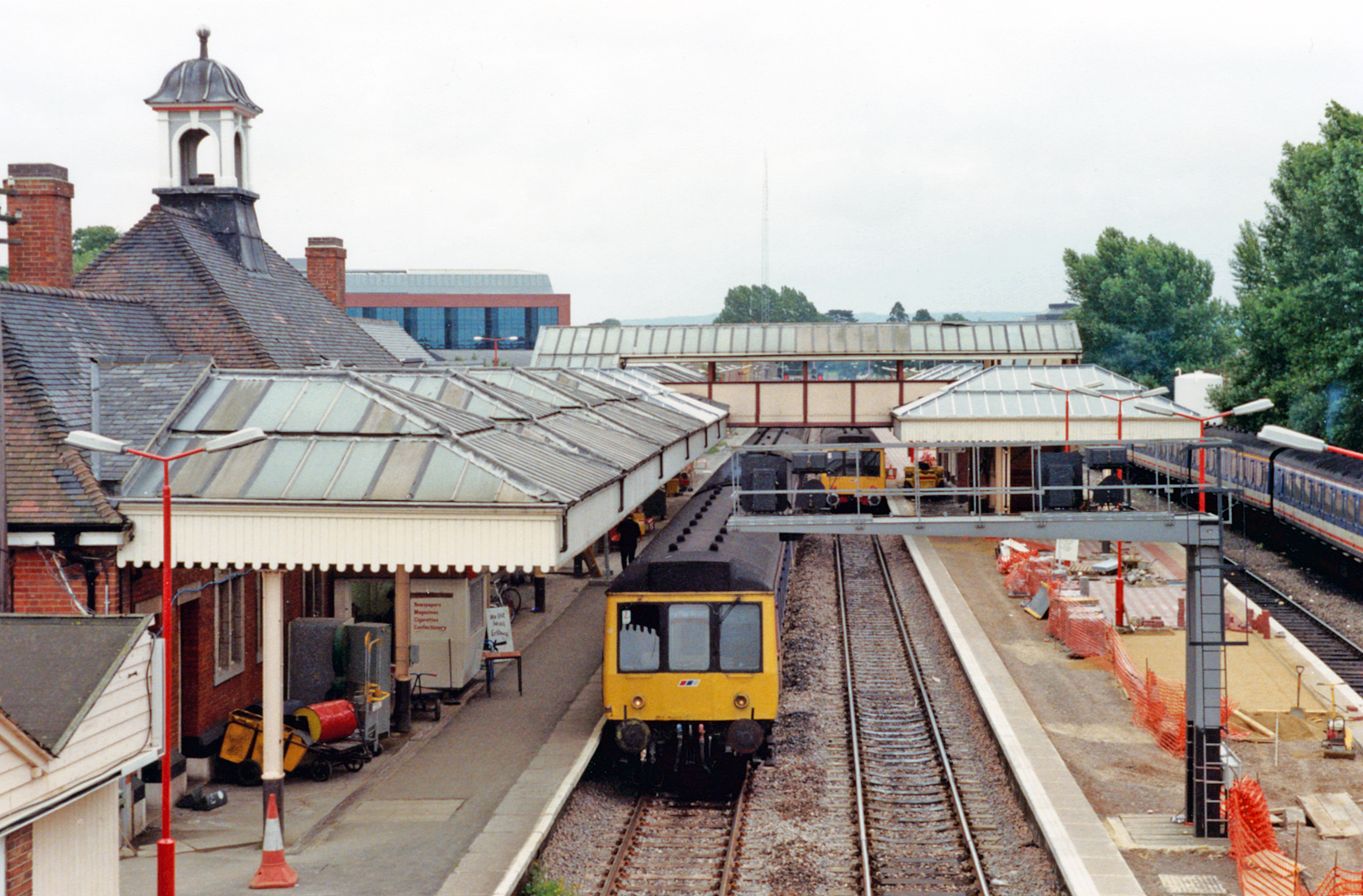
Aylesbury Railway Station
Aylesbury railway station is a railway station in Aylesbury, Buckinghamshire, England, on the London–Aylesbury line from via Amersham. It is from Aylesbury to Marylebone. A branch line from on the Chiltern Main Line terminates at the station. It was the terminus for London Underground's Metropolitan line until the service was cut back to Amersham in 1961. The station was also known as Aylesbury Town under the management of British Railways from until the 1960s. History The first station on the site was opened in 1863 by the Wycombe Railway, which in 1867 was taken over by the Great Western Railway. In 1868 the Aylesbury & Buckingham Railway (later part of the Metropolitan Railway) reached Aylesbury. When opened, the line to Aylesbury from Princes Risborough was broad gauge. To avoid mixed gauge track when the standard gauge Aylesbury and Buckingham arrived at the station in 1868, the section to Princes Risborough was converted to standard gauge, and therefore until th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakerloo Line
The Bakerloo line () is a London Underground line that goes from in suburban north-west London to in south London, via the West End. Printed in brown on the Tube map, it serves 25 stations, 15 of which are underground, over . It runs partly on the surface and partly in deep-level tube tunnels. The line's name is a portmanteau of its original name, the Baker Street & Waterloo Railway. From to Harrow & Wealdstone (the section above ground), the line shares tracks with the London Overground Watford DC line and runs parallel to the West Coast Main Line. There is, however, a short tunnel at the western end of . Opened between 1906 and 1915, many of its stations retain elements of their design to a common standard: the stations below ground using Art Nouveau decorative tiling by Leslie Green, and the above-ground stations built in red brick with stone detailing in an Arts & Crafts style. It is the ninth-busiest line on the network, carrying more than 111 million passengers annu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bushey Railway Station
Bushey is a railway station in Hertfordshire which serves Bushey and Oxhey. It is situated on the West Coast Main Line, north of Harrow & Wealdstone, on an embankment. North of the station, the railway crosses the Colne valley on several viaducts. The station is served by London Northwestern Railway semi-fast trains on the West Coast main line, and by London Overground services on the Watford DC line, a slow local service along the West Coast route. At Bushey, this branches west on a loop to serve Watford High Street railway station, before rejoining the main line at Watford Junction. History The London and Birmingham Railway first ran through here on 20 July 1837. A station was not initially provided, as the area was then sparsely populated. A station was provided later in a similar red brick style to others along the route, larger than most although smaller than that at Harrow & Wealdstone. London Underground's Bakerloo line trains served the station from 16 April 1917 u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knightsbridge Tube Station
Knightsbridge is a London Underground station in Knightsbridge, London. It is on the Piccadilly line between South Kensington and Hyde Park Corner, and is in Travelcard Zone 1. History The station was opened on 15 December 1906 by the Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway (GNP&BR, now the Piccadilly line). When opened, the platforms were accessed in the standard manner by four lifts and an emergency staircase connecting to parallel passageways and bridges to midway along the platforms. The original station building designed by Leslie Green was located on Brompton Road a short distance west of its junction with Knightsbridge and Sloane Street. A rear entrance was located on Basil Street. The location of the station in a busy and fashionable shopping district meant that patronage at the station was high from the beginning, particularly due to the presence locally of the Harrods and Harvey Nichols emporiums. This contrasted with the next station on the line westward †... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
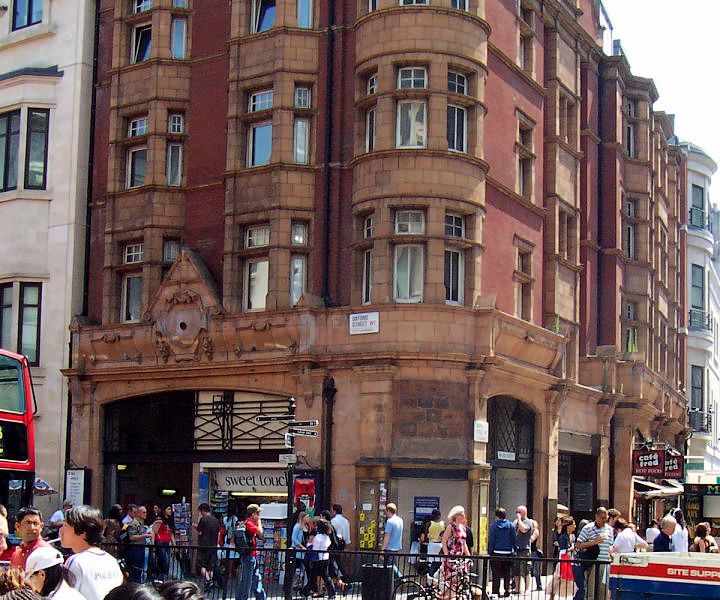
Brompton Road Tube Station
Brompton Road is a disused station on the Piccadilly line of the London Underground, located between Knightsbridge and South Kensington stations. It was closed in 1934, nearly 28 years after being opened by the Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway company. During the Second World War it was used as the command centre of the 26th (London) Anti-Aircraft Brigade. In 2014, the owner of the site, the Ministry of Defence, sold it to a Ukrainian businessman, Dmytro Firtash, who claimed an intention to convert it to residential use. History Brompton Road was opened on 15 December 1906 by the Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway (GNP&BR). The station was located at the junction of Brompton Road and Cottage Place. Although it was conveniently situated for both the Brompton Oratory and the Victoria and Albert Museum, it saw little passenger usage and by October 1909 some services passed through without stopping. The station closed on 4 May 1926 due to the genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
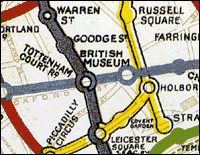
British Museum Tube Station
British Museum was a station on the London Underground, located in Holborn, central London. It was latterly served by the Central line and took its name from the nearby British Museum in Great Russell Street. The station was opened by the Central London Railway in 1900. In 1933, with the expansion of Holborn station, less than 100 yards away, British Museum station was permanently closed. It was subsequently utilised as a military office and command post, but in 1989 the surface building was demolished. A portion of the eastbound tunnel is used to store materials for track maintenance, visible from passing trains. History British Museum station was opened on 30 July 1900 by the Central London Railway (CLR; now the Central line), with its entrance located at No. 133, High Holborn (now Hogarth House, a co-working/workspace venue), near the junction with New Oxford Street. In December 1906, Holborn station was opened by the Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway (G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Tramway
The Brill Tramway, also known as the Quainton Tramway, Wotton Tramway, Oxford & Aylesbury Tramroad and Metropolitan Railway Brill Branch, was a six-mile (10 km) rail line in the Aylesbury Vale, Buckinghamshire, England. It was privately built in 1871 by the 3rd Duke of Buckingham as a horse tram line to help transport goods between his lands around Wotton House and the national rail network. Lobbying from the nearby village of Brill led to its extension to Brill and conversion to passenger use in early 1872. Two locomotives were bought but trains still travelled at an average speed of . In 1883, the Duke of Buckingham planned to upgrade the route to main line standards and extend the line to Oxford, creating the shortest route between Aylesbury and Oxford. Despite the backing of the wealthy Ferdinand de Rothschild, investors were deterred by costly tunnelling. In 1888 a cheaper scheme was proposed in which the line would be built to a lower standard and avoid tunnelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brill Railway Station
Brill railway station was the terminus of a small railway line in Buckinghamshire, England, known as the Brill Tramway. Built and owned by the 3rd Duke of Buckingham, it was later operated by London's Metropolitan Railway, and in 1933 briefly became one of the two north-western termini of the London Underground, despite being and over two hours' travelling time from the City of London. Approximately of a mile (1.2 km) north of Brill, the station was opened in March 1872 as the result of lobbying from local residents and businesses. As the line was cheaply built and ungraded and the locomotives were of poor quality, services were very slow, initially taking 1 hour 45 minutes to traverse the six miles (10 km) from Brill to the junction station with main line services at Quainton Road. Although serving a lightly populated area and little-used by passengers, the station was a significant point for freight traffic, particularly as a carrier of milk from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Line (London Underground)
The Central line is a London Underground line that runs through central London, from , Essex, in the north-east to and in west London. Printed in red on the Tube map, the line serves 49 stations over . It is one of only two lines on the Underground network to cross the Greater London boundary, the other being the Metropolitan line. One of London's deep-level railways, Central line trains are smaller than those on British main lines. The line was opened as the Central London Railway in 1900, crossing central London on an east–west axis along the central shopping street of Oxford Street to the financial centre of the City of London. It was later extended to the western suburb of Ealing. In the 1930s, plans were created to expand the route into the new suburbs, taking over steam-hauled outer-suburban routes to the borders of London and beyond to the east. These projects were mostly realised after Second World War, when construction stopped and the unused tunnels were used as air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blake Hall Tube Station
Blake Hall is a disused former station on the London Underground in the civil parish of Stanford Rivers, and south from the village of Bobbingworth in Essex. It was latterly on the Central line (London Underground), Central line, between North Weald railway station, North Weald and Ongar railway station, Ongar, but was originally served by the Epping Ongar Railway, Epping to Ongar shuttle service branch line. It was opened in 1865 and named after Blake Hall, a country house located a mile or so to the northeast and inhabited by a family of substantial local land-owners. The station was closed in 1981. History Blake Hall station was opened by the Great Eastern Railway on 24 April 1865, serving principally as a goods station, goods yard carrying agricultural produce from the nearby farms into London. Steam locomotives operated by British Railways for the Underground ran Epping Ongar Railway, a shuttle service from Epping tube station, Epping to Ongar railway station, Ongar, stop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiltern Railways
Chiltern Railways, formally The Chiltern Railway Company Limited, is a British train operating company that has operated the Chiltern Railways franchise since July 1996. Since 2009, it has been a subsidiary of Arriva UK Trains. Chiltern Railways was founded as M40 Trains by a group of ex- British Rail managers backed by John Laing and 3i; in June 1996, it was announced that M40 Trains had been awarded the Chiltern Railways franchise. On 21 July 1996, it took over operations from British Rail. The company promptly commenced the redoubling of the Chiltern Main Line under the ''Evergreen'' initiative and ordered the Class 168 ''Clubman'' diesel multiple units (DMUs) to supplement its ex-British Rail fleet. Following the awarding of a 20-year franchise to Chiltern Railways in August 2000, Evergreen phase 2 works begun to raise line speeds around Beaconsfield, built two new platforms at its London Marylebone terminus. In January 2010, a ÂŁ250 million upgrade package was agreed fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |